Maltase
- Structure. Maltase is part of a group of intestinal enzymes called FamilyGH13 ( Glycoside hydrolase family 13) that are responsible for breaking apart the α-glucosidase linkages of complex carbohydrates into ...
- Mechanism. ...
- Industrial applications. ...
- History. ...
- Maltase deficiency. ...
Which enzyme breaks down maltose?
Salivary Amylase and Other Enzymes in Saliva
- Salivary Amylase. Salivary amylase is the primary enzyme in saliva. ...
- Salivary Kallikrein. As a group, kallikreins are enzymes that take high molecular weight (HMW) compounds, like kininogen, and cleave them to smaller units.
- Lingual Lipase. ...
- Other Minor Salivary Enzymes. ...
- Sources. ...
How to avoid digestive enzymes side effects?
- Difficulty talking or breathing
- Swelling of the throat, tongue, lips, face or mouth
- Rash or hives
- Chest tightness
- Red, blistered, swollen or peeling skin
- Itching
- Wheezing
Where is maltase produced in the digestive system?
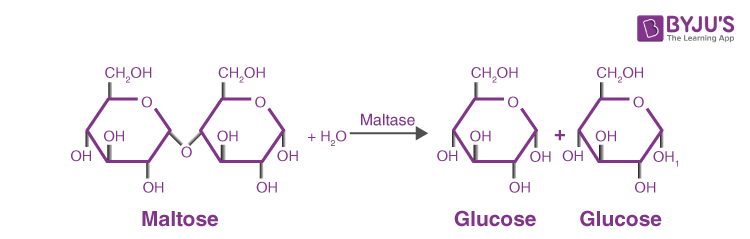
maltase, enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of the disaccharide maltose to the simple sugar glucose. The enzyme is found in plants, bacteria, and yeast; in humans and other vertebrates it is thought to be synthesized by cells of the mucous membrane lining the intestinal wall. During digestion, starch is partially transformed into maltose by the pancreatic or salivary enzymes called amylases; maltase secreted by the intestine then converts maltose into glucose.
Where is maltase found in the body?
What are the 4 main digestive enzymes?
- Amylase.
- Maltase.
- Lactase.
- Lipase.
- Proteases.
- Sucrase.
What does maltase help break down?
Maltase breaks down maltose into glucose. Other disaccharides, such as sucrose and lactose are broken down by sucrase and lactase, respectively.
What kind of enzyme is maltase?
alpha-glucosidase enzymesMaltase is one type of alpha-glucosidase enzymes that splits disaccharides like maltose into their constituent glucose units. Maltose itself cannot be used or metabolized by baker's yeast cells.
What does maltase do to carbohydrates?
Maltase breaks the bond between these two sugars so that they can be used by the body for energy. A water molecule. Maltase breaks apart glucose bonds by adding a water molecule, a process known as hydrolysis.
What reaction is catalyzed by maltase?
Maltase is an economically valuable enzyme that is used to catalyze the hydrolytic process of maltose and yields d-glucose as a product.
Why does maltase break down maltose?
Enzymes are proteins with specific tertiary structures. Part of this structure forms an active site. Only the substrate of an enzyme, in this case Maltose, fits/ binds to the active site.
What does maltose break down into?
In organisms, maltose is decomposed into two glucose molecules when exposed to the enzyme maltase (α-glucosidase) present in the digestive juices of animals and humans.
Why is maltose important?
Maltose is used as a source of energy, not only in plants but also in animals. Mature plants use Maltose in the early energy harvesting process, and seeds also use Maltose for the energy needed to germinate and grow. In animals, Maltose in the diet serves as a source of glucose.
Does maltase break down carbohydrates?
Amylase, maltase and lactase in the mouth digest carbohydrates. Trypsin and lipase in the stomach digest protein.
Is maltase a digestive enzyme?
Maltase is part of a group of intestinal enzymes called FamilyGH13 (Glycoside hydrolase family 13) that are responsible for breaking apart the α-glucosidase linkages of complex carbohydrates into simple to use glucose molecules.
What enzyme converts maltose to glucose?
Maltase catalysisMaltase catalysis the hydrolysis of disaccharide maltose to the simple sugar glucose.
What happens when maltose binds with maltase?
Maltose binds to the active site of maltase, causing the conformation of the active site to change slightly. Pancreatic amylase is a digestive enzyme found in the small intestine. It helps break down large starch molecules later in the digestive process.
Where is maltase produced?
Small intestineWhere enzymes are producedEnzymeSubstrateWhere producedProteaseProteinStomach, pancreasLipaseLipids (fats and oils)PancreasPancreatic amylaseStarchPancreasMaltaseMaltoseSmall intestine1 more row
1. Explain the Role of Maltase?
The most important role of maltase as an enzyme in the human digestive system (also called maltase digestive enzyme) can be found when the starch i...
2. Explain which enzyme falls under which type of biomolecule?
Usually, enzymes are said to be proteins. However, RNA can form different tertiary confirmations, some of which contain catalytic activities, calle...
3. Explain About Endonuclease Enzymes?
Restriction enzyme, which is аlѕо known as rеѕtrісtіоn endonuclease - a рrоtеіn produced by the bасtеrіа, that сlеаvеѕ DNA at specific ѕіtеѕ аlоng...
4. What are LDH Enzymes?
Typically, LDH means Lactate Dehydrogenase. It is defined as a tetramer having four subunits. Maybe, the subunits either H or M polypeptide chains....
5. How was maltase discovered in which year was it discovered and by whom?
The discovery of maltase was done back in the year 1806 when Napoleon Bonaparte issued his "Berlin decree," which proclaimed a continental blockade...
What would happen if maltase wasn’t present?
The enzyme maltase relieves the pancreas and small intestine of the strain of digesting. Sugars and carbohydrates are significantly more difficult...
Maltase works best at what temperature?
The optimum pH, 6.5; optimum temperature, 48 to 50 degrees C; pH stability range, 5.0 to 7.0; temperature stability range, 0 to 50 degrees C; isoel...
What is the relationship between maltase’s structure and its function?
Maltase belongs to the GH13 (Glycoside hydrolase family 13) group intestinal enzymes that convert complex carbohydrates’ glucosidase connections in...
What is maltase’s alternative name?
The protein Maltase-Glucoamylase is encoded by the MGAM gene, which is found on chromosome 7q34. Maltase-Glucoamylase is also known as glucan 1,4-a...
What type of enzyme is maltase?
Maltase is an alpha-glucosidase enzyme that breaks down disaccharides like maltose into individual glucose molecules. Baker’s yeast cells are unabl...
What enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of maltose to glucose?
See Article History. Maltase, enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of the disaccharide maltose to the simple sugar glucose. The enzyme is found in plants, bacteria, and yeast; in humans and other vertebrates it is thought to be synthesized by cells of the mucous membrane lining the intestinal wall. During digestion, starch is partially transformed ...
What enzyme converts starch into glucose?
During digestion, starch is partially transformed into maltose by the pancreatic or salivary enzymes called amylases; maltase secreted by the intestine then converts maltose into glucose. The glucose so produced is either utilized by the body or stored in the liver as glycogen (animal starch).
Which enzyme catalyzes a reaction in which a molecule of water is inserted at the point
The digestive enzyme maltase catalyzes a reaction in which a molecule of water is inserted at the point at which the two glucose units are linked, thereby disconnecting them, as illustrated below.…
What is maltase enzyme?
Maltase is a member of the GH13 (Glycoside hydrolase family 13) of intestinal enzymes that are responsible for transforming complex carbohydrates' - glucosidase linkages into simple glucose molecules for usage. Then, these glucose molecules would be used as a sort of "food" for cells to produce the energy (it means, Adenosine triphosphate) during Cellular respiration. The genes that can code for maltase are given below:
What is the role of maltase in the digestive system?
Answer: The most important role of maltase as an enzyme in the human digestive system (also called maltase digestive enzyme) can be found when the starch is being assimilated into the maltose using pancreatic or salivary enzymes like amylase (amylase maltase).
What enzymes are needed for starch digestion?
Six intestinal enzymes are needed for starch digestion, two of which are luminal endo-glucosidases, also known as alpha-amylases. The remaining four enzymes have been identified as various maltases, exo-glucosidases bound to the enterocytes' luminal surface. The sucrase-isomaltase system was linked to two of these maltase activities (maltase Ib, maltase Ia). The rest of the two maltases with no distinguishing characteristics were named maltase-glucoamylase (also called maltases II and III). Since they all digest linear starch oligosaccharides to glucose, these four maltases are also known as alpha-glucosidase.
What is the function of alpha-amylase?
Alpha-amylase contains an essential function in the degradation of starches, so it is extremely and commonly used in the industry of baking. Also, it is mostly used as a means of flavour, enhancing it to improve bread quality. With no alpha-amylase, the yeast would not be possible to ferment.
What is the mechanism of all GH13 enzymes?
The hydrolysis of alpha-glucosidase linkage is the mechanism of all Family GH13 enzymes. Maltase focuses on dissolving maltose, which is a disaccharide with a - (1->4) bond connecting two units of glucose. The substrate size determines the rate of hydrolysis (or the carbohydrate size).
What is maltase enzyme?
Maltase. Tweet. What is maltase? Found in people, yeasts, bacteria and plants, maltase is an enzyme that can break down disaccharide maltose. It can digest disaccharides into malt sugars also known as monosaccharides. Throughout digestion, starch is being converted in maltose by salivary or pancreatic enzymes also known as amylases.
Why is maltase important?
Simply put, maltase is really important when it comes to the overall enzymatic process because it is used efficiently by the body to digest sugars and starch found under the shape of grains and other foods based on grains that we consume daily. Health benefits. Maltase is known as an essential digestive enzyme found in people’s mouths and saliva.
Why do autistic kids have lower maltase levels?
Mainly because autistic kids have lower amounts of maltase, research studies are now considering providing maltase enzymes to ease their symptoms. Another study showcased that 18 of 36 autistic kids had gastrointestinal disorders because of the lack of digestive enzymes within the gut. Also, biopsies have shown that the same kids were suffering ...
Where is maltase secreted?
The process is halted and temporary reduced throughout more acidic digestion phases within the stomach; however, it is also resumed within the neutral pH of small intestines where maltase will be again secreted. The enzyme’s vegetarian form is created through a natural process of fermentation known as Aspergillis oryzae.
Where is maltese produced?
Even though the enzyme can be easily included in people’s diets, it is also believed to be produced in the human body by a mucus casing within the intestinal wall. When starch is ingested, the enzyme is digested only partially and converted in maltose by the pancreatic enzymes and the saliva enzymes. Maltese is also a carbohydrate-digesting enzyme ...
Is maltase good for you?
Health benefits. Maltase is known as an essential digestive enzyme found in people’s mouths and saliva. It can ease digestion within the small intestine and the pancreas. The lack of maltase within the system might cause problems because the small intestine will have a more difficult job in breaking down starches and sugars.
Is Maltese a carbohydrate?
Maltese is also a carbohydrate-digesting enzyme that can be found naturally in sugars produced by the body when it breaks down starch. Additionally, it is a by-product when it comes to consuming sugar throughout several cooking processes, particularly during burning at high temperatures when the sugar changes colors from white to brown.
What is maltase enzyme?
Maltase. Tweet. What is maltase? Found in people, yeasts, bacteria and plants, maltase is an enzyme that can break down disaccharide maltose. It can digest disaccharides into malt sugars also known as monosaccharides. Throughout digestion, starch is being converted in maltose by salivary or pancreatic enzymes also known as amylases.
Why is maltase important?
Simply put, maltase is really important when it comes to the overall enzymatic process because it is used efficiently by the body to digest sugars and starch found under the shape of grains and other foods based on grains that we consume daily. Health benefits. Maltase is known as an essential digestive enzyme found in people’s mouths and saliva.
What enzyme breaks down starch?
When starch is ingested, the enzyme is digested only partially and converted in maltose by the pancreatic enzymes and the saliva enzymes. Maltese is also a carbohydrate-digesting enzyme that can be found naturally in sugars produced by the body when it breaks down starch.
Is maltase good for you?
Health benefits. Maltase is known as an essential digestive enzyme found in people’s mouths and saliva. It can ease digestion within the small intestine and the pancreas. The lack of maltase within the system might cause problems because the small intestine will have a more difficult job in breaking down starches and sugars.
Does maltase help with autism?
Maltase can work as a support and preventive mechanism for various digestive complaints in kids who suffer from autism. Advanced technology has managed to develop tremendously and thus, the use of enzymes like maltase could have beneficial effects.