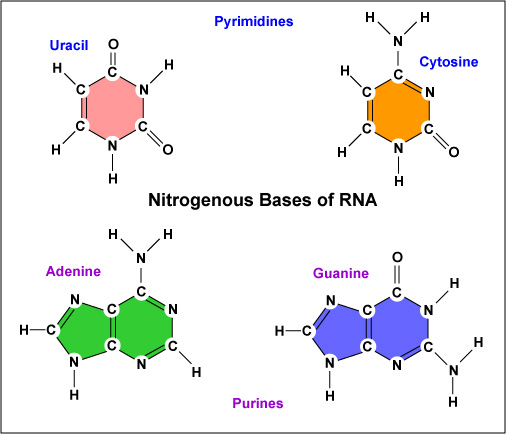
Which base matches up to adenine?
Adenine
- 1 Structures
- 2 Names and Identifiers. Computed by Lexichem TK 2.7.0 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) Computed by InChI 1.0.6 (PubChem release 2021.05.07)
- 3 Chemical and Physical Properties. ...
- 4 Spectral Information. ...
- 6 Chemical Vendors
- 7 Drug and Medication Information
- 8 Pharmacology and Biochemistry. ...
- 9 Use and Manufacturing. ...
- 10 Safety and Hazards. ...
- 11 Toxicity. ...
What is nitrogen base always pairs up with adenine?
The nitrogenous bases form hydrogen bonds between opposing DNA strands to form the rungs of the "twisted ladder" or double helix of DNA or a biological catalyst that is found in the nucleotides. Adenine is always paired with thymine, and guanine is always paired with cytosine. These are known as base pairs.
Which of these RNA bases pairs with adenine?
The RNA that base pairs with the adenine in DNA are Thymine. The hydrogen bonds them together. However, it is the Uracil having a similar structure of Thymine form the base pair in RNA.
What base bonds with adenine in a DNA strand?
Within the DNA molecule, adenine bases located on one strand form chemical bonds with thymine bases on the opposite strand. The sequence of four DNA bases encodes the cell's genetic instructions.
See more
What base does adenine always pair with?
thymineIn base pairing, adenine always pairs with thymine, and guanine always pairs with cytosine.
Which base does adenine pair with in RNA?
In DNA base pairing, adenine always pairs with thymine, and guanine always pairs with cytosine. Adenine is also one of the bases in RNA. There it always pairs with uracil (U).
What bases pair in RNA?
The four bases that make up this code are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C). Bases pair off together in a double helix structure, these pairs being A and T, and C and G. RNA doesn't contain thymine bases, replacing them with uracil bases (U), which pair to adenine1.
Is adenine paired with uracil?
Uracil (U) is one of the four nucleotide bases in RNA, with the other three being adenine (A), cytosine (C) and guanine (G). In RNA, uracil pairs with adenine. In a DNA molecule, the nucleotide thymine (T) is used in place of uracil.
What is the parent compound of adenine?
Adenine is the precursor for adenosine and deoxyadenosine nucleosides. Adenine is the parent compound of the 6-aminopurines, composed of a purine having an amino group at C-6.
What is the purpose of adenine?
Adenine is one of four nitrogenous bases utilized in the synthesis of nucleic acids. A modified form of adenosine monophosphate ( cyclic AMP) is an imporant secondary messenger in the propagation of many hormonal stimuli. Adenine is an integral part of the structure of many coenzymes.
What is adenine used for?
Adenine is one of four nitrogenous bases utilized in the synthesis of nucleic acids. A modified form of adenosine monophosphate ( cyclic AMP) is an imporant secondary messenger in the propagation of many hormonal stimuli. Adenine is an integral part of the structure of many coenzymes. Adenosine (adenine with a ribose group) causes transient heart block in the AV node of the heart. In individuals suspected of suffering from a supraventricular tachycardia (SVT), adenosine is used to help identify the rhythm. Certain SVTs can be successfully terminated with adenosine.
What is the name of the nucleoside that forms when ribose is attached to aden
Adenine forms adenosine, a nucleoside, when attached to ribose, and deoxyadenosine when attached to deoxyribose, and it forms adenosine triphosphate ( ATP ), which drives many cellular metabolic processes by transferring chemical energy between reactions.
What is the role of adenine in the heart?
Adenine is an integral part of the structure of many coenzymes. Adenosine (adenine with a ribose group) causes transient heart block in the AV node of the heart. In individuals suspected of suffering from a supraventricular tachycardia (SVT), adenosine is used to help identify the rhythm.
What is the name of the compound that is attached to the carbon at position 6?
Adenine. More... Adenine is a purine nucleobase with an amine group attached to the carbon at position 6. Adenine is the precursor for adenosine and deoxyadenosine nucleosides. Adenine is the parent compound of the 6-aminopurines, composed of a purine having an amino group at C-6.
Is a Daphnia magna a human metabolite?
It has a role as a human metabolite, a Daphnia magna metabolite, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolite, an Escherichia coli metabolite and a mouse metabolite. It is a purine nucleobase and a member of 6-aminopurines. It derives from a hydride of a 9H-purine. A purine base and a fundamental unit of adenine nucleotides.
What are Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, and Cytosine?
Albrecht Kossel received a Nobel prize in 1910 for his work in uncovering the chemical nature of life (over forty years before Watson and Crick's more famous Nobel for the structure of DNA!).
Overview of DNA Structures
Together, these four bases help construct deoxyribonucleic acid, better known as DNA. DNA is a double helix, meaning it is composed of two complementary (more on that later) strands (this explains the double) that coil around one another in a twist (also known as a helix -like structure).
DNA Complementary Bases
Each base has a complementary partner with which it can basepair. Strict rules govern the complementary pairing, which Erwin Chargaff first discovered in 1949 and are called Chargaff's Rules in his honor. Chargaff's rules were instrumental in helping Watson and Crick explain the structure of DNA in 1954.