Strong organic bases such as LDA (Lithium DiisopropylAmide) can be used to drive the ketone-enolate equilibrium completely to the enolate side. LDA is a strong base that is useful for this purpose. The steric bulk of its isopropyl groups makes LDA non-nucleophilic. Even so, it’s a strong base. LDA is prepared by the deprotonation of diisopropyl amine using a very strong base such as n-butyl lithium as shown.
What is LDA used for in elimination reactions?
Although less common, LDA can also be used for the formation of “ Hoffman ” products in elimination reactions. The usual base for this is potassium t-butoxide, but LDA can do it too: This diagram below shows the reaction between LDA and the ketone.
What is the role of aldol in LDA reaction?
LDA is a sterically hindered strong base and therefore, it deprotonates the less substituted carbon of the ketone: The directed aldol reaction works for other C-H acids such esters and nitriles as well:
What is the most common use of LDA?
So LDA can’t reach into tight spaces the same way that NaNH 2 can. In other words: LDA is a strong, bulky base. The most common use of LDA is in the formation of enolates . In the example below, notice how both carbons flanking the C=O have C-H bonds?
How do you make LDA from LDA?
LDA is prepared by the deprotonation o diisopropyl amine using a very strong base such as n-butyl lithium as shown. N H H+N diisopropyl amine CH3CH2CH2CH2 pKa = 35
What does LDA do to Ester?
LDA is very good for making enolates of esters, aldehydes and ketones since it can give essentially 100% (quantitative conversion) to the enolate. This allows the enolate to be alkylated or acylated with less chance of self-condensation reactions.
Do ketones react with LDA?
Many ketones form enolates cleanly with LDA, for example cyclohexanone: Although the reaction of carbonyl compounds with sodium hydride is slow, sodium enolates are formed with the loss of hydrogen, and no other organic compounds are produced.
What does LDA do to alkynes?
– Terminal alkynes can also be converted to alkyne anions by reaction with sodium hydride or lithium diisopropylamide (LDA). – Because water is a stronger acid than terminal alkynes, hydroxide ion is not a strong enough base to convert a terminal alkyne to an alkyne anion.
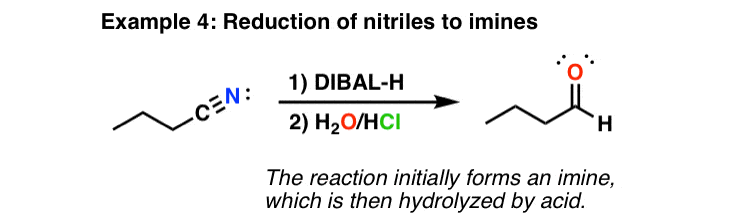
What does LDA do to a nitrile?
The reaction given involves the direct alkylation of a nitrile containing compound by the production of an enolate ion. The alpha hydrogen to the nitrile group which is weakly acidic can be deprotonated in the presence of a base. LDA is a mild base that converts these compounds to the enolate ion.
What does LDA do in organic Chem?
Strong organic bases such as LDA (Lithium DiisopropylAmide) can be used to drive the ketone-enolate equilibrium completely to the enolate side. LDA is a strong base that is useful for this purpose. The steric bulk of its isopropyl groups makes LDA non- nucleophilic. Even so, it's a strong base.
Is LDA a reducing agent?
Lithium Diisopropylamide (LDA) as an Efficient Reducing Agent for Thioketones—Mechanistic Consideration. Treatment of thiocarbonyl compounds with excess of lithium diisopropylamide (LDA) leads to corresponding thiols or sulfides depending on the work-up procedure.
Which position would be deprotonated by LDA?
2-positionDeprotonation of a dihydrothiazine ring, followed by a reaction with an electrophile, is most straightforward in benzothiazin-3-ones (general structure 35), which are deprotonated at the 2-position by lithium diisopropyl amide (LDA).
Can you use LDA for aldol condensation?
Directed aldol reactions are a variation of the crossed aldol reaction. The enolate is prepared with one carbonyl compound using LDA. This causes the other carbonyl compound to be the electrophile. Even though both components have alpha hydrogens only one acts as an enolate because it is formed with LDA.
What does NaOEt do in a reaction?
Treatment with the strong base sodium ethoxide (NaOEt) gives two alkenes (trans and cis) which follow Zaitsev's rule. The trans product dominates over the cis product (due to less steric crowding), but what's really interesting is the byproduct obtained: 2-ethoxy butane, obtained with inversion of stereochemistry.
What does LDA Deprotonate?
LDA has been shown to deprotonate the methyl group, which is the kinetic course of the deprotonation. To ensure the production of the kinetic product, a slight excess (1.1 equiv) of lithium diisopropylamide is used, and the ketone is added to the base at –78 °C.
Why LDA is called amide?
The anionic conjugate bases of amines are known as amides. Thus lithium amide may also refer to lithium salts of amines e.g. Li+NR2-. An example of a lithium amide is lithium diisopropylamide (LDA), which is quite commonly used.
What is the structure of LDA?
C6H14LiNLithium diisopropylamide / Formula
Why doesn't sodium hydroxide work for directed aldol reactions?
Sodium hydroxide and ethoxides don’t work for directed aldol reactions because the enolate is not formed irreversibly and self-condensation reactions can occur because there is still a lot of carbonyl present in the equilibrium mixture.
Why is aldehyde converted to enolate?
This happens because each aldehyde has an ɑ hydrogen and therefore, can be converted into an enolate to react with the carbonyl form of itself or the other molecule. The structure of the aldol addition product depends on which aldehyde served as the enolate and which one reacted as the electrophile: Because of this, crossed aldol reactions are ...
How to prevent self condensation reaction?
The strategy is to mix the benzaldehyde with sodium hydroxide and add the acetaldehyde to this solution in a dropwise manner to keep its concentration very low. This allows to have a huge excess of the benzaldehyde over the enolate that is forming thus preventing the self-condensation reaction:
Can propanal react with itself?
However, there is one thing we have not consider here and that is the fact that propanal can still react with itself.
Is crossed aldol a good example of organic synthesis?
Because of this, crossed aldol reactions are generally not useful in organic synthesis. One exception is the reaction of aldehydes with no ɑ hydrogens. A good example of are benzaldehyde and formaldehyde: The lack of the ɑ hydrogens prevents it from converting into an enolate. So, if we react it with propanal in presence of a base, ...
Can crossed aldol be synthetically useful?
However, chemists wouldn’t tolerate such a limitation and luckily it was found that any crossed aldol reaction can be synthetically useful by selectively and irreversibly convert ing one ...
Is LDA a strong base?
LDA is a sterically hindered strong base and therefore, it deprotonates the less substituted carbon of the ketone: The directed aldol reaction works for other C-H acids such esters and nitriles as well: To react on the more substituted ɑ-carbon of the ketone, sodium hydride is often used as a strong unhindered base: