What are the 5 components of a river system?
- Tributaries. A tributary is a river that feeds into another river, rather than ending in a lake, pond, or ocean.
- Up and down, right and left. …
- Headwaters. …
- Channel. …
- Riverbank. …
- Floodplains. …
- Mouth/Delta. …
- Wetlands.
- Tributaries. A tributary is a river that feeds into another river, rather than ending in a lake, pond, or ocean.
- Up and down, right and left. ...
- Headwaters. ...
- Channel. ...
- Riverbank. ...
- Floodplains. ...
- Mouth/Delta. ...
- Wetlands.
What is the most important part of a river?
What are the different parts of a river called?
What are the different parts of a river?
All rivers are different, but they are comprised of common parts. River system parts include the river source, river mouth, downstream, upstream, flood plain, main-river, meander, tributary, watershed boundary, and wetlands. A river’s source is the beginning of the stream. Sometimes this area is called headwaters.
What are the main parts of a river system?
There are three main parts to every river system. The collecting system consists of the branches or tributaries in the headwater region, upstream. These tributaries, other rivers and streams, collect the water that runs off of fields and areas at higher elevations, and carries debris, sediment and water toward the main river.
What are parts of a river called?
Rivers are split up into three parts: the upper course, the middle course, and the lower course. The upper course is closest to the source of a river. The land is usually high and mountainous, and the river has a steep gradient with fast-flowing water.Dec 24, 2021
What are the 11 parts of a river?
Riverspot holes.V-shaped valleys.interlocking spurs.waterfalls.rapids.gorges.
What are the 3 main parts of a river system?
The upper course, middle course, and lower course make up the river. The source of a river is closest to the upper course. The land is high and mountainous, and the river is fast-flowing.
What makes up a river?
A river forms from water moving from a higher elevation to a lower elevation, all due to gravity. When rain falls on the land, it either seeps into the ground or becomes runoff, which flows downhill into rivers and lakes, on its journey towards the seas.
What is the upper part of a river?
The upper course, middle course, and lower course make up the river. The source of a river is closest to the upper course. The land is high and mountainous, and the river is fast-flowing.
What are the 4 parts of a river system?
What are the 4 parts of a river system? A river system is a network of a source, tributaries, flood plains, and wetlands in relation to the main river.Dec 4, 2021
What are the five parts of a river?
What Makes a River?Tributaries. A tributary is a river that feeds into another river, rather than ending in a lake, pond, or ocean.Up and down, right and left. ... Headwaters. ... Channel. ... Riverbank. ... Floodplains. ... Mouth/Delta. ... Wetlands.More items...
What landforms are formed by river?
The work of the river is mainly deposition, building up its bed and forming an extensive flood plain. Landforms like braided channels, floodplains, levees, meanders, oxbow lakes, deltas etc.Jan 31, 2019
What landforms are created by the river in your area?
Erosion and deposition within a river channel cause landforms to be created:Potholes.Rapids.Waterfalls.Meanders.Braiding.Levees.Flood plains.Deltas.Dec 6, 2021
How do you make a river?
Most rivers begin life as a tiny stream running down a mountain slope. They are fed by melting snow and ice, or by rainwater running off the land. The water follows cracks and folds in the land as it flows downhill. Small streams meet and join together, growing larger and larger until the flow can be called a river.
Where is the source of a river?
A river’s source is the beginning of the stream. Sometimes this area is called headwaters. Often, this source is located in mountains, from glacial melt, a ground spring, or run off caused by melting snow or rain.
What is the name of the place where a river runs into a larger body of water?
The place where the river runs into a larger body of water such as a lake, the ocean, or another river is referred to as the river’s mouth. When the stream runs in a direction near the river’s mouth it is called a downstream. However, the river may run in a direction closer to its source that is then considered upstream.
What is a meandering river?
Such channels are called meanders. Just as the name implies meandering rivers run back and forth not straight down stream. Tributaries are small streams that connect to the main river or another stream. Tributaries drain tracts of land called watersheds. Watershed boundaries mark the furthest channels of watersheds, or drainage divides.
What is the name of the system where rivers drain land?
All rivers are parts of a larger system called a watershed, where a river and its branches drain land. Rivers are better defined as large, natural streams flowing through channels draining into even larger water bodies. All rivers are different, but they are comprised of common parts.
How does human interaction affect the quality of a river?
Negative human interaction may impact a watershed’s boundaries. When this occurs havoc may take place within other river system parts, such as tributaries and the river mouth. Human interaction greatly affect river quality. Wetlands assist with river quality maintenance.
What is inner drainage?
Inner drainage inhibits dry to semi-arid areas such as deserts from having great river systems. This is the same as polar regions, which tend to expand their glaciers with any drainage. Often humid areas with a lot of limestone deposits prevent major river systems from forming.
Why is flood plain nutrient rich?
Often its soil is nutrient rich because of the deposits that run through rivers. The river runs through channels and through its course there is one primary channel. This channel is the main-river.
What are the parts of a river?
The Parts of a river The main ones are the high, medium and low courses. A River Is a constant flow of water that travels across a land surface until it reaches its destination, which is usually a larger body of water, such as the ocean or some lake. They start from the highest parts of the earth to the lowest parts and are created from streams ...
What is the widest part of a river?
Low course. Called"old river", this is the widest part of the river and slower because it is on the lower surface and less steep, in fact in most cases the low course is on a flat surface. It no longer has the strength to have a fast current and reaches its mouth.
What happens when a river is branched?
The deltas on the other hand occur when the main stream of water is branched creating a division of several streams or streams. These become narrow and shallow. Some of the most famous rivers have this low course time, as is the case of the Nile River and the Amazon River. When old rivers are not segmented into deltas, ...
What causes a river to form?
In very cold places, the thawing of snow or glaciers can create a river. In warm places, the basins located on the slopes of the mountains can suffer leaks from their waters, when this happens the waters form streams. The streams of several slopes, create streams and the streams in turn, will create the upper part of the river.
Why do rivers need small streams?
The rivers adapt to the environment and to the territory that surrounds them, can grow much with rains but also with contamination can dry. Global warming , for example, has caused several small streams feeding rivers to dry.
Why are rivers important?
Rivers have always been sources of water. Thanks to the animals that inhabit it, it has also been a source of food. With hydroelectric power, it has become a source of electricity and also represents a way to transport between cities and places, using boats, boats and canoes.
Why are old rivers harvested?
When old rivers are not segmented into deltas, they are often harvested by communities and farms, since this is the best part of the river to have agricultural production and where it is easier to extract water and fish.
What Are The Components And Characteristics Of A River System?
A river system is a network of a source, tributaries, flood plains, and wetlands in relation to the main river.
What are the components of the river system?
What are the components of a river system? River system parts include the river source, river mouth, downstream, upstream, flood plain, main-river, meander, tributary, watershed boundary, and wetlands. A river’s source is the beginning of the stream.
What are the 5 components of a river system?
Tributaries. A tributary is a river that feeds into another river, rather than ending in a lake, pond, or ocean.
What are the characteristics of river?
A river is a ribbon-like body of water that flows downhill from the force of gravity. A river can be wide and deep, or shallow enough for a person to wade across. A flowing body of water that is smaller than a river is called a stream, creek, or brook.
What are the 4 characteristics of a river?
The river is small and flows quickly. Some features expected in this section of the river are V- shaped valleys, interlocking spurs, a river bed with large rocks and stones,gorges, fast flowing rapids and waterfalls.
What are the 3 main parts of a river system?
The upper course, middle course, and lower course make up the river. The source of a river is closest to the upper course.
What is the main channel of a river?
The river channel is at its widest and deepest as it flows towards its mouth. Deposition is the main process in this part of the river, which creates large floodplains and deltas .
What happens at the end of a river?
The end of a river is its mouth, or delta. At a river’s delta, the land flattens out and the water loses speed, spreading into a fan shape. Usually this happens when the river meets an ocean, lake, or wetland. As the river slows and spreads out, it can no longer transport all of the sand and sediment it has picked up along its journey from the headwaters. Because these materials and nutrients help build fertile farmland, deltas have been called “cradles” of human civilization. Deltas are “cradles” for other animals as well, providing breeding and nesting grounds for hundreds of species of fish and birds.
What is a tributary in a river?
Tributaries. A tributary is a river that feeds into another river, rather than ending in a lake, pond, or ocean. If a river is large, there’s a good chance that much of its water comes from tributaries. How do geographers decide which river is the “main” river and which is the “tributary” when they’re naming rivers?
What is the flow of water?
“Flow” refers to the water running in a river or stream. There are two important aspects to a river’s natural flow. First, there is the amount of water that flows in the river. Some rivers get enough water from their headwaters, tributaries, and rain to flow all year round. Others go from cold, raging rivers to small, warm streams as the snowpack runs out, or even stop flowing completely. A river’s natural ups and downs are called “pulses.” Like a human being’s pulse, a river’s natural flow of water is life support for animals, plants, and fish, delivering what they need to survive at the right times. When we divert water away from a river, we change the river’s natural flow.
What is the beginning of a river called?
The beginning of a river is called its headwaters . Even if a river becomes big and powerful, its headwaters often don’t start out that way. Some headwaters are springs that come from under the ground. Others are marshy areas fed by mountain snow. A river’s headwaters can be huge, with thousands of small streams that flow together, or just a trickle from a lake or pond. What happens in the headwaters is very important to the health of the whole river, because anything that happens upstream affects everything downstream.
Why is it important to know what happens in the headwaters of a river?
What happens in the headwaters is very important to the health of the whole river, because anything that happens upstream affects everything downstream.
Why are riverside areas important?
These areas also provide valuable services like protection from erosion during floods, and filtering polluted run-off from cities and farms.
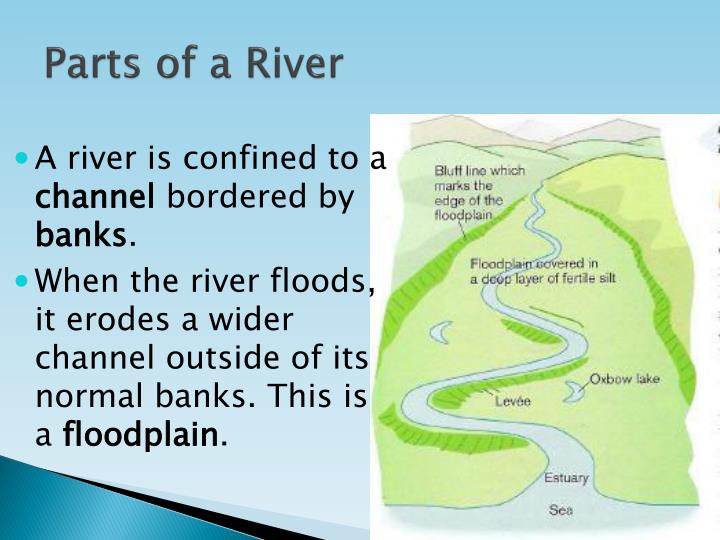
What is a floodplain?
Floodplains. Floodplains are low, flat areas next to rivers, lakes and coastal waters that periodically flood when the water is high. The animals and plants that live in a floodplain often need floods to survive and reproduce.
What is the middle part of a river called?
The middle part of a river is called a mature river. A mature river makes a riverbed that is U-shaped. It might be very deep and run fast. It sweeps over small rocks and boulders, and makes big turns around hills and mountains. It is much wider than a young river, but not as wide as an old river. To cross over a mature river, people use bridges. Many cities and towns are built on the banks of mature rivers. Many farms that keep animals such as dairy cows, horses and sheep are along mature rivers because the animals can drink from the river every day.
How does a river end?
A river usually ends by flowing into an ocean, a lake or a bigger river. The place where the river flows out into a bigger body of water is called the 'mouth' of the river. As a river flows towards its mouth, the countryside around the river often changes from hilly to flat.
How do rivers flow?
Some rivers flow underground through caves. Underground rivers form in places where there are lots of cracks in the rocks above, so that in rainy weather, the water runs downs and collects in small underground streams. Sometimes the underground water trickles or gushes out of the ground to form a small spring of water.
What are the animals that live in estuaries?
Many kinds of fish, clams, molluscs and other sealife live at estuaries. Many of the world's largest cities and harbours are at estuaries. Where a river flows out to the sea, it sometimes flows very slowly through sandy or muddy land, making lots of little islands as it flows.
What is the beginning of a river called?
The beginning of a river. The start of a river is called the source or head water. The part of the river that is near the source is called a 'young' river. A young river is often in a V-shaped river bed, and flows quickly downhill over stones, and around big rocks. Young rivers often have lots of small waterfalls and rapids.
Why do rivers have dams?
Rivers sometimes have dams to hold the water for people to drink, or to make electricity. Rivers can be used for leisure and sports such as swimming, boating, fishing and just walking by the river. Rivers often have beautiful scenery.
What are the crops that can be grown in an old river?
Old rivers are the most useful type of river for growing crops. Corn, rice, fruit, cotton, hay, tobacco and sugar are some of the crops that are grown near old rivers.