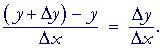Quick Overview
- The first derivative primarily tells us about the direction the function is going. That is, it tells us if the function is increasing or decreasing.
- The first derivative can be interpreted as an instantaneous rate of change.
- The first derivative can also be interpreted as the slope of the tangent line.
How do you calculate first derivative?
g(z) = f (x0 +az,y0 +bz) g ( z) = f ( x 0 + a z, y 0 + b z) where x0 x 0, y0 y 0, a a, and b b are some fixed numbers. Note that this really is a function of a single variable now since z z is the only letter that is not representing a fixed number.
What does first and second derivative mean?
- The first one is how position is changing over time. So, at periodic points, the position is measured. ...
- The second one is the measure of speed (because we are not considering direction), how much the position changes per unit time period. This is the first derivative.
- The third one is the acceleration, how much the velocity changes per unit time period. ...
How do you find the derivative of something?
It’s an appropriate setting given how much this derivative action movie borrows from other movies ... Elevating what could have been pure schlock into something more artful, he uses the freedom afforded by the film’s genre-mashing concept to tell ...
How to find the derivative?
With hundreds of pairs available to trade on centralized exchanges, developers at Maverick have caught the eye of an opportunity that will allow derivatives to grow on DEXs.
What does first derivative test tell you?
First-derivative test. The first-derivative test examines a function's monotonic properties (where the function is increasing or decreasing), focusing on a particular point in its domain. If the function "switches" from increasing to decreasing at the point, then the function will achieve a highest value at that point.
What does first and second derivative tell you?
In other words, just as the first derivative measures the rate at which the original function changes, the second derivative measures the rate at which the first derivative changes. The second derivative will help us understand how the rate of change of the original function is itself changing.
What does a derivative tell us about a function?
The derivative function tells you the rate of change of f for any given x, which is equivalent to telling you the slope of the graph of f for any given x. When the derivative is positive, the function is increasing. When the derivative is negative, the function is decreasing.
Why is the first derivative useful?
The first derivative will allow us to identify the relative (or local) minimum and maximum values of a function and where a function will be increasing and decreasing.
What does the first derivative tell you about concavity?
Our definition of concave up and concave down is given in terms of when the first derivative is increasing or decreasing. We can apply the results of the previous section and to find intervals on which a graph is concave up or down. That is, we recognize that f′ is increasing when f″>0, etc.
Is the first derivative velocity?
1st derivative is velocity In the SI (metric) system, it is measured in meters per second (m/s). The scalar absolute value (magnitude) of velocity is speed. For example, "5 metres per second" is a speed and not a vector, whereas "5 metres per second east" is a vector.
What is first order derivative?
First-Order Derivative The first order derivatives tell about the direction of the function whether the function is increasing or decreasing. The first derivative math or first-order derivative can be interpreted as an instantaneous rate of change. It can also be predicted from the slope of the tangent line.
What does the derivative represent?
The derivative is the instantaneous rate of change of a function with respect to one of its variables. This is equivalent to finding the slope of the tangent line to the function at a point.
What does the 2nd derivative tell you?
The second derivative tells whether the curve is concave up or concave down at that point. If the second derivative is positive at a point, the graph is bending upwards at that point. Similarly if the second derivative is negative, the graph is concave down.
What does it mean if the first derivative is greater than zero?
If the first derivative is positive on an interval, the function is increasing on this interval. If the first derivative is negative on an interval, the function is decreasing on this interval. INCREASING/DECREASING TEST: If f ' > 0 on an interval, the function is increasing on that interval.
Why are derivatives important in math?
Its importance lies in the fact that many physical entities such as velocity, acceleration, force and so on are defined as instantaneous rates of change of some other quantity. The derivative can give you a precise intantaneous value for that rate of change and lead to precise modeling of the desired quantity.
What does derivative mean in real life?
Application of Derivatives in Real Life To calculate the profit and loss in business using graphs. To check the temperature variation. To determine the speed or distance covered such as miles per hour, kilometre per hour etc. Derivatives are used to derive many equations in Physics.
What Is The Second Derivative Of A Function?
The second derivative of a function f (x) is the derivative of the derivative of f (x). In other notation:
What Does Second Derivative Tell You?
The second derivative f’’ (x) tells you how fast the first derivative f’ (x) is changing. However, there is a lot more that the second derivative can tell us, such as:
Conclusion
Now you know what the second derivative tells you and what it is. You also have some examples of how it is used to give us more information about a function and its shape.
What is the first order of a derivative?
The first order derivatives tell about the direction of the function whether the function is increasing or decreasing. The first derivative math or first-order derivative can be interpreted as an instantaneous rate of change. It can also be predicted from the slope of the tangent line.
What is the process of finding the derivative of a function?
The process of finding the derivative is called differentiation . The inverse process is called anti-differentiation. Let’s find the derivative of a function y = f (x). It is the measure of the rate at which the value of y changes with respect to the change of the variable x. It is known as the derivative of the function “f”, with respect to the variable x.
What is derivative in math?
Derivatives are defined as the varying rate of change of a function with respect to an independent variable. The derivative is primarily used when there is some varying quantity, and the rate of change is not constant. The derivative is used to measure the sensitivity of one variable (dependent variable) with respect to another variable ...
Why are derivatives divided into smaller parts?
Derivatives can be divided into smaller parts so that the given expressions can be easily evaluated. In the process of splitting the expressions or functions, the terms are separated based on the operator such as plus (+), minus (-) or division (/). This can be better understood using the examples given below.
How to differentiate a power of x?
To differentiate a power of x that is in the denominator, first express it as a power with a negative exponent. Eg. Derivative rules simplify the process of differentiating polynomial functions. To differentiate a radical, first, express it as a power with a rational exponent.