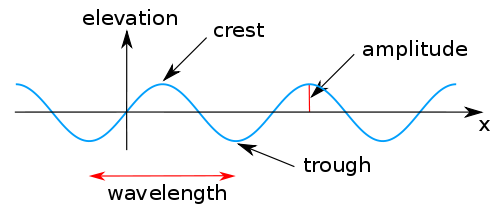
What does it mean when a wave's amplitude is high?
A high amplitude wave carries a large amount of energy; a low amplitude wave carries a small amount of energy. Click to see full answer. Similarly, it is asked, what does it mean when a wave's amplitude increases Brainpop?
How do you find the amplitude of a sound wave?
An oscilloscope is a popular and accurate way to do so. You can also determine the amplitude mathematically if it is the only variable and you know the frequency and wavelength. What happens when the amplitude of a sound wave increases?
What is the relationship between amplitude and energy?
The amplitude of a wave is related to the amount of energy it carries. A high amplitude wave carries a large amount of energy; a low amplitude wave carries a small amount of energy. Click to see full answer.
How does synchronization affect the amplitude of brain waves?
Synchronized activity increases the amplitude of brain waves and hence increases their amplitude. Amplitude is hence directly related to the level of synchronization. This shows up as larger peaks on the FFT. What synchronization exactly does to the brain boils down to down to is the classic interpretation of EEG frequency bands (Table 1).
What is brain waves?
Brain waves are a colloquial term for EEG recordings. EEG recordings are gross potential recordings, in other words, they represent the responses of thousands of neurons together. Much of the background is stochastically determined, meaning it represents, basically, random activity. In other words, oftentimes neurons fire stochastically ...
What is slow wave deep sleep?
Certain stages of sleep, most notably slow-wave deep sleep, is characterized by gross synchronized, slow-wave activities across the cortex, showing up in the raw EEG. In fact, simply closing ones eyes has marked effects on the cortical synchronization on the raw EEG.
Does synchronization increase amplitude?
Synchronized activity increases the amplitude of brain waves and hence increases their amplitude. Amplitude is hence directly related to the level of synchronization. This shows up as larger peaks on the FFT. What synchronization exactly does to the brain boils down to down to is the classic interpretation of EEG frequency bands (Table 1).