What color is the cytoplasm?
Cytoplasm is the jellylike material outside the cell nucleus in which the organelles are located. Color and label the cytoplasm pink. All cells, even prokaryotes (bacteria) contain small bodies called ribosomes.
What does a cytoplasm look like for kids?
Cytoplasm is a watery, gel-like substance made of mostly salt and water that provides a structure for the cell parts so they can move freely within the cell membrane. Enzymes, which help digest and break down other molecules for food, are also found in cytoplasm.Dec 7, 2021
How is a cytoplasm like a swimming pool?
The cytoplasm represents the pathways / grass around the grounds of the pool because they take everyone to the different parts of the pool and the cytoplasm carries waste and food around to the other organelles.
What is a cytoplasm for school?
Cytoplasm is like the hallways of the school. The hallways are where everyone travels through the school. in or out. The Cell Wall is like the beams in a school because it provides the school support.
What is cytoplasm?
The cytoplasm is the fluid present in the cell enclosed within the cell membrane that comprises water and enzymes, salts, and various organelles.
What is the important function of cytoplasm?
The cytoplasm is responsible for holding the components of the cell and protects them from damage. It stores the molecules required for cellular pr...
What would happen if the cell had no cytoplasm?
A cell would be deflated and flat and would not be able to retain its shape without the cytoplasm. The organelles will not be able to suspend in th...
What would happen if there was no nucleus in the cell?
The nucleus contains the hereditary material and is responsible for cell division. It is known as the brain of the cell and controls all its activi...
What is the charge in the cytoplasm?
For every single ATP molecule, 3 sodium ions are exported to the extracellular space of the cell while two potassium ions are imported to the cytop...
What is the pH of cytoplasm?
The pH of the cytoplasm is 7.4.
What is the cytoplasm?
Cytoplasm. In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm.
Why is the flow of cytoplasmic components important?
The flow of cytoplasmic components play s an important role in many cellular functions which are dependent on the permeability of the cytoplasm.
What are the organelles of the maternal gamete?
The cytoplasm, mitochondria and most organelles are contributions to the cell from the maternal gamete. Contrary to the older information that disregards any notion of the cytoplasm being active, new research has shown it to be in control of movement and flow of nutrients in and out of the cell by viscoplastic behavior and a measure of the reciprocal rate of bond breakage within the cytoplasmic network.
What is the material inside the nucleus?
The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The main components of the cytoplasm are cytosol (a gel-like substance), the organelles (the cell's internal sub-structures), and various cytoplasmic inclusions. The cytoplasm is about 80% water and usually colorless.
What is the outer layer of the cell called?
The concentrated inner area is called the endoplasm and the outer layer is called the cell cortex or the ectoplasm . Movement of calcium ions in and out of the cytoplasm is a signaling activity for metabolic processes. In plants, movement of the cytoplasm around vacuoles is known as cytoplasmic streaming .
What is the cytosol?
Main article: Cytosol. The cytosol is the portion of the cytoplasm not contained within membrane-bound organelles. Cytosol makes up about 70% of the cell volume and is a complex mixture of cytoskeleton filaments, dissolved molecules, and water.
What are the organelles in the cell?
Some major organelles that are suspended in the cytosol are the mitochondria, the endoplasmic reticulum, the Golgi apparatus, vacuoles, lysosomes, and in plant cells, chloroplasts .
What is the cytoplasm?
Cytoplasm consists of all of the contents outside of the nucleus and enclosed within the cell membrane of a cell. It is clear in color and has a gel-like appearance. Cytoplasm is composed mainly of water but also contains enzymes, salts, organelles, and various organic molecules.
What are the two parts of the cytoplasm?
The cytoplasm can be divided into two primary parts: the endoplasm ( endo -,- plasm) and ectoplasm ( ecto -,-plasm). The endoplasm is the central area of the cytoplasm that contains the organelles. The ectoplasm is the more gel-like peripheral portion of the cytoplasm of a cell.
What is the structure that separates the cytoplasm from the extracellular fluid?
The cell membrane or plasma membrane is the structure that keeps cytoplasm from spilling out of a cell. This membrane is composed of phospholipids, which form a lipid bilayer that separates the contents of a cell from the extracellular fluid. The lipid bilayer is semi-permeable, meaning that only certain molecules are able to diffuse across the membrane to enter or exit the cell. Extracellular fluid, proteins, lipids, and other molecules may be added to a cell's cytoplasm by endocytosis. In this process, molecules and extracellular fluid are internalized as the membrane turns inward forming a vesicle. The vesicle encloses the fluid and molecules and buds off from the cell membrane forming an endosome. The endosome moves within the cell to deliver its contents to their appropriate destinations. Substances are removed from the cytoplasm by exocytosis. In this process, vesicles budding from Golgi bodies fuse with the cell membrane expelling their contents from the cell. The cell membrane also provides structural support for a cell by serving as a stable platform for the attachment of the cytoskeleton and cell wall (in plants).
What is the function of the cytoplasm?
Cytoplasm Functions. The cytoplasm functions to support and suspend organelles and cellular molecules. Many cellular processes also occur in the cytoplasm, such as protein synthesis, the first stage of cellular respiration (known as glycolysis ), mitosis, and meiosis. The cytoplasm helps to move materials, such as hormones, ...
What are the three types of inclusions in the cytoplasm?
Three types of inclusions found in the cytoplasm are secretory inclusions, nutritive inclusions, and pigment granules . Examples of secretory inclusions are proteins, enzymes, and acids. Glycogen (glucose storage molecule) and lipids are examples of nutritive inclusions.
What are some examples of organelles?
Examples of organelles include mitochondria, ribosomes, nucleus, lysosomes, chloroplasts, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus. Also located within the cytoplasm is the cytoskeleton, a network of fibers that help the cell maintain its shape and provide support for organelles.
What is cytoplasmic streaming?
Cytoplasmic Streaming. Cytoplasmic streaming, or cyclosis, is a process by which substances are circulated within a cell. Cytoplasmic streaming occurs in a number of cell types including plant cells, amoeba, protozoa, and fungi. Cytoplasmic movement may be influenced by several factors including the presence of certain chemicals, hormones, ...
What is the cytoplasm in a cell?
It is a semi-liquid jelly-like material, which joins the nucleus and the cell membrane. In the cell, the cytoplasm is embedded, while other cell organelles such as endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, ribosomes, vacuoles, etc. are all suspended within it.
What is the function of the cytoplasm?
One of the major functions of cytoplasm is to enable cells to maintain their turgidity, which enables the cells to hold their shape. Other functions of cytoplasm are as follows: The jelly-like fluid of the cytoplasm is composed of salt and water and is present within the membrane of the cells and embeds all of the parts of the cells and organelles.
What is the membrane of a cell?
The plasma membrane or cell membrane is a bi-lipid membranous layer, parting the cell organelles from its outside environment and from the different cells. It is the external covering of a cell where all different parts, including cytoplasm and nucleus, are enclosed. Next, is the nucleus, one of the biggest organelle.
What is the whole cellular content of a living cell called?
The whole cellular content of a living cell is called protoplasm. The cytoplasm, nucleus and all other living components of the cell together make up the protoplasm of a cell. Further Reading: Difference Between Cytoplasm and Protoplasm.
What happens if the cytosol is not in the cytoplasm?
The cells, without cytoplasm, would deflate and substances will not permeate easily from one to the other organelle . A part of the cytoplasm, the cytosol has no organelles.
What are the three main organelles of a cell?
All these structures are distinct and perform specific functions. Cells have three main elements i.e., plasma membrane, and cytoplasm and the nucleus.
What is the fluid that fills up cells called?
What is Cytoplasm? The fluid that fills up the cells is referred to as the cytoplasm. It encompasses the cytosol with filaments, ions, proteins, and macromolecular structures and also other organelles suspended in the cytosol. But new research suggests that the traditional definition of cytoplasm is no longer valid.
What does cytoplasm mean in narration?
Narration. Cytoplasm's a funny term. So what does "cyto" mean? "Cyto" means "cell", "plasm" means "stuff", so it's "cell stuff". So think about a cell as a big water balloon, and the water balloon has little pieces of fruit floating around in it. And the cytoplasm is the water in the water balloon, and it's a little bit thicker than water, ...
What is the liquid that fills the inside of a cell?
Cytoplasm. Cytoplasm is the gelatinous liquid that fills the inside of a cell. It is composed of water, salts, and various organic molecules.
What is the cytoplasm?
Cytoplasm is a clear substance that is gel-like in the cell membrane but is on the outside of the nucleus. It contains mostly water with the addition of enzymes, organelles, salts and organic molecules. Cytoplasm will liquefy when it is stirred or agitated. It is often referred to as cytosol, meaning "substance of the cell.".
How to see the large picture of a cytoplasm analogy of a restaurant?
In order to see the large picture of a cytoplasm analogy of a restaurant it is best to represent the entire cell through an analogy. The entire cell represents the entire restaurant, as it requires many different parts inside to function, just as cells have organelles for specific functions.
What is the function of the cytoplasm in cell division?
Cytoplasm is also a means of transportation for genetic material in cell division. It is a buffer to protect the genetic material of the cell and keep the organelles from damage when they move and collide with each other. If a cell would be without cytoplasm it could not retain its shape and would be deflated and flat.
What is the role of the nucleus in eukaryotic cells?
It is a structure containing the hereditary information, and its job is to control the growth and reproduction of a cell.
What is the function of the cytoplasm?
Cytoplasm supports and suspends cellular molecules and organelles. Organelles are tiny cellular structures within the cytoplasm that perform specific functions in bacteria or prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells of plants, animals and humans.
What is the function of the Golgi bodies in a cell?
The Golgi bodies serve to sort and transfer substances to be used in the cell or to transfer them out of the cell.
What are the different types of particles in the cytoplasm?
Cytoplasm contains proteins that are 20 to 25 percent soluble, and this includes enzymes. Carbohydrates, lipids and inorganic salts are particles in cytoplasm.
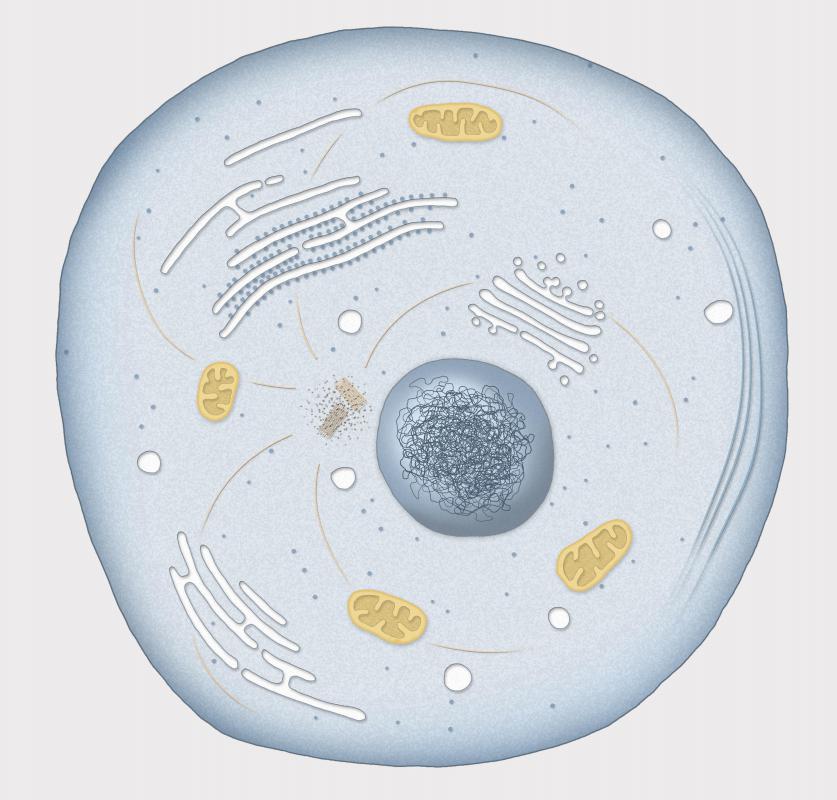
Overview
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The main components of the cytoplasm are cytosol (a gel-like substance), the organelles (the cell's internal sub-structures), and various cytoplasmic inclusions. The cytoplasm is about 80% water and is usually colorless.
History
The term was introduced by Rudolf von Kölliker in 1863, originally as a synonym for protoplasm, but later it has come to mean the cell substance and organelles outside the nucleus.
There has been certain disagreement on the definition of cytoplasm, as some authors prefer to exclude from it some organelles, especially the vacuoles and sometimes the plastids.
Physical nature
It remains uncertain how the various components of the cytoplasm interact to allow movement of organelles while maintaining the cell's structure. The flow of cytoplasmic components plays an important role in many cellular functions which are dependent on the permeability of the cytoplasm. An example of such function is cell signalling, a process which is dependent on the manner in which signaling molecules are allowed to diffuse across the cell. While small signalin…
Constituents
The three major elements of the cytoplasm are the cytosol, organelles and inclusions.
The cytosol is the portion of the cytoplasm not contained within membrane-bound organelles. Cytosol makes up about 70% of the cell volume and is a complex mixture of cytoskeleton filaments, dissolved molecules, and water. The cytosol's filaments include the protein filaments such as actin filaments and microtubules that make up the cytoskeleton, as well as soluble proteins and …
See also
• Amoeboid movement – Mode of locomotion in eukaryotic cells
• Cytoplasmic streaming – Flow of the cytoplasm inside the cell
• Protoplasm – Alternative term for cytoplasm or cytoplasm and nucleoplasm
External links
• Luby-Phelps K (2000). "Cytoarchitecture and physical properties of cytoplasm: volume, viscosity, diffusion, intracellular surface area". Microcompartmentation and Phase Separation in Cytoplasm (PDF). Int Rev Cytol. International Review of Cytology. Vol. 192. pp. 189–221. doi:10.1016/S0074-7696(08)60527-6. ISBN 9780123645968. PMID 10553280. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 September 2008.
Divisions
Components
- Prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria and archaeans, do not have a membrane-bound nucleus. In these cells, the cytoplasm consists of all of the contents of the cell inside the plasma membrane. In eukaryotic cells, such as plant and animal cells, the cytoplasm consists of three main components. They are the cytosol, organelles, and various particles and granules called cytopla…
Cytoplasmic Streaming
- Cytoplasmic streaming, or cyclosis, is a process by which substances are circulated within a cell. Cytoplasmic streaming occurs in a number of cell types including plant cells, amoeba, protozoa, and fungi. Cytoplasmic movement may be influenced by several factors including the presence of certain chemicals, hormones, or changes in light or temperature. Plants employ cyclosis to shutt…
Cell Membrane
- The cell membrane or plasma membrane is the structure that keeps cytoplasm from spilling out of a cell. This membrane is composed of phospholipids, which form a lipid bilayer that separates the contents of a cell from the extracellular fluid. The lipid bilayer is semi-permeable, meaning that only certain molecules are able to diffuse across the membrane to enter or exit the cell. Extracell…
Sources
- “Cytoplasmic inclusions.” The Free Dictionary, Farlex,
- “Ectoplasm.” The Free Dictionary, Farlex,
- “Endoplasm.” The Free Dictionary, Farlex, .
- Goldstein, Raymond E., and Jan-Willem van de Meent. “A physical perspective on cytoplasmic streaming.” Interface Focus 5.4 (2015):20150030.