Physical geography
Physical geography (also known as geosystems or physiography) is one of the two major sub-fields of geography. Physical geography is that branch of natural science which deals with the study of processes and patterns in the natural environment like the atmosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, an…
Middle Colonies
The Middle Colonies were a subset of the thirteen colonies in British America, located between the New England Colonies and the Southern Colonies. Along with the Chesapeake Colonies, this area now roughly makes up the Mid-Atlantic states.
What are the physical features in the Mid Atlantic colonies?
13 Colonies Regions
- New England Colonies
- Middle (Mid-Atlantic) Colonies
- Southern Colonies
What were the geographical features of the Middle Colonies?
ORDERING PROCESS
- Fill in the order form. Issue instructions for your paper in the order form. ...
- Payment Procedure. Your payment is processed by a secure system. ...
- The Writing Process. Clarify all the questions with customer support representatives and upload all the necessary files for the writer to use.
- Download Your Paper. Check your paper. ...
What are the geographic features of the Middle Colonies?
Read the Intolerable Acts as they were written in 1774:
- Boston Port Bill. Date Passed: March 31, 1774.
- Administration of Justice Act. Date Passed: May 20, 1774.
- Massachusetts Government Act. Date Passed: May 20, 1774.
- Quartering Act. Date Passed: June 2, 1774.
- Quebec Act. Date Passed: June 22, 1774.
What were the disadvantages of the Middle Colonies?
Welcome To The Middle Colonies
- Playground Disadvantages. ...
- Importance Of Toys And Games In World War II. ...
- Egg Project Analysis Paper. ...
- Life In The Middle Colonies. ...
- Kidsworldfun Speech. ...
- Code Of Practice. ...
- Industrial Revolution DBQ Essay. ...
- Honors Housing. ...
- American Colonial Slavery System. ...
- The Populist Movement. ...
What are some physical features of the southern colonies?
The southern colonies were made up of mostly coastal plains and piedmont areas. The soil was good for farming and the climate was warm, including hot summers and mild winters. The growing season here was longer than any other region.
What is the middle colonies known for?
The Middle colonies, like Delaware, New York, and New Jersey, were founded as trade centers, while Pennsylvania was founded as a safe haven for Quakers. The Middle colonies were also called the “Breadbasket colonies” because of their fertile soil, ideal for farming.
What features made the middle colonies unique?
The Middle Colonies flourished economically due to fertile soil, broad navigable rivers, and abundant forests. The Middle Colonies were the most ethnically and religiously diverse of the British colonies in North America, with settlers coming from all parts of Europe and a high degree of religious tolerance.
What geographic features attracted colonists to the middle colonies?
Abundant forests attracted both the lumbering and shipbuilding industries to the Middle Colonies. These industries, along with the presence of deep river estuaries, led to the appearance of important ports like New York and Philadelphia.
What are 5 facts about the Middle Colonies?
In comparison to the other Colonies, the Middle Colonies were more tolerant and diverse. All ethnic and religious backgrounds were accepted and welcomed. Religious groups included Quakers, Amish, Mennonites, Lutherans, Dutch Calvinists, and Presbyterians. There was no domination by any one group.
What are 3 facts about Middle Colonies?
It was named New York after the Duke of York, King James II's brother. Delaware Colony was established in 1638 by Peter Minuit. Pennsylvania was founded in 1682 by William Penn, after having been granted the land in 1680 by the king. New Jersey Colony was established in 1664 by English colonists.Dec 6, 2021
What made the Middle Colonies?
The middle colonies included Pennsylvania, New York, New Jersey, and Delaware. Advantaged by their central location, the middle colonies served as important distribution centers in the English mercantile system. New York and Philadelphia grew at a fantastic rate.
What was it like in the Middle Colonies?
The middle colonies had deep, rich soil. The fertile soil was good for farming. These colonies had mild winters and warm summers. The growing season was longer than in New England because there was more sun and lots of rain.
What resources were in the Middle Colonies?
In addition to fertile farmland, the natural resources of the Middle colonies included iron ore and wood from the forests. Factories produced iron goods, paper, and textiles. Like the grain, these products were used in the colonies as well as shipped to England. Shipbuilding was important as well.
Which of the following was a primary feature of the Middle Colonies?
Which of the following was a primary feature of the middle colonies? They developed plantation economies based on exporting staple crops.
Why was land in the Middle Colonies attractive to immigrants?
1 Answer. It was fertile land, and was protected on the North by New England, and protected on the South by Virginia.Jun 21, 2016
What might be some typical jobs of colonists in the Middle Colonies?
Largely agricultural, farms in this region grew numerous kinds of crops, most notably grains and oats. Logging, shipbuilding, textiles production, and papermaking were also important in the Middle Colonies.Dec 10, 2021
What was the geography like in the middle colonies?
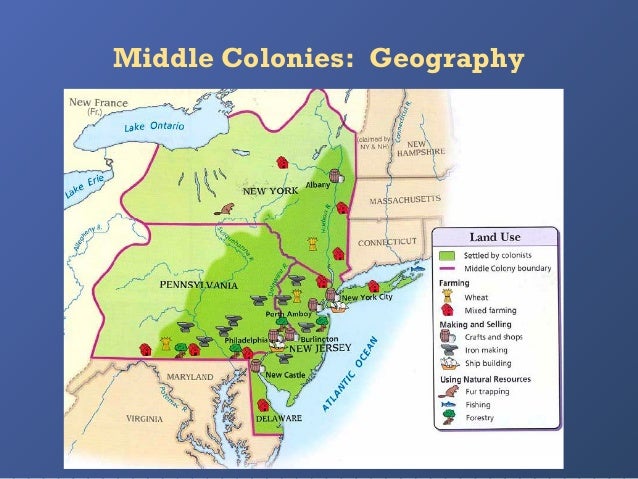
The Middle Colonies regional geography include physical features of coastlines, rivers, good soil, forests, and mountainous fringes, and the human...
Why were the middle colonies so economically successful?
The Middle Colonies were economically successful for two reasons: 1) their cultural focus on the importance of the economy and 2) their success in...
What are some characteristics of the middle colonies?
The characteristics of the Middle Colonies were the amount of cultural importance put on their economic production, the lack of main religion, and...
The Middle Colonies
The Middle Colonies were composed of four states: New York (NY), Delaware (DE), New Jersey (NJ), and Pennsylvania (PA). Founded in the years 1626 (NY), 1638 (DE), 1664 (NJ), and 1682 (PA), they make up some of the youngest colonies in the original thirteen colonies.
The Middle Colonies Geography
The Middle Colonies' geography starts with New York, Delaware, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania. Today, they have similar state shapes as they did in colonial times. New York and Pennsylvania were significantly larger in size than New Jersey and Delaware, enabling them to dominate the colonial region.
The Middle Colonies Climate and Environment
The Middle Colonies climate was a useful contrast of the warm season and the cold season, sunshine and rainfall that was just enough. The Middle Colonies had cold winters (10-25 F) and hot summers (84-99 F). The region has a notably milder winter than the New England Colonies to the north did.
What did the Middle Colonies produce?
Sure, winters were relatively cold compared to those found in the South, but the growing season was much longer than New England's, yet not quite hot enough for the cash crops of the South. As a result, agriculture in the Middle Colonies tended to be focused on crops like wheat, rye, and corn. In other words, these colonies produced massive amounts of food that could easily be exported to other colonies and to other parts of the British Empire. In fact, these colonies earned the nickname 'Breadbasket Colonies.'
How did the geography and climate of the Middle Colonies affect who would settle there?
Finally, the geography and climate of the Middle Colonies affected who would settle there by dictating the economic activities of the region. As they were so focused on commerce, the Middle Colonies didn't care too much about enforcing one particular religion over another, unlike New England. As a result, they soon all passed local laws of religious freedom, focusing more on the commerce of the region than any social ideals. Additionally, the prosperity of these colonies, due to the fertile land for farming and the ports that made exporting products easy, attracted more and more people. Land grants were still available for those who wanted to settle the frontier, gaining the interest of yet another group of potential residents. These pioneers would press on to form more towns and farms.
Why were New York and Philadelphia important?
Surely they had to be important. And because of the geography and climate of the Middle Colonies, they were. For starters, both were well suited as ports, with New York at the mouth of the Hudson River and Philadelphia on the Delaware River. However, both had massive hinterlands, or areas from where they funneled hundreds of tons of agricultural and natural resources towards the world's trade routes.
What crops did the Middle Colonies grow?
As a result, agriculture in the Middle Colonies tended to be focused on crops like wheat, rye, and corn. In other words, these colonies produced massive amounts of food that could easily be exported to other colonies and to other parts of the British Empire. In fact, these colonies earned the nickname 'Breadbasket Colonies.'.
Why did the colonies have so much prosperity?
Additionally, the prosperity of these colonies, due to the fertile land for farming and the ports that made exporting products easy, attracted more and more people.
Did the Middle Colony make ships?
Yet it wasn't just what was going onto the ships, but the ships themselves. With enormous forests nearby, many Middle Colony towns made names for themselves with shipbuilding. In fact, historians have letters from English shipbuilders complaining that it wasn't fair that ships could be built more cheaply by the colonists!
What landforms were found in the Middle Colonies?
The landforms in the middle colonies included mountains, rivers forests and the Atlantic coastline. These landforms shaped the economy and culture of the middle colonies.
What were the major rivers in the Middle Colonies?
The rivers in the region were critical to the middle colonies. The Hudson, Susquehanna and Delaware rivers ensured a shipping industry and attracted a multitude of other businesses. Imports to coastal harbors as well as fishing and shellfish caught in the Atlantic could be transported inland to other settlements on these river. Hunters and trappers flocked to the Hudson for pelts and game. The rivers allowed timber to be shipped from the abundant forests in the area and provided an export means for the harvest, which included flax, hemp and grains. These agricultural products grew abundantly in the middle colonies' fertile soil.