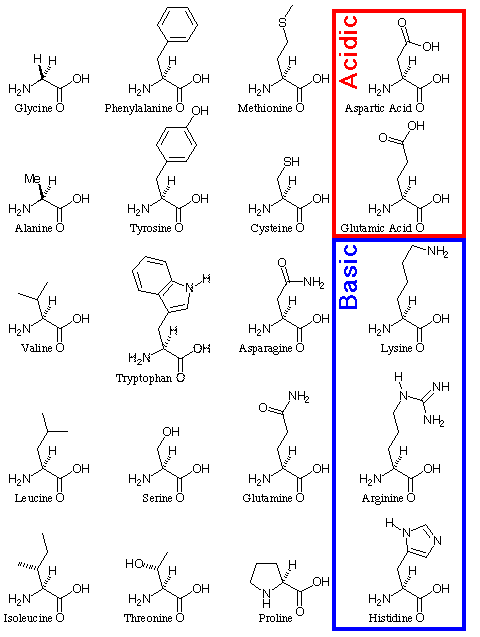
- Non-polar, aliphatic R-group. The R-group in this class of amino acids are non polar (or) hydrophobic. ...
- Aromatic R groups. Phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan, with their aromatic side chains, are relatively non-polar. All can participate in hydrophobic interactions.
- Polar-uncharged R groups. The R groups of these amino acids are more soluble in water or more hydrophilic, than those of the non polar amino acids because they contain ...
- Positively charged (basic) R-groups. The most hydrophilic R groups are those that are either positively (-NH3+) or negatively (-C00-) charged.
- Negatively charged (Acidic) R groups. The two amino acids having R groups with a net negative charge at pH 7.0 are aspartate and glutamate.
- Essential amino acids. Certain amino acids can not be synthesized by the living organisms. ...
- Non-essential amino acids. Certain amino acids can be synthesized in the cells from essential amino acids or from other compounds.
- Non protein amino acids. Certain amino acids which do not exist in proteins are called non protein amino acids eg. Ornithine and b-alanine etc ...
- Peptide bonds. In proteins, amino acids are linked together by linkages called peptide bonds. ...
What are the four functional groups of amino acids?
These are:
- Amino Acids with Nonpolar side chains These are amino acids or organic compounds that have no “charge” on the R group. ...
- Amino Acids with Polar Side Chains These are amino acids or organic compounds that can identified as either positively or negatively charged. ...
- Amino Acids that have electrically charged side chains
What makes the 20 amino acids different?
The 20 to 22 amino acids that comprise proteins include:
- Alanine
- Arginine
- Asparagine
- Aspartic Acid
- Cysteine
- Glutamic acid
- Glutamine
- Glycine
- Histidine
- Isoleucine
What are the names of all the amino acids?
The amino acids are organic compounds formed by carboxyls and amines. These compounds bind to form proteins and other macromolecules. They are divided into two groups: essential and non-essential. Essential amino acids are those that can not be synthesized by the human body autonomously. For this reason, this type of amino acid must be ingested ...
What are the 4 parts of amino acids?
What are the 4 main components of an amino acid? Amino acids are made up of a central carbon bonded to an amino group (–NH2), a carboxyl group (–COOH), and a hydrogen atom. The central carbon’s fourth bond varies among the different amino acids, as seen in these examples of alanine, valine, lysine, and aspartic acid.
What is the R group called?
1:053:51what are R-groups? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipInto another functional group an alkane. And when you develop this reaction this reaction works onMoreInto another functional group an alkane. And when you develop this reaction this reaction works on more than just the starter material that's shown in the molecule shown you works on lots of things in
How do you find the R group of an amino acid?
2:183:29R Groups - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo the amino acids in their sequence with the side chains. The way they are will cause the proteinMoreSo the amino acids in their sequence with the side chains. The way they are will cause the protein to fold the circling. You know always hold that certainly if it doesn't thing we have.
What are the different R groups?
There are basically three major classifications for amino acids (1) those with nonpolar R group, (2) those with uncharged polar R groups, and (3) those with charged polar R group.
What is the R in a functional group?
The letter R is used in molecular structures to represent the “Rest of the molecule”. It consists of a group of carbon and hydrogen atoms of any size. It is used as an abbreviation since a group of carbon and hydrogen atoms does not affect the functionality of the compound.
Which amino acid has an amine group?
In biochemistry, amino acids which have the amine group attached to the (alpha-) carbon atom next to the carboxyl group have particular importance. They are known as 2-, alpha-, or α-amino acids (generic formula H 2 NCHRCOOH in most cases, where R is an organic substituent known as a " side chain "); often the term "amino acid" is used ...
What are the elements in amino acids?
The key elements of an amino acid are carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), and nitrogen (N), although other elements are found in the side chains of certain amino acids.
How many amino acids are there in the human body?
Aside from the 22 proteinogenic amino acids, many non-proteinogenic amino acids are known. Those either are not found in proteins (for example carnitine, GABA, levothyroxine) or are not produced directly and in isolation by standard cellular machinery (for example, hydroxyproline and selenomethionine ).
What are the roles of amino acids in proteins?
Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis .
Which amino acid is the only proteinogenic amino acid whose side-group links to the -amino
Proline is the only proteinogenic amino acid whose side-group links to the α-amino group and, thus, is also the only proteinogenic amino acid containing a secondary amine at this position.
Why are amino acids important?
Because of their biological significance, amino acids are important in nutrition and are commonly used in nutritional supplements, fertilizers, feed, and food technology. Industrial uses include the production of drugs, biodegradable plastics, and chiral catalysts .
How is nitrogen assimilated into organic compounds?
In plants, nitrogen is first assimilated into organic compounds in the form of glutamate, formed from alpha-ketoglutarate and ammonia in the mitochondrion. For other amino acids, plants use transaminases to move the amino group from glutamate to another alpha-keto acid. For example, aspartate aminotransferase converts glutamate and oxaloacetate to alpha-ketoglutarate and aspartate. Other organisms use transaminases for amino acid synthesis, too.