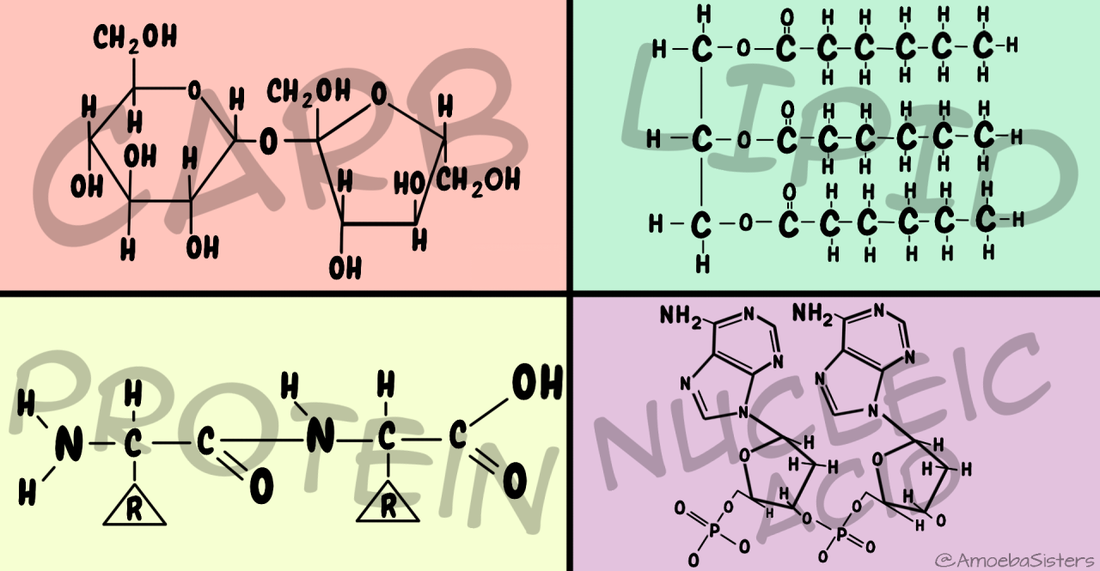
Accordingly, what do all 4 biomolecules have in common? The 4 main categories of biological (organic) molecules are carbohydrates, nucleic acids
Nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, or large biomolecules, essential for all known forms of life. Nucleic acids, which include DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid), are made from monomers known as nucleotides. Each nucleotide has three compone…
What are the four basic types of bio molecules?
What are the different types of biomolecules and their functions?
- Carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are a vital part of a healthy diet.
- Proteins. Proteins are unbranched polymers of amino acid residues.
- Nucleic Acids. Nucleic acids are macromolecules present in cells and viruses, and they are involved in the storage and transfer of genetic information.
- Lipids.
What elements compose each of the four types of biomolecules?
- Radioactive Carbon: C-14 in place of normal C-12
- Radioactive Hydrogen: H-3 (tritium) instead of normal H-1
- Radioactive Phosphorus: P-32 instead of normal P-31
- Radioactive Sulfur: S-35 instead of normal S-32.
What are the 4 families of biomolecules?
Biochemistry 1: Monomers and Polymers; The Four Families of Biological Molecules (Interactive Tutorial)
- We’re all built from the same stuff: the four families of biological molecules. Think of the five most different living things that you can imagine. ...
- Monomers and Polymers. If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device. ...
- Dehydration synthesis is how monomers become polymers. ...
- Hydrolysis is how polymers become monomers. ...
What are the three elements found in all biomolecule?
There are several derivatives of monosaccharide’s, some of which are physiologically important:
- Amino sugars: When one or more hydroxyl groups of the monosaccharide’s are replaced by amino groups, the products formed are amino sugars e.g. D-glucosamine, D-galactosamine. ...
- Deoxysugars: These are the sugars that contain one oxygen less than that present in the parent molecule. ...
- L-Ascorbic acid (vitamin C):
What are similarities between the 4 biomolecules?
What elements do all 4 biomolecule groups have in common?
What do all biological molecules have in common?
What are the characteristics of biomolecules?
- Most of them are organic compounds.
- They have specific shapes and dimensions.
- The functional group determines their chemical properties.
- Many of them are asymmetric.
- Macromolecules are large molecules and are constructed from small building block molecules.
What are the 4 main elements making up proteins?
Which of the 4 types of biomolecules contain nitrogen atoms?
- Usually, proteins and nucleic acids are the biomolecules that contain nitrogen.
- Proteins are composed up of amino acids that have an amine group.
- DNA and RNA have nitrogen as a ring structure.
What are the four main types of molecules in cell?
What are the four main categories of biomolecules?
The four main categories of biomolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids . While there are some special cases to be found, these four molecules make up the bulk of living bodies, and each plays an essential role in regulating the body's chemistry.
What are the two main types of energy that the body uses?
Carbohydrates are the starches and sugars that bodies use for energy. Brains, for example, consume large amounts of glucose with consumption rising in areas of the brain that are the most active. Lipids help the body store the energy it needs in the form of fats and oils. Wax, of the type secreted by honeybees, is another form of lipid. Proteins are the workhorses of the body's machinery. Proteins carry out specific functions inside cells, and they act as enzymes to catalyze reactions all over the body. Amylase, lactase and pepsin are all proteins used in digestion, for example. Proteins are typically large molecules that can be built up from chains of amino acids called polypeptides. Nucleic acids are central to the function of living cells. Arranged in a linear sequence within DNA, they code for the structure and function of the body's proteins. Nucleic acids also form RNA, which acts to transmit DNA-based instructions to the cellular machinery.
What are the proteins used in digestion?
Amylase, lactase and pepsin are all proteins used in digestion, for example. Proteins are typically large molecules that can be built up from chains of amino acids called polypeptides. Nucleic acids are central to the function of living cells.
How many types of biomolecules are there?
Each of 4 major types of biomolecules is an important cell component and performs a wide variety of functions.
What are the most important macromolecules for the continuity of life?
Lipids (triglycerides, phospholipids, steroids) Proteins. Nucleic Acids (DNA, RNA) Besides their specific roles, carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins can serve as a source of energy, while nucleic acids are the most important macromolecules for the continuity of life.
What are the two types of organic compounds?
There are two main types of structures of organic compounds: 1 Structural isomers 2 Stereoisomers
How do plants produce carbohydrates?
Plants and algae produce millions of tons of carbohydrates each year through photosynthesis.
What type of structure does carbon form?
Carbon atoms attaching to each other can form straight or branched chains and ringed structures of organic compounds.
Why are stereoisomers different from other types of atoms?
Because of their different structures, they have different properties and are metabolized differently. Stereoisomers have similar placements of their covalent bonds but differ in how these bonds are made to the surrounding atoms. Stereoisomers can be geometrical or optical.
Which functional group of amino acids reacts to each other to form peptide bonds?
Amino and carboxyl functional groups of amino acids react to each other to form peptide bonds of proteins.
What are the different types of biomolecules?
Types of Biomolecules. There are four major classes of Biomolecules – Carbohydrates, Proteins, Nucleic acids and Lipids. Each of them is discussed below.
What are the most essential organic molecules?
Biomolecules are the most essential organic molecules, which are involved in the maintenance and metabolic processes of living organisms. These non-living molecules are the actual foot-soldiers of the battle of sustenance of life.
What is the monomeric unit of nucleic acids?
The monomeric unit of nucleic acids is known as nucleotide and is composed of a nitrogenous base, pentose sugar, and phosphate. The nucleotides are linked by a 3’ and 5’ phosphodiester bond. The nitrogen base attached to the pentose sugar makes the nucleotide distinct.
What are lipids in water?
Lipids are organic substances that are insoluble in water , soluble in organic solvents, are related to fatty acids and are utilized by the living cell. They include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins, mono-, di- or triglycerides, phospholipids, etc. Unlike carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids, lipids are not polymeric molecules.
What are the four nitrogenous bases in DNA?
There are 4 major nitrogenous bases found in DNA: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. In RNA, thymine is replaced by uracil. The DNA structure is described as a double-helix or double-helical structure which is formed by hydrogen bonding between the bases of two antiparallel polynucleotide chains.
What is the function of nucleic acids?
There are two types of nucleic acids namely, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). The main function of nucleic acid is the transfer of genetic information and synthesis ...
What is the class of biomolecules that make up the bulk of the cellular dry weight?
Proteins are another class of indispensable biomolecules, which make up around 50per cent of the cellular dry weight. Proteins are polymers of amino acids arranged in the form of polypeptide chains. The structure of proteins is classified as primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary in some cases. These structures are based on the level of ...
Answer
Accordingly, what do all 4 biomolecules have in common? The 4 main categories of biological (organic) molecules are carbohydrates, nucleic acids, proteins, and lipids . All four of those types of molecules contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
Answer
All biomolecules share in common a fundamental relationship between structure and function, which is influenced by factors such as the environment in which a given biomolecule occurs
New questions in Science
2. Which component of biodiversity deals in the genetic information that organisms contain?A ecosystem B. speciesC. geneticsD. functional