| A | B |
| Name the living tissues in bone. | bone tissue, cartilage, dense connective ... |
| List functions of the skeletal system | support and protect softer tissues, prov ... |
| explain how bones are classified. | four classifications- by shape (long, sh ... |
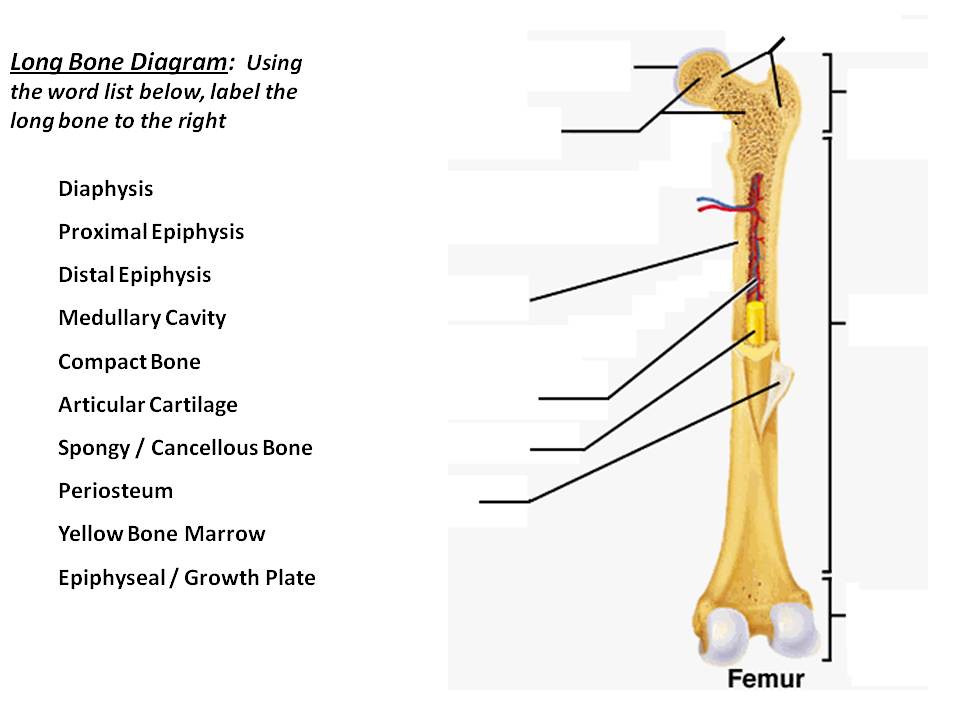
| list the five major parts of a long bone ... | epiphysis- part that forms a joint ... |
What are the primary structures of a long bone?
The structure of a long bone consists of several sections:
- Diaphysis: This is the long central shaft.
- Epiphysis: Forms the larger rounded ends of long bones.
- Metaphysis: Area between the diaphysis and epiphysis at both ends of the bone.
- Epiphyseal Plates: Plates of cartilage, also known as growth plates which allow the long bones to grow during childhood. ...
Can you identify the parts of a long bone?
All of the bones in the arms and legs, except the patella, and bones of the wrist, and ankle, are long bones. A typical long bone consists of the following parts: The diaphysis (growing between) is the shaft of a long bone — the long, cylindrical, main portion of the bone.
What is the main function of the long bone?
The function of long bones is centered on supporting the weight of your body as well as facilitating the movement of your body. Short bones have very equal proportions and are roughly shaped like a cube. Examples can be found in the bones of your wrists and ankles.
What are the 7 types of bones?
List of Bones in the Human Body
- Bones at a Glance. Would you like to write for us? ...
- Frontal Bone. This bone forms the forehead, the roof of the orbital cavity (eye socket), and the root of the nose.
- Parietal Bones. ...
- Temporal Bones. ...
- Occipital Bone. ...
- Sphenoid Bone. ...
- Ethmoid Bone. ...
- Facial Bones at a Glance. ...
- Mandible. ...
- Maxilla. ...
What are the 5 main parts of the long bone?
List five major parts of a long bone. Epiphysis, diaphysis, periosteum, yellow marrow, medullary cavity, compact bone, spongy bone, articular cartilage.
What are the major parts of a long bone?
A long bone has two parts: the diaphysis and the epiphysis. The diaphysis is the tubular shaft that runs between the proximal and distal ends of the bone. The hollow region in the diaphysis is called the medullary cavity, which is filled with yellow marrow.
What are the 4 parts of a long bone?
Examples of long bones include the femur, tibia, radius and ulna.Epyphysis. Every long bone is capped with wide areas on each end which are called epiphyses. ... Diaphysis. The largest part of any long bone is the long cylindrical middle, called the diaphysis. ... Metaphysis. ... Medullary Cavity.
What are the 5 different types of bones?
There are five types of bones in the skeleton: flat, long, short, irregular, and sesamoid. Let's go through each type and see examples.
What are the parts of a long bone quizlet?
Terms in this set (11)Diaphysis. Long main portion of a bone.Epiphysis. End of a long bone.Metaphyses. region of a long bone between the epiphysis and diaphysis.Articular Cartilage. Covers end of bones to prevent friction.Periosteum. ... Medullary Cavity. ... Endosteum. ... Red Bone Marrow.More items...
What are the 3 main parts of a long bone?
Long bones are longer than they are wide. They can be divided into three regions - epiphysis, metaphysis and the diaphysis. The epiphysis contains the spongy bone (also called cancellous), which in turn contains the red bone marrow that is responsible for synthesizing blood cells.
What are the 6 parts of a long bone?
A typical bone can be broken down into multiple parts, each with a particular function:Epiphysis. This part is at the extreme ends of the bone (epi = above), where joints (articulations) form.Articular cartilage. ... Diaphysis. ... Metaphysis. ... Periosteum. ... Medullary (or marrow) cavity. ... Endosteum.
What are the major structures of the bone?
Bones consist of different types of tissue, including compact bone, spongy bone, bone marrow, and periosteum. All of these tissue types are shown in Figure below. Compact bone makes up the dense outer layer of bone. Its functional unit is the osteon.
What are the 4 main types of bones?
There are four different types of bone in the human body:Long bone – has a long, thin shape. ... Short bone – has a squat, cubed shape. ... Flat bone – has a flattened, broad surface. ... Irregular bone – has a shape that does not conform to the above three types.
What are the 5 functions of the skeletal system?
The skeletal system works as a support structure for your body. It gives the body its shape, allows movement, makes blood cells, provides protection for organs and stores minerals. The skeletal system is also called the musculoskeletal system.
How many long bones are in the body?
90 long bonesHow many long bones are in the body? There are approximately 90 long bones in the human body. They are known as clavicle, femur, tibia, fibula, humerus, radius, ulna, metacarpals, metatarsals, and phalanges of the hands and feet.
What are the ends of long bones called?
The wider section at each end of the bone is called the epiphysis (plural = epiphyses), which is filled with spongy bone.
What is the structure of a long bone?
Long bone structure. A typical long bone consists of the following parts: The diaphysis (growing between) is the shaft of a long bone — the long, cylindrical, main portion of the bone. The epiphyses (growing over; singular is epiphysis) are the proximal and distal ends of the bone. The metaphyses (between; singular is metaphysis) ...
What is a long bone?
Long bone anatomy. A long bone is a bone that has greater length than width. A long bone has a shaft and 2 ends. Long bones have a thick outside layer of compact bone and an inner medullary cavity containing bone marrow. The ends of a long bone contain spongy bone and an epiphyseal line. The epiphyseal line is a remnant ...
What is the medullary cavity?
The medullary cavity (medulla- = marrow), or marrow cavity, is a hollow, cylindrical space within the diaphysis that contains fatty yellow bone marrow and numerous blood vessels in adults. This cavity minimizes the weight of the bone by reducing the dense bony material where it is least needed.
What is the articular cartilage?
The articular cartilage is a thin layer of hyaline cartilage covering the part of the epiphysis where the bone forms an articulation (joint) with another bone. Articular cartilage reduces friction and absorbs shock at freely movable joints.
Why is articular cartilage not covered by periosteum?
Because articular cartilage lacks a perichondrium and lacks blood vessels, repair of damage is limited. The periosteum is a tough connective tissue sheath and its associated blood supply that surrounds the bone surface wherever it is not covered by articular cartilage.
What is the epiphyseal line?
The epiphyseal line is a remnant of an area that contained hyaline cartilage that grew during childhood to lengthen the bone. Long bones contain yellow bone marrow and red bone marrow, which produce blood cells. The thigh bone (femur) is a long bone.
How do doctors describe fractures?
Doctors describe fractures to other doctors using classification systems. The location of the fracture (the tibial shaft is divided into thirds: distal, middle, and proximal) The pattern of the fracture (for example, the bone can break in different directions, such as crosswise, lengthwise, or in the middle)
What is a long bone?
Long bone. The long bones are those that are longer than they are wide. They are one of five types of bones: long, short, flat, irregular and sesamoid. Long bones, especially the femur and tibia, are subjected to most of the load during daily activities and they are crucial for skeletal mobility. They grow primarily by elongation ...
What is the definition of long bones?
FMA. 7474. Anatomical terms of bone. The long bones are those that are longer than they are wide. They are one of five types of bones: long, short, flat, irregular and sesamoid. Long bones, especially the femur and tibia, are subjected to most of the load during daily activities and they are crucial for skeletal mobility.
What are the congenital disorders of the long bones?
There are two congenital disorders of the long bones. In a disorder known as rachitis fetalis anularis the ends of the long bones (epiphyses) are enlarged. Another disorder is known as rachitis fetalis micromelica in which there is a deficiency in the growth (as a shortness) of the bones.
What is the outer shell of a long bone?
This is covered by a membrane of connective tissue called the periosteum. Beneath the cortical bone layer is a layer of spongy cancellous bone.
Which bone is compact?
Additionally, the outer shell of the long bone is compact bone, then a deeper layer of cancellous bone (spongy bone) which contains in the medullary cavity the bone marrow .
What is the bone that makes up the leg?
The other primary skeletal component of height are the vertebrae and skull . The outside of the bone consists of a layer of connective tissue called the periosteum.
How do long bones grow?
The longitudinal growth of long bones is a result of endochondral ossification at the epiphyseal plate.
What Are Long Bones in the Body?
There are many different organ systems within the human body. One of these organ systems is known as the musculoskeletal system. It comprises all of the muscles and bones in the body. The bone structure consists of 206 bones in the adult human skeleton.
Examples of Long Bones & Types
The long bones in the human skeleton are present in both extremities: arms and legs. All of the bones of the arms, legs, hands, and feet are examples of long bones, except the bones of the wrists and ankles. Furthermore, there is one long bone present outside of the extremities and this is called the clavicle.
What are the functions of bones?
List the major functions of bones. Support and protection, Movement, Hemopoiesis, Storage of mineral and energy reserves. Distinguish between the functions of red marrow and yellow marrow. Yellow marrow stores fat and does not produce red blood cells. Red marrow produces most blood cells.
Which part of the bone connects to the diaphysis?
epiphysis- part that forms a joint Metaphysis-connects epiphysis to diaphysis Diaphysis- shaft of the bone Articular cartilage- cartilage on the bone at the epiphysis to cushion the joint Medulary cavity- space containing yellow bone marrow.
How does endochondral bone develop?
Describe how an endochondral bone developes. Endochondrinal bone forms from masses of hyaline cartilage. this cartilage grows and develops the support system for the bone, then breaks down. Connective tissue begins to form around degenerating cartilage allowing for the development of bony structure to start growing.
What are the functions of the skeletal system?
List functions of the skeletal system. support and protect softer tissues, provide points of attachment for muscle tissue, house blood producing cells, storage of inorganic salts. explain how bones are classified. four classifications- by shape (long, short, flat and irregular bones) list the five major parts of a long bone.