Functions of Epithelia
- Protecting underlying structures. Examples include the outer layer of the skin and the epithelium of the oral cavity, which protect the underlying structures from abrasion.
- Acting as a barrier. Epithelium prevents many substances from moving through it. ...
- Permitting the passage of substances. ...
- Secreting substances. ...
- Absorbing substances. ...
What are the four main functions of epithelial tissue?
Tissue types
- Epithelial tissue creates protective boundaries and is involved in the diffusion of ions and molecules.
- Connective tissue underlies and supports other tissue types.
- Muscle tissue contracts to initiate movement in the body.
- Nervous tissue transmits and integrates information through the central and peripheral nervous systems.
What is the function of simple epithelium?
Simple squamous epithelium- structure, functions, examples
- Simple squamous epithelium definition. Simple squamous epithelium is a type of simple epithelium that is formed by a single layer of cells on a basement membrane.
- Structure of the simple squamous epithelium. ...
- Functions of the simple squamous epithelium. ...
- Location and Examples. ...
- References and Sources. ...
What are the characteristics of epithelium?
The characteristics of stratified squamous epithelium are :
- They are multilayered as well as multicellular.
- They represent a squamous shape that is a flat shape.
- The nucleus they have is flat.
- The overview they have is polygonal.
- The width of the cell is less as compared to length of the cell.
- The outermost cells are flattened.
- Rest of the cells may be cuboidal.
- Only one layer is attached with basal membrane.
What are the 7 types of epithelial tissue?
Types of epithelial tissue : 1. Squamous epithelium : Simple squamous epithelial cells are extremely thin and flat and form a delicate lining. The oesophagus and the lining of the mouth are also covered with squamous epithelium. The skin, which protects the body, is also made of squamous epithelium. 2.
What is the epithelium?
Epithelium is one of only 4 types of human body tissues. Like all types, it is formed by cells within an extracellular matrix (ECM). The cells in this tissue are tightly packed within a thin ECM. Forming sheets that cover the internal and external body surfaces (surface epithelium) and secreting organs (glandular epithelium). ...
What is the epithelial tissue?
Epithelial tissue is one of the four tissue types. It is found lining the inner and outer body surfaces and comprising the parenchyma of the glands. It is divided into surface (covering) and glandular (secreting) epithelium. Surface epithelium consists of one or more cell layers, stacked over a thin basement membrane.
Why doesn't the epithelium have blood vessels?
This is one reason why epithelia doesn't have blood vessels, as abrasion could result in tearing of the vessel and bleeding. Epithelia specialized for protection, such as the stratified squamous keratinized epithelium of the skin, are multilayered and have a high cell renewal rate. This means that they repair quickly after injury.
What is stratified epithelium?
Stratified epithelium consists of two or more cell layers. Based on the shape of their most apical cell layer, they are further classified into squamous, cuboidal and columnar. There are also two types of specialized stratified epithelium: keratinized and transitional.
What is pseudo-seudostratified epithelium?
Pseudostratified epithelium is a type of simple columnar epithelium. It is termed “pseudo” because, although single, it appears to have multiple layers. All the cells are attached to the basement membrane but not all of them reach the free surface, thus forming a sheet of cells with different heights and irregularly located nuclei.
Where is the cuboidal epithelium found?
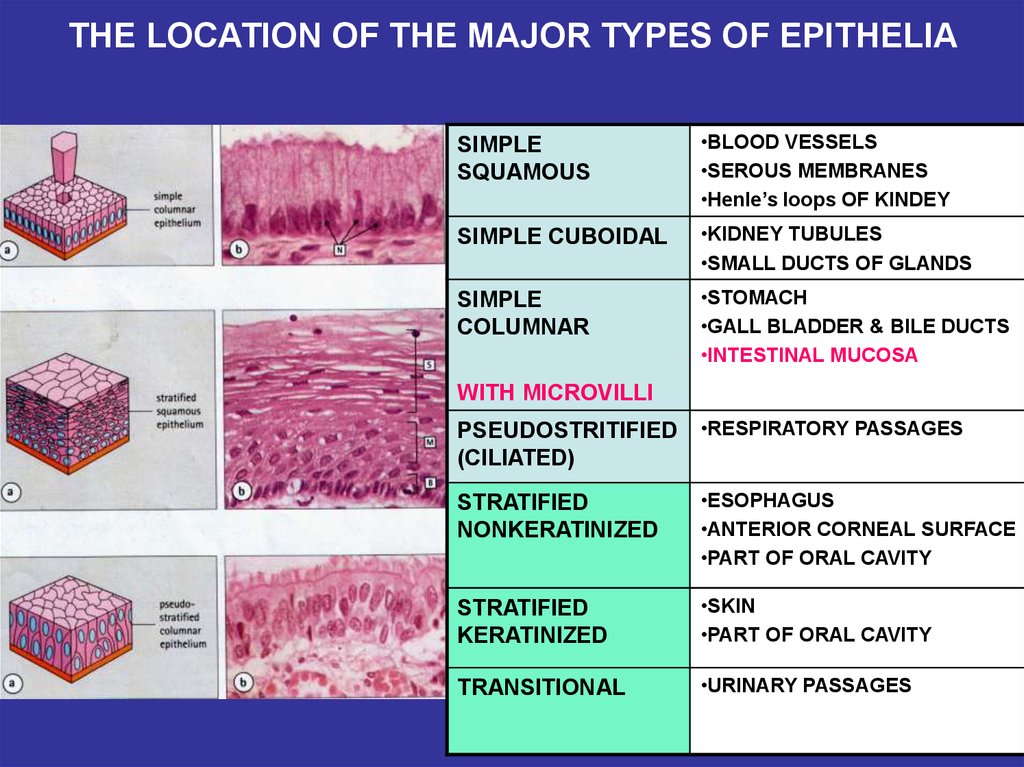
Simple cuboidal epithelium is found in organs with these functions, such as the ducts of the salivary glands, liver, pancreas and other exocrine glands. It forms thyroid follicles, kidney tubules, seminiferous tubules of male testis, and covers the surface of the ovaries (germinal epithelium).
Which epithelium is best for absorption?
Absorption function is best exampled by surface epithelia with apical microvilli which significantly increase the absorptive surface area. Columnar epithelium in the small intestine is a good example. These cells function to absorb nutrients from the digestive tract, then transport the digested substances into the circulation.
What is the function of the simple columnar epithelium?
Their function is to allow the movement of materials and nutrients through the cells, that is, passive diffusion. Simple Columnar Epithelium. These are elongated column shaped cells that are found at the base of cells. They line the stomach and intestines, as well as present in the nose, ears and on the tongue.
How are epithelial tissues classified?
Epithelial tissues are classified according to their cellular morphology and the number of layers in the cell. When the tissue is just one cell thick, it is called simple epithelium and when it is two or more cells thick, is it called a stratified epithelium. Let us have a look at each of these cells in detail.
What is stratified squamous epithelium?
The stratified squamous epithelium consists of flattened cell layers. They are present on the surface of the skin, lining of mouth, esophagus, anus and vagina. These cells help in protecting the underlying tissues. The outer areas of the tissue undergo keratinization that helps in making the skin waterproof.
What are the different types of epithelial cells?
The simple epithelial cells are further classified according to the shape of the cells. These include the simple squamous, simple cuboidal, simple columnar and pseudostratified cells.
What are some examples of squamous epithelial cells?
Examples of squamous epithelial cells include endothelium, pericardium, alveolar epithelium, and kidney capillaries. These cells are very thin and therefore, do not offer any protection to any organs. Their function is to allow the movement of materials and nutrients through the cells, that is, passive diffusion.
Which epithelial cells are spherical?
The columnar epithelial cells in the intestine contain microvilli that helps in increasing the surface are for absorption. These cells are cuboid in shape and have a spherical nucleus. These cells are present in the exocrine gland of the pancreas and the lining of kidney tubules.
Where are ciliated epithelial cells located?
Thus, they are also known as ciliated epithelial cells. They are present in the nose, bronchi, uterus, Fallopian tubes. Pseudostratified cells help in trapping of pathogens, foreign particles, as well help in propelling the ovum from the ovaries into the uterus.