What is Paw (mean airway pressure)?
Mean Airway Pressure (Paw) defines the mean pressure applied during positive-pressure mechanical ventilation and correlates with alveolar ventilation, arterial oxygenation and hemodynamic performance. 1. Mean Airway Pressure Calculator 2.
How do you calculate the amount of inspiratory Paw?
Paw is determined by PIP, the fraction of time devoted to the inspiratory phase (T i /T tot, where T tot is total respiratory cycle time), and PEEP. Paw = ((Inspiratory Time x Frequency) / 60) x (PIP – PEEP) + PEEP
What is peak airway pressure in a ventilator?
In volume control, the pressure measured by the ventilator is the peak airway pressure, which is really the pressure at the level of the major airways. Dyssynchrony is a term which describes a patient fighting the ventilator.
Is weaning from ventilator the right or wrong concept?
Weaning from ventilator is a wrong concept. Liberation from ventilator is the right concept. Weaning with decreasing pressure support day by day is a poor strategy. When the primary lung pathology is reversed, we should aim for liberation from ventilator. Changing from square wave to ramp pattern increases the I-time, if the flow rate is constant.
What is Paw anesthesia machine?
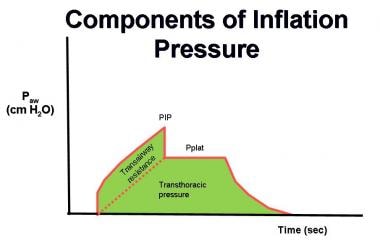
Paw is airway pressure, PIP is peak airway pressure, Pplat is plateau pressure. Some researchers have suggested that plateau pressures should be monitored as a means to prevent barotrauma in the patient with ARDS. Plateau pressures are measured at the end of the inspiratory phase of a ventilator-cycled tidal volume.
How do you calculate Paw ventilation?
For constant flow-volume ventilation, in which the airway pres- sure waveform is triangular, Paw can be calculated as: Paw 0.5 (PIP PEEP) (TI/Ttot) PEEP. During pressure ventilation, in which the airway pressure wave- form is rectangular, Paw can be estimated as: Paw (PIP PEEP) (TI/Ttot) PEEP.
What is Paw in Hfov?
THE EFFECT OF MEAN AIRWAY PRESSURE (Paw) ON DEAD SPACE/TIDAL VOLUME RATIO(VD/VT) DURING HIGH-FREQUENCY OSCILLATORY VENTILATION (HFOV). † 1138 | Pediatric Research.
What is a normal peak inspiratory pressure?
Normal peak inspiratory pressure (PIP) is 25-30 cm H2O. Peak inspiratory pressure (PIP) should be kept below 20 to 25 cm H2O whenever positive-pressure ventilation is required, especially if pneumothoraces, or fresh bronchial or pulmonary suture lines, are present.
How much PEEP is too much?
Increasing PEEP to 10 and higher resulted in significant declines in cardiac output. A PEEP of 15 and higher resulted in significant declines in oxygen delivery.
What does fio2 mean on a ventilator?
FiO2: Percentage of oxygen in the air mixture that is delivered to the patient. Flow: Speed in liters per minute at which the ventilator delivers breaths. Compliance: Change in volume divided by change in pressure.
What is Delta P HFO?
Delta P or power is the variation around the MAP. Mechanism. Oxygenation and CO2 elimination are independent. Oxygenation is. dependent on MAP.
What is MAP in HFOV?
High frequency oscillatory ventilation (HFOV) is a type of mechanical ventilation that uses a constant distending pressure (mean airway pressure [MAP]) with pressure variations oscillating around the MAP at very high rates (up to 900 cycles per minute). This document is only valid for the day on which it is accessed.
What is mPaw on HFOV?
High-frequency oscillatory ventilation (HFOV) delivered high mean airway pressure (mPaw) and extremely small tidal volumes to prevent alveolar derecruitment/overdistention as well as avoid the repeated opening/closing of individual alveolar [9].
What is difference between PEEP and PIP?
2. Applying an end-expiratory breath-hold allows measurement of end-expiratory alveolar pressure. The difference between PEEP set and the pressure measured during this maneuver is the amount of auto-PEEP. PIP = peak inspiratory pressure.
Is peak the same as PIP?
The peak inspiratory pressure (PIP) is the highest pressure measured during the respiratory cycle and is a function of both the resistance of the airways and the compliance of the respiratory system.
What is the difference between PEEP and plateau pressure?
Peak pressure applies when there is airflow in the circuit, i.e. during inspiration. What determines the peak pressure is the airway resistance in the lungs. So it follows that if there is a problem with the airways the peak pressure will rise. Plateau pressure applies when there is not airflow in the circuit.
What is APRV in ventilatory support?
Airway pressure release ventilation (APRV, also known as Bi-Level and Bi-phasic is a time-cycled, pressure-targeted form of ventilatory support. APRV is actually a variation of pressure-targeted SIMV that allows spontaneous breathing (with or without pressure support) to occur during both the inflation and the deflation phases. APRV differs from conventional pressure-targeted SIMV in the inspiratory: expiratory (I: E) timing. Specifically, conventional pressure-targeted SIMV uses a "physiological" inspiratory time with I: E ratio less than 1:1. Spontaneous breaths thus occur during the expiratory phase. In contrast, APRV uses prolonged inspiratory time producing so-called inverse ratio ventilation (I: E ratios of up to 4 or 5:1). Spontaneous breaths thus now occur during this prolonged inflation period.
What is PRVC in ventilators?
Pressure-regulated volume control (PRVC or VC+), in which all breaths are mandatory, the rate is fixed, and the inspiratory pressure is varied to maintain a preset tidal volume. Most people think that PRVC is a volume control mode because we are setting up a target tidal volume. However, it is a pressure controlled and time cycled mode , which by definition is a pressure control mode. For each breath, the ventilator adjusts the driving pressure based on lung compliance and resistance, to deliver target tidal volume.
What is peak pressure?
The peak pressure is the pressure measured by the ventilator in the major airways, and if plateau pressure is normal, it strongly reflects airways resistance. In pressure controlled ventilation, the pressure limit is (usually) the plateau pressure due to the dispersion of gas in inspiration.
How does pressure support work?
In pressure support, the patient triggers the ventilator and a pressure-limited breath is delivered: the patient determines the rate, the duration of inspiration and the tidal volume. The physician can determine how much work the ventilator can take from the patient, by altering the pressure limit.
What is the work of breath?
Work of breath = Volume x Pressure. It is the work required to overcome the mechanical impedance to respiration. In other words, it is the work needed to overcome both elastic and airflow resistance. The time constant is a measure of the time needed for alveolar pressure to reach 63% of the change in airway pressure.
What is driving pressure used for?
Part of this driving pressure is used to overcome the resistance and thus air will flow into alveoli. The remaining pressure is used to overcome the elastic recoil force, resulting in alveolar distension. Now add the driving pressure to the extrinsic PEEP, you get the peak pressure.
What is respiratory failure?
Respiratory failure is caused by failure to oxygenate (Type I respiratory failure), with resultant decreae in PO2 or failure to ventilate (Type II respiratory failure), with a resultant increase in PCO2.