Key Points of Glycolysis
- It is the process in which a glucose molecule is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate.
- The process takes place in the cytoplasm of plant and animal cells.
- Six enzymes are involved in the process.
- The end products of the reaction include 2 pyruvate, 2 ATP and 2 NADH molecules.
What is the ultimate end result of glycolysis?
The combined end product of glycolysis is two molecules of pyruvate per molecule of glucose entering the process, plus two molecules of ATP and two of NADH, a so-called high-energy electron carrier. The complete net reaction of glycolysis is: C6H12O6 + 2 NAD+ + 2 ADP + 2 P → 2 CH3(C=O)COOH + 2 ATP + 2 NADH + 2 H+.
What does glycolysis make and why is it important?
what is the evolutionary significance of glycolysis
- BioC.09.010.Glycolysis (7-10) – Significance | Dr. Prashant Sharma
- Evolutionary perspective of glycolysis, unit 32, miller and harley
- Glycolysis || Definition * Site * Significance * Phases * Energetics * Regulation * Inhibitors
- Significance of Glycolysis, Pasteur effect, Crabtree effect and Rapaport-Leubering cycle
What are the inputs and outputs of Krebs cycle?
Products of the citric acid cycle
- two carbons enter from acetyl , and two molecules of carbon dioxide are released;
- three molecules of and one molecule of are generated; and
- one molecule of or is produced.
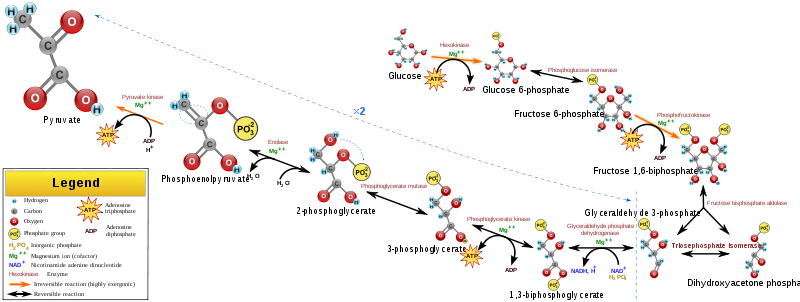
What are the various steps in glycolysis?
What are the steps of glycolysis simplified?
- Reaction 1: glucose phosphorylation to glucose 6-phosphate.
- Reaction 2: isomerization of glucose 6-phosphate to fructose 6-phosphate.
- Reaction 3: phosphorylation of fructose 6-phosphate to fructose 1,6-bisphosphate.
- Reaction 4: cleavage of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate into two three-carbon fragments.
What are the input and outputs of glycolysis?
Input for the breakdown of 1 glucose molecule in glycolysis is 2 ATP and the output is 4 ATP, 2 NADH and 2 pyruvate molecules. Metabolic pathway which provides anaerobic source of energy in all organisms is glycolysis.
What are the major products output of glycolysis?
Outcomes of Glycolysis Glycolysis begins with glucose and produces two pyruvate molecules, four new ATP molecules, and two molecules of NADH.
What are the two main outputs of glycolysis?
Glycolysis starts with one molecule of glucose and ends with two pyruvate (pyruvic acid) molecules, a total of four ATP molecules, and two molecules of NADH.
Which of the following are outputs of glycolysis quizlet?
Output of Glycolysis are: NADH, ATP, and pyruvate. in glycolysis, the six-carbon sugar glucose is converted to two molecules of pyruvate (three carbons each), with the net production of 2 ATP and 2 NADH per glucose molecule.
What is the final output of glycolysis?
The final product of glycolysis is pyruvate in aerobic settings and lactate in anaerobic conditions. Pyruvate enters the Krebs cycle for further energy production.
What are the products of glycolysis quizlet?
What are the products of glycolysis? The products of glycolysis are 4 ATP (net gain of 2 ATP), 2 pyruvic acid, and 2 NADH.
What is the outcome of glycolysis quizlet?
During glycolysis, glucose is broken down into two pyruvate molecules. Energy is captured and stored in the high-energy molecules ATP and NADH.
What are the reactants and products of glycolysis?
Glucose is the reactant; while ATP and NADH are the products of the Glycolysis reaction.
Is NAD+ an input or output of glycolysis?
Glycolysis is the first step in cellular respiration, occurring in all living cells. Overall, the input for glycolysis is one glucose, two ATP and two NAD+ molecules giving rise to two pyruvate molecules, four ATP and two NADH.
What is not an output of glycolysis?
In glycolysis, the six-carbon sugar glucose is converted to two molecules of pyruvate (three carbons each), with the net production of 2 ATP and 2 NADH per glucose molecule. There is no O2 uptake or CO2 release in glycolysis.
Is pyruvate an input or output?
18 Cards in this Setglycolisis locationcytoplasmpyruvate processing inputspyruvate, NAD+NPpyruvate processing outputsacetyl coA, NADH, co2(CAN)citric acid cycle locationmitochondrial matrixcitric acid cycle inputsFAD+,NAD+, ATP,acetyl coANAFA13 more rows
What are the outputs of cellular respiration?
The products of cellular respiration are carbon dioxide and water. Carbon dioxide is transported from your mitochondria out of your cell, to your red blood cells, and back to your lungs to be exhaled. ATP is generated in the process.
How does glycolysis occur?
Glycolysis occurs in both aerobic and anaerobic states. In aerobic conditions, pyruvate enters the citric acid cycle and undergoes oxidative phosphorylation leading to the net production of 32 ATP molecules. In anaerobic conditions, pyruvate converts to lactate through anaerobic glycolysis. Anaerobic respiration results in the production of 2 ATP molecules.[5] Glucose is a hexose sugar, meaning it is a monosaccharide with six carbon atoms and six oxygen atoms. The first carbon has an attached aldehyde group, and the other five carbons have one hydroxyl group each. During glycolysis, glucose ultimately breaks down into pyruvate and energy; a total of 2 ATP is derived in the process (Glucose + 2 NAD+ + 2 ADP + 2 Pi --> 2 Pyruvate + 2 NADH + 2 H+ + 2 ATP + 2 H2O). The hydroxyl groups allow for phosphorylation. The specific form of glucose used in glycolysis is glucose 6-phosphate.
What is glycolysis in cells?
Even if cells primarily use oxidative phosphorylation, glycolysis can serve as an emergency backup for energy or serve as the preparation step before oxidative phosphorylation. In highly oxidative tissue, such as the heart, the production of pyruvate is essential for acetyl-CoA synthesis and L-malate synthesis.
How many ATP molecules are produced in glycolysis?
In glycolysis, 2 ATP molecules are consumed, with the production of 4 ATP, 2 NADH, and 2 pyruvates per molecule of glucose. The pyruvate can be used in the citric acid cycle or serve as a precursor for other reactions. [2][3][4] Fundamentals. Glycolysis ultimately splits glucose into two pyruvate molecules.
How does glucose transporter work?
Glucose transporters (GLUT) transport glucose from the outside of the cell to the inside. Cells containing GLUT can increase the number of GLUT in the cell's plasma membrane from the intracellular matrix, therefore increasing the uptake of glucose and the supply of glucose available for glycolysis. There are five types of GLUTs. GLUT1 is present in RBCs, the blood-brain barrier, and the blood-placental barrier. GLUT2 is in the liver, beta-cells of the pancreas, kidney, and gastrointestinal (GI) tract. GLUT3 is present in neurons. GLUT4 is in adipocytes, heart, and skeletal muscle. GLUT5 specifically transports fructose into cells. Another form of regulation is the breakdown of glycogen. Cells can store extra glucose as glycogen when glucose levels are high in the cell plasma. Conversely, when levels are low, glycogen can be converted back into glucose. Two enzymes control the breakdown of glycogen: glycogen phosphorylase and glycogen synthase. The enzymes can be regulated through feedback loops of glucose or glucose 1-phosphate, or via allosteric regulation by metabolites, or from phosphorylation/dephosphorylation control. [8]
What is the pyruvate used for?
The pyruvate can be used in the citric acid cycle or serve as a precursor for other reactions. [2][3][4] Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway and an anaerobic source of energy that has evolved in nearly all types of organisms. Another name for the process is the Embden-Meyerhof pathway, in honor of the major contributors towards its discovery ...
How does pyruvate convert to lactate?
In anaerobic conditions, pyruvate converts to lactate through anaerobic glycolysis. Anaerobic respiration results in the production of 2 ATP molecules.[5] . Glucose is a hexose sugar, meaning it is a monosaccharide with six carbon atoms and six oxygen atoms.
How does a GLUT increase glucose?
Cells that contain GLUT can increase the number of GLUT in the plasma membrane of the cell from the intracellular matrix, therefore increasing the uptake of glucose and the supply of glucose available for glycolysis. There are five types of GLUTs.
What is the preparatory phase of glycolysis?
This phase is also called glucose activation phase. In the preparatory phase of glycolysis, two molecules of ATP are invested and the hexose chain is cleaved into two triose phosphates.
How many enzymes are involved in glycolysis?
Glycolysis is a lengthy process and made possible by a total of 11 enzymes. There are two phases of the glycolytic pathway. Payoff phase. Glucose is converted to pyruvate in 10 steps by glycolysis.
What is the sequence of reactions for the breakdown of glucose (6-carbon molecule) to two molecules of pyru?
Glycolysis can be defined as the sequence of reactions for the breakdown of Glucose (6-carbon molecule) to two molecules of pyruvic acid (3-carbon molecule) under aerobic conditions; or lactate under anaerobic conditions along with the production of small amount of energy. This pathway was described by Embden, Meyerhof and Parnas.
What is the name of the process of breakdown of glucose?
Glycolysis : All Steps with Diagram, Enzymes, Products, Energy Yield and Significance. Glycolysis is derived from the Greek words ( glykys = sweet and lysis = splitting ). It is a universal catabolic pathway in the living cells. Glycolysis can be defined as the sequence of reactions for the breakdown of Glucose (6-carbon molecule) ...
How is glucose-6 phosphate isomerised?
Glucose-6-phosphate is isomerised to fructose-6-phosphate by phosphohexose isomerase. For the reaction to take place, it needs the help of aldose-ketose isomerization using a catalyst phosphohexose i somerase . It causes glucopyranose ring’s opening to a linear structure changing the structure of the furanose ring of fructose-6-phosphate.
How many times does each step in the payoff phase occur?
Because Glucose is split to yield two molecules of D-Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, each step in the payoff phase occurs twice per molecule of glucose. The steps after 5 constitute payoff phase.
Where does glycolysis take place?
Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm of virtually all the cells of the body.