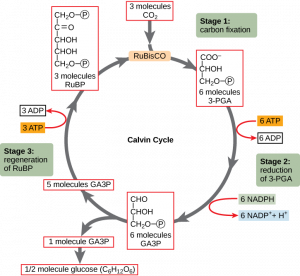
- The C3 cycle is the dark reaction of photosynthesis.
- Calvin cycle also known as the C3 cycle has 3 steps which include carbon fixation, reduction and regeneration.
- The raw materials - energy (ATP) and NADPH - required for the Calvin cycle are provided by the light reactions.
- The sugar produced in the form of glucose is used for long term energy storage.
- The RuBP produced in the third step helps in more carbon fixation
- In the first stage of the calvin cycle, the reaction is initiated and carbon dioxide is fixed.
- In the second stage- the reduction stage- the 3-PGA molecules created through carbon fixation are converted into G3P, which in turn produces simple sugar glucose.
- The Calvin cycle is crucial for maintaining the balance in the ecosystem.
What are the four steps in the Calvin cycle?
What are the 6 steps of photosynthesis?
- Light Dependent. CO2 and H2O enter the leaf.
- Light Dependent. Light hits the pigment in the membrane of a thylakoid, splitting the H2O into O2.
- Light Dependent. The electrons move down to enzymes.
- Light Dependent. …
- Light independent. …
- Light independent. …
- calvin cycle.
What three things are required to drive the Calvin cycle?
- Carbon fixation. A molecule combines with a five-carbon acceptor molecule, ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate ( RuBP ). ...
- Reduction. In the second stage, ATP and NADPH are used to convert the 3-PGA molecules into molecules of a three-carbon sugar, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate ( G3P ). ...
- Regeneration. ...
What are the three phases of the Calvin cycle?
The products of the Calvin cycle are as follows:
- One molecule of carbon is fixed at every turn of the cycle
- One molecule of G3P is formed in 3 turns of the cycle
- 2 molecules of G3P combine to form one molecule of glucose
- 3 molecules of ATP and 2 molecules of NADPH are used in the reduction phase to convert 3-PGA to G3P and the regeneration of RuBP.
What are the three things the Calvin cycle requires?
The different steps involved in the Calvin cycle include:
- Carbon fixation
- Reduction
- Regeneration
What are the 3 steps in Calvin cycle?
Calvin cycle or C3 cycle can be divided into three main stages:Carbon fixation. The key step in the Calvin cycle is the event that reduces CO2. ... Reduction. It is the second stage of Calvin cycle. ... Regeneration. It is the third stage of the Calvin cycle and is a complex process that requires ATP.
What are the basic stages of the Calvin cycle?
The Calvin cycle is organized into three basic stages: fixation, reduction, and regeneration.
What are the three phases of the Calvin cycle quizlet?
What are the three phases or steps of the Calvin Cycle? Fixation, reduction, and regeneration.
What are the 3 reactants of the Calvin cycle?
calvin cycle. reactant: carbon dioxide NADPH ATP. product: ADP phospahte NADP+ glucose.
What are the three stages of light-independent reaction or Calvin cycle?
The light-independent reactions (also known as the Calvin cycle) can be organized into three basic stages: fixation, reduction, and regeneration (Video 13.6.
Why is the third stage of Calvin cycle called the regeneration stage?
Why is the 3rd stage of the Calvin Cycle called the regeneration Stage? Because RuBP, which starts the cycle is regenerated from G3P.
What is the first stage of the Calvin cycle quizlet?
Whats the first step of the Calvin Cycle, and what is it called? Carbon dioxided combines with the five carbon sugar phosphate (RuBP) ribulose biphosphate, its known as Carbon Dioxide fixation because it "fixes carbon dioxide into an organic molecule.
What happens in phase 1 of the Calvin cycle?
During the first phase of the Calvin cycle, carbon fixation occurs. The carbon dioxide is combined with ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate to form two 3-phosphoglycerate molecules (3-PG). The enzyme that catalyzes this specific reaction is ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase (RuBisCO).
What is the Calvin cycle quizlet?
Calvin Cycle. A biochemical pathway of photosynthesis in which carbon dioxide is converted into glucose using ATP and NADPH. Carbon Fixation. The incorporation of carbon from carbon dioxide into an organic compound by an autotrophic organism.
What happens during the Calvin cycle?
The Calvin cycle is part of photosynthesis, which occurs in two stages. In the first stage, chemical reactions use energy from light to produce ATP and NADPH. In the second stage (Calvin cycle or dark reactions), carbon dioxide and water are converted into organic molecules, such as glucose.
What is the 3 carbon molecule that has become the energy storage during the Calvin cycle?
ATP and NADPH use their stored energy to convert the three-carbon compound, 3-PGA, into another three-carbon compound called G3P.
What is Calvin cycle 3-PGA?
3-Phosphoglyceric acid (3PG, 3-PGA, or PGA) is the conjugate acid of 3-phosphoglycerate or glycerate 3-phosphate (GP or G3P). This glycerate is a biochemically significant metabolic intermediate in both glycolysis and the Calvin-Benson cycle. The anion is often termed as PGA when referring to the Calvin-Benson cycle.
Photosynthesis and Its Stages
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants use light energy and carbon dioxide to produce nutrients and organic molecules along with oxygen as the by-product. Photosynthesis is very important for the maintenance of life on earth.
Calvin Cycle: Definition
Calvin Cycle also known as the C3 Cycle consists of a series of reactions which reduces carbon dioxide and other compounds into glucose with the help of ATP and NADPH. It takes place in the stroma of chloroplasts during photosynthesis. To produce the organic molecules, the plant cells use the raw materials provided by the light reaction.
Sample Questions
Ques. How many ATP and NADPH molecules are required to synthesize one molecule of glucose in a C3 cycle? (2 marks)
What is the Calvin cycle?
The Calvin cycle. How the products of the light reactions, ATP and NADPH, are used to fix carbon into sugars in the second stage of photosynthesis.
How many turns of the Calvin cycle are needed to make one G3P molecule that can exit the cycle and go
Three turns of the Calvin cycle are needed to make one G3P molecule that can exit the cycle and go towards making glucose. Let’s summarize the quantities of key molecules that enter and exit the Calvin cycle as one net G3P is made. In three turns of the Calvin cycle:
What is the second stage of ATP and NaDPH?
Reduction. In the second stage, ATP and NADPH are used to convert the 3-PGA molecules into molecules of a three-carbon sugar, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate ( G3P ). This stage gets its name because NADPH donates electrons to, or reduces, a three-carbon intermediate to make G3P. [Details of this step]
How many molecules are made in a G3P cycle?
In order for one G3P to exit the cycle (and go towards glucose synthesis), three molecules must enter the cycle, providing three new atoms of fixed carbon. When three molecules enter the cycle, six G3P molecules are made.
What is the reaction of three molecules of a three-carbon compound?
3 molecules combine with three molecules of the five-carbon acceptor molecule (RuBP), yielding three molecules of an unstable six-carbon compound that splits to form six molecules of a three-carbon compound (3-PGA). This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme rubisco. In the second stage, six ATP and six NADPH are used to convert ...
How many turns does it take to make a glucose molecule?
A G3P molecule contains three fixed carbon atoms, so it takes two G3Ps to build a six-carbon glucose molecule. It would take six turns of the cycle, or , ATP, and NADPH, to produce one molecule of glucose. [References and attribution]
What is the second stage of photosynthesis?
Carbon atoms end up in you, and in other life forms, thanks to the second stage of photosynthesis, known as the Calvin cycle (or the light-independent reactions ).
What is the Calvin cycle?
Stage 2-The Calvin cycle, which takes place in the stroma, uses ATP and NADPH to convert carbon dioxide to sugar.
What is the starting compound of the Calvin cycle?
• makes sugar.#N#• starting compound called RuBP, #N#• each turn of the Calvin cycle, there are chemical inputs and outputs.#N#• The inputs are carbon dioxide from the air and the ATP and NADPH produced by the light reactions.#N#• cycle uses carbon from the carbon dioxide, energy from the ATP, and high-energy electrons and hydrogen ions from the NADPH.#N#• The cycle's output is an energy-rich sugar molecule.#N#• That sugar is not yet glucose, but a smaller sugar named G3P.#N#• The plant cell uses G3P as the raw material to make glucose and other organic molecules it needs.
Answer
The Calvin cycle has three stages. In stage 1, the enzyme RuBisCO incorporates carbon dioxide into an organic molecule. In stage 2, the organic molecule is reduced. In stage 3, RuBP, the molecule that starts the cycle, is regenerated so that the cycle can continue.
Answer
Calvin cycle was discovered by Melvin Calvin while radioactive studies of alga. It occurs in all photosynthetic plants whether they have C_ {3}C3 or C_ {4}C4 pathway.
New questions in Biology
x x x x (jóîn) bsr-cpzg-adv6x 10-1'coulomb or one unit. The ratio, mass for each of the particle is 9.58 x 10" per gram. Hence, the mass of each of thi …
Where do Calvin cycle reactions occur?
need for energy to move fixed carbon in C4 compound into bundle sheath cells. The Calvin cycle reactions only occur in bundle sheath cells in a C4 plant. to shield the Calvin cycle reactions from O2 in the leaf spaces. Not all molecules contain the same amount of chemical energy.
How many molecules of ATP are needed for the Calvin cycle?
The production of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P) in the Calvin cycle requires 6 molecules each of ATP and NADPH.
What color are carotenoids?
Carotenoids are found in high concentrations in yellow and orange leaves or vegetables. This color is seen because the carotenoid pigments. Reflect and transmit yellow and orange wavelengths of light. The localization of the electron transport chains to the thylakoid membrane ensures that.