Ethereal oil cells—common throughout basal angiosperms—and columellate pollen grains with a perforate tectum are synapomorphies for all extant angiosperms except Amborella and Nymphaeaceae (Doyle and Endress, 2001). The evidence for Amborella
What are angiosperms and gymnosperms?
Angiosperms are commonly known as flowering plants that can be clearly distinguished from gymnosperms by certain "derived" characteristics. In botany, these characteristics are specifically termed as synapomorphies.
What is the difference between angiosperms and angiophyta?
According to botanists, Angiosperms form a single coherent group known as Angiophyta. As already stated above, their classification is based on differences in various structures and the mode of fertilization, therefore they are a much more differentiated plant species. The differences between the two types are mentioned below.
What are synapomorphies in botany?
In botany, these characteristics are specifically termed as synapomorphies. Gymnosperms are known as the ancestors of flowering plants that were known to exist 140 million years ago.
What are the basal angiosperms?
The first flowering plants that deviate from the initial angiosperms are called basal angiosperms. Delving into the evolutionary past of basal angiosperms, one finds few groups that branch off, before the true 'dicots' appear. The basal angiosperms consisted of the Ambroella, Nymphaeales, and Austrobaileyales.
What is the Synapomorphy of gymnosperms and angiosperms?
latifolia is classified in the phylum Magnoliophyta which is the same as Angiosperms. The first red arrow points to a synapomorphy that separate gymnosperms and angiosperms from the rest of the other plants. Both of these have vascular tissues, pollen, and seeds.
What are 3 characteristics of an angiosperm?
Like gymnosperms, angiosperms are seed-producing plants. They are distinguished from gymnosperms by characteristics including flowers, endosperm within their seeds, and the production of fruits that contain the seeds.
What are the characteristics of angiosperms?
Classification of AngiospermsThe seeds have a single cotyledon.The leaves are simples and the veins are parallel.This group contains adventitious roots.Each floral whorl has three members.It has closed vascular bundles and large in number.For eg., banana, sugarcane, lilies, etc.
What are the 4 groups of angiosperms?
The Angiosperm Phylogeny Group (APG) (2009) classifies flowering plants into Magnolids (four orders), Monocots (seven orders), Commelinids (five orders), and Eudicots (36 orders), plus a few taxa of uncertain affinity.
What are 4 characteristics of angiosperms?
All angiosperms have flowers, carpels, stamens, and small pollen grains. They are extremely successful plants and can be found all over the world.
What are the advanced characteristics of angiosperms?
Angiosperms have reduced pollen to 3 cells, allowing more efficient pollination and fertilization. Stamens produce pollen and allow various pollination schemes. Embryo sacs in the ovules contain just 7 cells and 8 nuclei, allowing faster fertilization.
What are major characteristics of angiosperms Class 9?
Characteristics of angiosperms: (i) The seeds produced by these plants are enclosed within the fruit. (ii) They are also called flowering plants because they produce flowers and their reproductive organs are aggregated within the flower. (iii) Plant embryos in seeds have a structure called cotyledons (seed leaves).
What 2 characteristics do all angiosperms share?
What two characteristics do all angiosperms share? First, they produce flowers. Second, they produce seeds that are enclosed in fruits.
How many groups are there in angiosperms?
Within the angiosperms are three major groups: basal angiosperms, monocots, and dicots.
What are the classes of angiosperm?
Based on the types of cotyledon present, angiosperms are divided into two classes. They are monocotyledons and dicotyledons. The dicotyledonous angiosperms have two cotyledons in their seeds and the monocotyledonous angiosperms have one cotyledon.
What are the two main groups of angiosperms?
Traditionally, the flowering plants have been divided into two major groups, or classes,: the Dicots (Magnoliopsida) and the Monocots (Liliopsida).
What is angiosperm and gymnosperm?
Share it! Angiosperms and gymnosperms are classifications of plants that have different characteristic properties. Their distinct features form the basis of their classification. Read on to know the details. Angiosperms are commonly known as flowering plants that can be clearly distinguished from gymnosperms by certain “derived” characteristics.
What are gymnosperms and angiosperms?
Angiosperms and Gymnosperms. Angiosperms and gymnosperms are classifications of plants that have different characteristic properties. Their distinct features form the basis of their classification. Read on to know the details. Home / Uncategorized / Angiosperms and Gymnosperms.
What is the suspensor in Gymnosperms?
Polyembryony, a common feature of gymnosperms, is also prevalent in some angiosperms and a suspensor is formed during the embryo development phase.
What is the name of the ancestor of the flowering plant?
Gymnosperms are known as the ancestors of flowering plants that were known to exist 140 million years ago. With the passing ages, flowering plants evolved with modifications in various organs, like flowers, leaves, stems, endosperm, etc., soon after which angiosperms and gymnosperms were classified and placed in different positions in ...
What is the classification of angiosperms?
According to botanists, Angiosperms form a single coherent group known as Angiophyta. As already stated above, their classification is based on differences in various structures and the mode of fertilization, therefore they are a much more differentiated plant species.
Do gymnosperms have vessels?
Apart from primary growth, their stem also undergoes expansion by secondary growth. Like angiosperms, gymnosperms also have vessels and companion cells.
Is gymnosperm haploid or triploid?
The endosperm formed in gymnosperms is a haploid tissue, while it’s triploid in angiosperms. This is because double fertilization and triple fusion are absent in the former category, as a result the endosperm is formed before fertilization; while in the latter, the endosperm is the product of a triple fusion.
What are the features of angiosperms?
There are two subtypes of angiosperms: monocotyledons and dicotyledons. The most prominent features of angiosperms is the ability to flower and produce fruits. There are over 2,50,000 species of angiosperms. 1. Angiosperms are able to grow in a variety of habitats.
What are the reproductive structures of angiosperms?
They are the reproductive structures of angiosperms. The flower has a thalamus that is a short axis and four whorls of sporophylls arranged on the thalamus. The four whorls of floral leaves include calyx , corolla, androecium and gymnocium. The sepals, petals, stamens and carpels make up the whorls. 7.
How many species of angiosperms are there?
There are over 2,50,000 species of angiosperms. 1. Angiosperms are able to grow in a variety of habitats. They can grow as trees, shrubs, bushes, as well as herbs. These plants have diploid (2n) sporophytes. Angiosperms have a distinctive underground root, as well as aerial shoot system. 2.
What is the most diverse and dominant group of plants among the two?
In the plant kingdom, the division Spermatophyta is divided into gymnosperms and angiosperms. The most diverse and dominant group of plants among the two are angiosperms, also referred to as magnoliophyta. In common terms, angiosperms are all flowering plants. They are distinguished from gymnosperms, by their ability to flower ...
What is angiosperm in plants?
In common terms, angiosperms are all flowering plants. They are distinguished from gymnosperms, by their ability to flower and produce seeds enclosed in fruits. There are a few other characteristics that are discussed in the following paragraphs.
What is the outer layer of the stem tissue?
Growth of stem tissues takes place due to a layer of cambium cells. The outer part of the stem tissues is covered with a layer of epidermis. 4. The root system of angiosperms is also very complex. The roots also contain cortex, phloem, xylem, and epidermis.
What are the characteristics of angiosperms?
Angiosperms are able to grow in a variety of habitats. They can grow as trees, shrubs, bushes, herbs, and small flowering plants. Some of the characteristics of angiosperms include: 1 All angiosperms have flowers at some stage in their life. The flowers serve as the reproductive organs for the plant, providing them a means of exchanging genetic information. 2 Angiosperms have small pollen grains that spread genetic information from flower to flower. These grains are much smaller than the gametophytes, or reproductive cells, used by non-flowering plants. This small size allows the process of fertilization to occur quicker in the flowers of angiosperms and makes them more efficient at reproducing. 3 All angiosperms have stamens. Stamens are the reproductive structures found in flowers that produce the pollen grains that carry the male genetic information. 4 Angiosperms have much smaller female reproductive parts than non-flowering plants, allowing them to produce seeds more quickly. 5 Angiosperms have carpels that enclose developing seeds that may turn into a fruit. 6 A great advantage for angiosperms is the production of endosperm. Endosperm is a material that forms after fertilization and serves as a highly nutritional food source for the developing seed and seedling.
What are some examples of angiosperms?
Some common examples of angiosperms include magnolia trees, roses, tulips, and tomatoes. Magnolia trees can be found towering all throughout the southern United States. These trees are prime examples of angiosperms. They are large trees growing up to 40 feet tall.
Why are angiosperms smaller than gametophytes?
This small size allows the process of fertilization to occur quicker in the flowers of angiosperms and makes them more efficient at reproducing. All angiosperms have stamens.
What are angiosperms pollinated by?
Angiosperms are pollinated by water, wind, insects and animals. Research how the following angiosperms are pollinated: oak tree, tomato plant, and tulips. Do any of these plants use more than one type of pollination?
Why are angiosperms important?
Angiosperms have carpels that enclose developing seeds that may turn into a fruit. A great advantage for angiosperms is the production of endosperm.
How many species of angiosperms are there?
Angiosperms: Definition. Angiosperms are the largest group of plants on Earth. There are approximately 270,000 known species alive today. There's probably one nearby right now. Angiosperms include all plants that have flowers and account for approximately 80% of all known living plants. {"error":true,"iframe":true}.
What are the three life patterns of angiosperms?
Angiosperms are flowering plants. There are three different life patterns of angiosperms: annuals, biennials, and perennials . Research the three life patterns of angiosperms. What are the differences between these angiosperm life patterns? What are some examples of each type of angiosperm?
Content
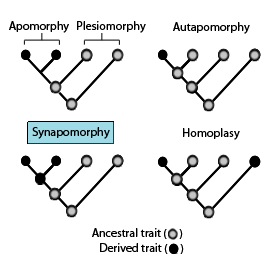
A synapomorphy it is any character that is unique to a group of species and the common ancestor that defines them. The term comes from the Greek and means "based on the shared form."
Utility of synapomorphies in evolutionary analysis
Only synapomorphies define the monophyly of a given taxon. Although some species seem not to show the presence of the character, there are two ways to interpret it.
Unique trajectory
In any case, synapomorphies are the characters used to define the evolutionary study groups in cladistics. To be considered as such, a synapomorphy must have resulted from a unique trajectory.
Ancestral characters
Finally, the simplesiomorphies represent the ancestral characters. That is, those that are shared by two related taxa by common ancestor. Synapomorphies obviously separate the two taxa and define them as such (that is, distinct).
Examples of synapomorphies
The examples that we will give later concern two large groups of living beings. However, synapomorphies can be found at any level of the hierarchical scale of classification of living beings.
Chordates
Chordates are a group of animals (with a phylum range) that are characterized by presenting a notochord or dorsal cord at some point in their development.
Spermatophytes
Spermatophytes represent the monophyletic group of vascular plants that includes all those that produce seeds.
Anthophyta: Evolutionary Wonders
The early Cretaceous saw the first appearance of flowering plants in the fossil record. By the mid Cretaceous, about 90 million years ago, flowering plants were the dominant life form on earth. This is a tremendously quick rise to dominance, geologically speaking.
Determining Evolutionary Relationships
The earliest evolutionary botanists relied primarly on morphology and the fossil record to try and make sense of flowering plant relationships. But as we know, the fossil record is incomplete, and cannot yiel important molecular and cellular information that may be more relevant to determining actual common ancestry.
Let's Meet the Anthophytes..
The most primitive flowering plants were once called "dicots," but we now know that this term is not monophyletic. Several groups have been removed and placed in separate taxa.