Here’s a brief summary of the main points in this article:
- The F-value in an ANOVA is calculated as: variation between sample means / variation within the samples.
- The higher the F-value in an ANOVA, the higher the variation between sample means relative to the variation within the samples.
- The higher the F-value, the lower the corresponding p-value.
- If the p-value is below a certain threshold (e.g. ...
What does F value stand for in ANOVA analysis?
The F value is a value on the F distribution. Various statistical tests generate an F value. The value can be used to determine whether the test is statistically significant. The F value is used in analysis of variance (ANOVA). It is calculated by dividing two mean squares.
What does it signify all means are equal in ANOVA?
ANOVA. The null hypothesis of ANOVA assumes that all means are equal. This is equivalent to stating that all samples were taken from the same population. The ANOVA test eliminates the problem of multiple t-tests on the same sample means by testing all the means at once to see if any of the means are different.
How is statistical significance calculated in an ANOVA?
- The first column lists the independent variable along with the model residuals (aka the model error).
- The Df column displays the degrees of freedom for the independent variable (calculated by taking the number of levels within the variable and subtracting 1), and the degrees of freedom ...
- The Sum Sq column displays the sum of squares (a.k.a. ...
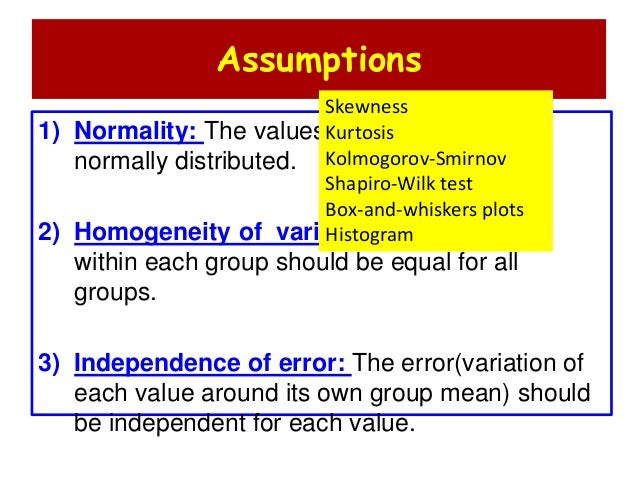
What are the basic assumptions of ANOVA?
Assumptions for One-Way ANOVA TestSection. There are three primary assumptions in ANOVA: The responses for each factor level have a normal population distribution. These distributions have the same variance. The data are independent. Note! Violations to the first two that are not extreme can be considered not serious.
How do you interpret F value in ANOVA?
The F ratio is the ratio of two mean square values. If the null hypothesis is true, you expect F to have a value close to 1.0 most of the time. A large F ratio means that the variation among group means is more than you'd expect to see by chance.
What does the F value tell you?
The F-statistic is simply a ratio of two variances. Variances are a measure of dispersion, or how far the data are scattered from the mean. Larger values represent greater dispersion. ... Unsurprisingly, the F-test can assess the equality of variances.18-May-2016
What does an F value of 1 mean in ANOVA?
A value of F=1 means that no matter what significance level we use for the test, we will conclude that the two variances are equal.05-Mar-2016
Is a high F value good?
If you get a large f value (one that is bigger than the F critical value found in a table), it means something is significant, while a small p value means all your results are significant. The F statistic just compares the joint effect of all the variables together.
What does an F value of 0 mean?
Here, the F statistic is the ratio of explained variance to unexplained variance. For F to equal exactly 0, the explained variance would have to be exactly 0. In an ANOVA context, that would imply that the means in every group were exactly equal.
What does it mean if the F ratio is less than 1?
When the null hypothesis is false, it is still possible to get an F ratio less than one. The larger the population effect size is (in combination with sample size), the more the F distribution will move to the right, and the less likely we will be to get a value less than one.
Can an F statistic be greater than 1?
If the F-score is much greater than one, the variance between is probably the source of most of the variance in the total sample, and the samples probably come from populations with different means.
What is the purpose of one way ANOVA?
A one-way ANOVA is used to determine whether or not the means of three or more independent groups are equal. A one-way ANOVA uses the following null and alternative hypotheses: H0: All group means are equal. HA: At least one group mean is different from the rest.
What does it mean when you don't have sufficient evidence to say that the studying technique used causes statistically significant differences
This means we don’t have sufficient evidence to say that the studying technique used causes statistically significant differences in mean exam scores. In other words, this tells us that the variation between the sample means is not high enough relative to the variation within the samples to reject the null hypothesis.
What is the F statistic?
An F-statistic is the ratio of two variances, or technically, two mean squares. Mean squares are simply variances that account for the degrees of freedom (DF) used to estimate the variance. Think of it this way. Variances are the sum of the squared deviations from the mean.
Why is it so difficult to interpret variances?
It’s difficult to interpret variances directly because they are in squared units of the data.
Can F-tests be used to determine if two variances are equal?
Given that F-tests evaluate the ratio of two variances, you might think it’s only suitable for determining whether the variances are equal. Actually, it can do that and a lot more! F-tests are surprisingly flexible because you can include different variances in the ratio to test a wide variety of properties.
Overview: What is the F-value in the context of ANOVA?
We need to start off by describing what we mean by ANOVA. ANOVA is a statistical hypothesis test that allows you to determine whether there is a statistical difference between the means of three or more groups.
3 benefits of the F-value
Here are some of the key benefits of using the F-value to make decisions about your group means.
Why is the F-value important to understand?
The F-value is a popular and powerful statistical tool for making decisions regarding differences in group means. It is important to understand for the following reasons.
An industry example of the F-value
A plant manager is trying to determine if there is any true difference between the productivity of his three manufacturing shifts. He has collected data based on the three shifts at the plant.
3 best practices when thinking about the F-value
While your statistical software will do all the calculations, there are some things you can do to be sure your results are meaningful
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about the F-value
References to F in statistics are named after Sir Ronald Fisher, a British mathematician, statistician, geneticist, and academic.
F-value recap
The F-value is the result of an ANOVA hypothesis test for determining whether there is a statistically significant difference in the means of three or more groups of data.
Why does ANOVA use the F test?
ANOVA uses the F-test to determine whether the variability between group means is larger than the variability of the observations within the groups. If that ratio is sufficiently large, you can conclude that not all the means are equal. This brings us back to why we analyze variation to make judgments about means.
How to use the F-test in ANOVA?
To use the F-test to determine whether group means are equal, it’s just a matter of including the correct variances in the ratio. In one-way ANOVA, the F-statistic is this ratio:
What is the F test?
F-tests are named after its test statistic, F, which was named in honor of Sir Ronald Fisher. The F-statistic is simply a ratio of two variances. Variances are a measure of dispersion, or how far the data are scattered from the mean. Larger values represent greater dispersion. Variance is the square of the standard deviation.
What is the F statistic?
The F-statistic is the test statistic for F-tests. In general, an F-statistic is a ratio of two quantities that are expected to be roughly equal under the null hypothesis, which produces an F-statistic of approximately 1. The F-statistic incorporates both measures of variability discussed above.
What is an ANOVA?
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) can determine whether the means of three or more groups are different. ANOVA uses F-tests to statistically test the equality of means. In this post, I’ll show you how ANOVA and F-tests work using a one-way ANOVA example.
What is the mean of a one way ANOVA?
One-way ANOVA has calculated a mean for each of the four samples of plastic. The group means are: 11.203, 8.938, 10.683, and 8.838. These group means are distributed around the overall mean for all 40 observations, which is 9.915. If the group means are clustered close to the overall mean, their variance is low. However, if the group means are spread out further from the overall mean, their variance is higher.
Why are standard deviations easier to understand than variances?
For us humans, standard deviations are easier to understand than variances because they’re in the same units as the data rather than squared units. However, many analyses actually use variances in the calculations. F-statistics are based on the ratio of mean squares.
Overview: What Is The F-value in The Context of ANOVA?
Why Is The F-value Important to Understand?
An Industry Example of The F-value
3 Best Practices When Thinking About The F-value
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About The F-value
F-value Recap
- The F-value is the result of an ANOVA hypothesis test for determining whether there is a statistically significant difference in the means of three or more groups of data. The F-value is the ratio of the sum of squares for the difference between each group mean and the grand mean (between variation) and the sum of squares for the difference of the ...