What are the four divisions of the Old Testament books?
- Law. Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers, and Deuteronomy.
- History. Joshua, Judges, Ruth, 1&2 Samuel, 1&2 Kings, 1&2 Chronicles, Ezra, Nehemiah, and Esther.
- Poetry and Wisdom books. Job, Psamls, Proverbs, Ecclesiastes, Song od Songs.
- Major Prophets.
- Minor Prophets.
What are the four major divisions of the Old Testament?
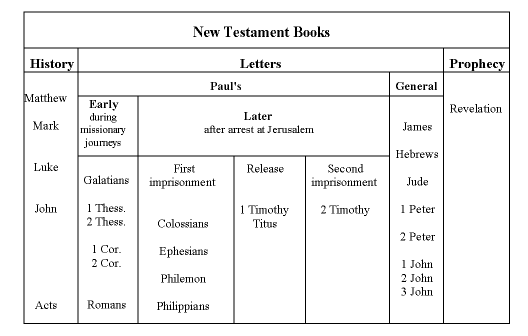
- Gospels. The first four books of the New Testament are the Gospels: Matthew, Mark, Luke and John.
- Acts. The fifth book of the New Testament is Acts of the Apostles, or simply "Acts." Acts recounts the early history of Christianity.
- Paul's Epistles and Hebrews.
- General Epistles.
- Revelation.
What is the chronological order of the Old Testament books?
CHRONOLOGICAL ORDER OF THE BOOKS While no arrangement of these books can be made with absolute confidence, the following dates are sufficiently reliable to serve the purpose of the Bible student. Old Testament Job–Unknown Genesis–1445-1405 B.C. Exodus–1445-1405 B.C. Leviticus–1445-1405 B.C. Numbers–1445-1405 B.C. Deuteronomy–1445-1405 B.C.
What are the four sections of the Old Testament?
Meanwhile, I immersed myself in yoga, Eastern meditation, chakra cleansing, astrology, divination, and other New Age practices. New Agers often view Christianity as having dogmatic rules, but they have their own rigid standards about what an “enlightened person” must and mustn’t do.
Which books belong in the Old Testament?
- Canon – The term “canon”, when applied to the Bible, denotes the collection of books that are accepted as authoritative.
- Old Testament, Hebrew Bible or Jewish Scriptures – These are the Bible books that were written before Jesus Christ was born. ...
- New Testament – These are the Bible books that were written after Jesus Christ was born. ...
What are the 4 basic divisions of the Old Testament?
The Old Testament contains 39 (Protestant), 46 (Catholic), or more (Orthodox and other) books, divided, very broadly, into the Pentateuch (Torah), the historical books, the "wisdom" books and the prophets.
What are the 4 divisions of the Bible?
The major divisions of the old and new testament Law books / Torah / pentateuch. Historical books. Poetic books. Prophetic books.
What are the divisions of the Old and New Testament?
The Old and New TestamentsBereshit - Genesis.Shemot - Exodus.Vayikra - Leviticus.Bamidbar - Numbers.Devarim - Deuteronomy.
What are the 4 parts of the New Testament books?
The New Testament contains 27 books written in Greek by 15 or 16 different authors between 50 C.E and 120 C.E. It can be divided into 4 groups: Gospels, Acts of the Apostles, Epistles, and Apocalypse. The New Testament contains 4 Gospels: Matthew, Mark, Luke, and John.
What are the four divisions of the Old Testament quizlet?
the four major divisions of the Old Testament are Pentateuch, Historical Books, Wisdom Books, and Prophetic Books.
What are the three divisions of the Old Testament?
The Hebrew Bible is often known among Jews as TaNaKh, an acronym derived from the names of its three divisions: Torah (Instruction, or Law, also called the Pentateuch), Neviʾim (Prophets), and Ketuvim (Writings).
What are the 5 major divisions of the New Testament?
Terms in this set (5)Gospels. The first four books of the New Testament are the Gospels: Matthew, Mark, Luke and John. ... Acts. The fifth book of the New Testament is Acts of the Apostles, or simply "Acts." Acts recounts the early history of Christianity. ... Paul's Epistles and Hebrews. ... General Epistles. ... Revelation.
How the Bible books are divided?
The Bible is divided into two major divisions: The Old Testament and the New Testament. The Old Testament consists of thirty-nine books and the New Testament is made up of twenty-seven books, a total of sixty-six books all together.
What are the five divisions of the Bible?
Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers, and Deuteronomy.
Why are the first four books of the New Testament called the Gospels?
The word gospel is derived from the Anglo-Saxon term god-spell, meaning “good story,” a rendering of the Latin evangelium and the Greek euangelion, meaning “good news” or “good telling.” Since the late 18th century the first three have been called the Synoptic Gospels, because the texts, set side by side, show a ...
What chapters are in the Old Testament?
ChaptersBook / DivisionChaptersExodus40Leviticus27Numbers36Deuteronomy3440 more rows
What are the historical books of Israel?
The Historical Books: Joshua, Judges, Ruth, First Samuel, Second Samuel, First Kings, Second Kings, First Chronicles, Second Chronicles, Ezra, Nehemiah, Esther - which tell the history of the nation of Israel and describe from the conquest of the Promised Land to Israel's Restoration after the Babylonian captivity. The Poetical Books (a.k.a.
What are the books of the law?
The Books of the Law (a.k.a. Pentateuch or Torah): Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers, Deuteronomy - written by Moses, which describe from the Creation to the end of the time the Jewish people spent in the wilderness. The Historical Books: Joshua, Judges, Ruth, First Samuel, Second Samuel, First Kings, Second Kings, First Chronicles, ...
Who are the minor prophets?
Minor Prophets - Hosea, Joel, Amos, Obadiah, Jonah, Micah, Nahum, Habakkuk, Zephaniah, Haggai, Zechariah, Malachi. * CTJ does NOT believe that the Song of Solomon and the apocryphal books are divinely inspired and therefore part of the Bible as they were not included in the original text up until the time of Jesus.
What are the four sections of the Bible?
The four sections of the Christian Bible are the Pentateuch, the Historical Books, the Prophetic Books, and the Wisdom literature. The Hebrew Bible used in the Jewish religious tradition has a different breakdown; they have the Torah, the Prophets, and the Writings. The Hebrew category of “Prophets” is then subdivided into ...
What is the conclusion of the Old Testament?
The conclusion of the Old Testament looks toward the fulfillment of God’s promises to His people, especially in the form of the Messiah (Hebrew for “anointed one”) of God. His coming would mark a definitive step for God’s revelation to His people and the salvation of all humankind. Sister Anna Marie McGuan, RSM, ...
What is the Hebrew category of prophets?
The Hebrew category of “Prophets” is then subdivided into the Former Prophets and the Latter Prophets. The Former Prophets include what the Christian tradition refers to as the Historical Books. The use of the category of “Prophets” for both historical and prophetic writing is fitting, however, as explained in the Catechism of the Catholic Church:
What is the first section of the Bible called?
In the Christian Bible, the Old Testament’s first section is usually called the Pentateuch. Pentateuch means “five volumes” or “five scrolls.”. Torah, the Hebrew word for these first five books, means “law.”.
What are the challenges of reading the Old Testament?
One challenge when reading the Old Testament is dealing with the amount of material contained therein. As a person reads along, he encounters narrative or story-like books or portions of books. The reader also encounters non-narrative passages, like poetry in the Psalms, genealogies, laws and regulations, and prophetic discourses.
What is wisdom literature?
The Wisdom literature or the Writings is a diverse collection of books. Perhaps the greatest of these books is the Psalms, which functioned like a prayer hymnal for the people of Israel and, now, also for the Church.
How can one keep one's orientation while reading through the Old Testament?
How can one keep one’s orientation while reading through the Old Testament? One helpful approach is to keep in mind the divisions of the Old Testament. Of course, the Old Testament is already divided into books, but those books are grouped together into four major sections in the Christian tradition and three distinct sections in ...
What are the books of the former prophets?
In the Hebrew arrangement, Joshua, Judges, and the books of Samuel and Kings form a group of books called "the Former Prophets" due to the prophetic view from which they are written. The Poetic and Wisdom writings include Job, Psalms, Proverbs, Ecclesiastes, and Song of Solomon.
Why are the Old Testament prophets considered major?
These books were declared "major" because of the amount of text, and not because they were considered more important than the "minor" prophetic books. The Old Testament prophet tended to be revealed during times of crisis. God used the prophets to provide direction and wisdom during times of crisis.
What are the minor prophets in the Bible?
The Minor Prophets include Hosea, Joel, Amos, Obadiah, Jonah, Micah, Nahum, Habakkuk, Zephaniah, Haggai, Zechariah, and Malachi. The books of the major and minor prophets were considered ...
What is the pentateuch in the Bible?
The Old Testament was composed over roughly a thousand year period and is divided by the grouping of the various books: The Pentateuch is the term commonly applied to the first five books of the Bible ; Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers, and Deuteronomy .
When did the classical prophets start?
The classical prophecy era began in the eighth century during the reign of Jeroboam II in the northern kingdom of Israel. Amos and Hosea were the earliest examples in the north, while Micah and Isaiah were the first known classical prophets in the southern kingdom of Judah.
Who are the prophets?
The Major Prophets include Isaiah, Jeremiah, Lamentations, Ezekiel, and Daniel.