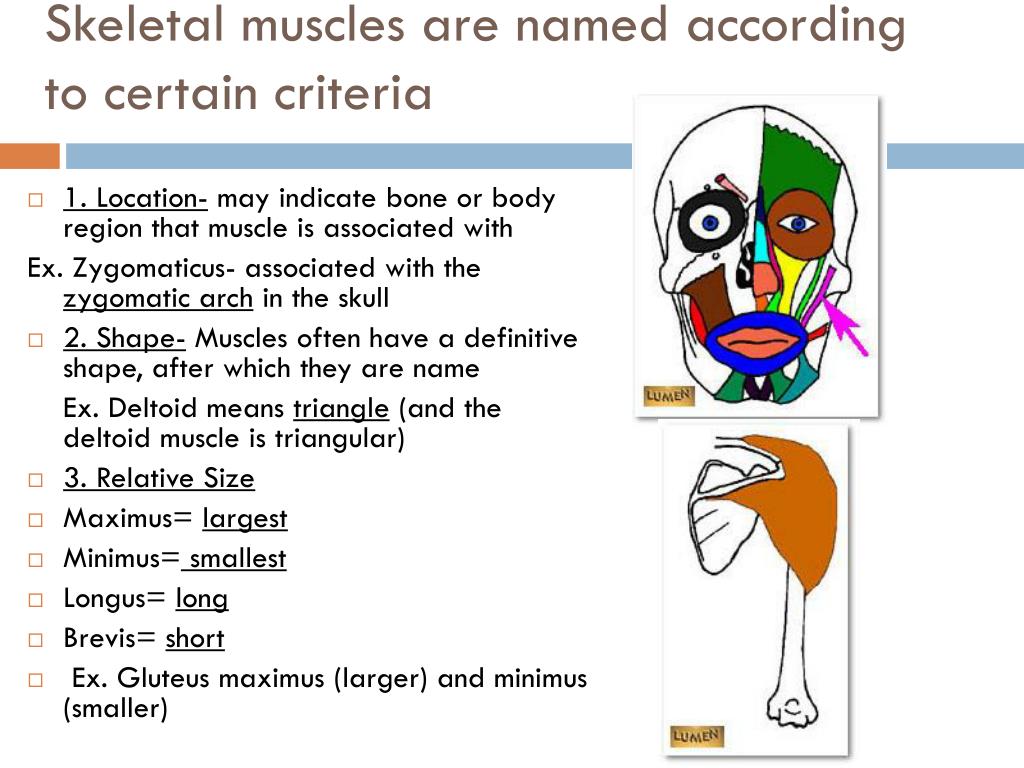
Each organ or muscle consists of skeletal muscle tissue, connective tissue, nerve tissue, and blood or vascular tissue. Skeletal muscles vary considerably in size, shape, and arrangement of fibers. They range from extremely tiny strands such as the stapedium muscle of the middle ear to large masses such as the muscles of the thigh.
- smallest. myofilament.
- myofibril.
- muscle fiber (cell)
- fascicle.
- muscle.
- largest. muscle group.
What is the structure of skeletal muscle?
Structure of Skeletal Muscle. The coverings also provide pathways for the passage of blood vessels and nerves. Commonly, the epimysium, perimysium, and endomysium extend beyond the fleshy part of the muscle, the belly or gaster, to form a thick ropelike tendon or a broad, flat sheet-like aponeurosis.
What are the three types of skeletal muscles?
Skeletal muscle is one of the three types of muscles in the human body- the others being visceral and cardiac muscles. In this lesson, skeletal muscles, its definition, structure, properties, functions, and types are explained in an easy and detailed manner.
What are the 4 properties of skeletal muscle?
Properties Of Skeletal Muscle The skeletal muscles have the following properties: Extensibility: It is the ability of the muscles to extend when it is stretched. Elasticity: It is the ability of the muscles to return to its original structure when released.
What is the smallest part of a muscle called?
What is the smallest part of a muscle? Myofibrils are assembled of repeated structures called sarcomeres – the smallest functional unit of muscle fiber. Each sarcomere is formed of actin (called thin) and myosin (called thick) filaments arranged in a precise order and of protein complexes which support the filament structures.
Which of the following is correct order from largest to smallest of muscle components?
Order of muscle components from largest to smallest is 2) fasciculus, muscle fiber, myofibril. Explanation: Fasciculus or fascicle is the largest muscle which is present in the human skeleton.
Which structure of the skeletal muscle is the smallest?
The sarcomere is the smallest functional unit of a skeletal muscle fiber and is a highly organized arrangement of contractile, regulatory, and structural proteins.
Which muscle component is largest?
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system that are mostly attached by tendons to bones of the skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are often known as muscle fibers.
What are the levels of organization of skeletal muscle?
Skeletal muscles contain connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves. There are three layers of connective tissue: epimysium, perimysium, and endomysium. Skeletal muscle fibers are organized into groups called fascicles. Blood vessels and nerves enter the connective tissue and branch in the cell.
Which of the following is the correct order from smallest structure to largest structure?
The order of these structures from smallest to largest is cells, tissues, organs, organ systems.
What is the smallest and biggest muscle in your body?
The largest muscle is the gluteus maximus (buttock muscle), which moves the thighbone away from the body and straightens out the hip joint. It is also one of the stronger muscles in the body. The smallest muscle is the stapedius in the middle ear.
Which of the following is smallest component of a muscle?
The smallest contractile unit of skeletal muscle is the muscle fiber or myofiber, which is a long cylindrical cell that contains many nuclei, mitochondria, and sarcomeres (Figure 1) [58].
Where is the smallest muscle?
earThe smallest muscle in the body is located inside the ear. It's called the stapedius, and it's less than 2 millimeters long, according to Guinness World Records. Its job is to support the smallest bone in the body, called the stapes, which is part of the middle ear and helps conduct vibrations to the inner ear.
What are the largest muscle groups?
The quads are by far the biggest muscle group in the body, both in men and women. They're roughly twice as large as the runner-up. 2. The next biggest muscle group is a tie between the gluteus maximus and the calves.
What are the 4 levels of organization of muscle tissue?
EXAMPLES. Using the circulatory system as an example, a cell in this system is a red blood cell, the heart's cardiac muscle is a tissue, an organ is the heart itself, and the organ system is the circulatory system. An organism is made up of four levels of organization: cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems.
Which is the correct listing of the hierarchy of skeletal muscle components beginning with the smallest?
CardsTerm The return of a contracted muscle fiber to its resting length is an active (energy requiring) process.Definition TrueTerm Which is a correct listing of the hierarchy of a skeletal muscle's components, beginning with the smallest?Definition a: Myofibrils b: Muscle fiber c: Fascicle d: Skeletal muscle94 more rows•Mar 25, 2014
Is myosin smaller than myofibril?
smaller than a myofibril. myofilaments made up of actin, troponin, and tropomyosin. myofilaments made up of myosin.
How big are skeletal muscle cells?
Skeletal muscle fibers can be quite large compared to other cells, with diameters up to 100 μ m and lengths up to 30 cm (11.8 in) in the Sartorius of the upper leg.
How is skeletal muscle supplied?
Every skeletal muscle is also richly supplied by blood vessels for nourishment, oxygen delivery, and waste removal. In addition, every muscle fiber in a skeletal muscle is supplied by the axon branch of a somatic motor neuron, which signals the fiber to contract. Unlike cardiac and smooth muscle, the only way to functionally contract a skeletal muscle is through signaling from the nervous system.
How to describe muscle contraction?
By the end of this section, you will be able to: 1 Describe the connective tissue layers surrounding skeletal muscle 2 Define a muscle fiber, myofibril, and sarcomere 3 List the major sarcomeric proteins involved with contraction 4 Identify the regions of the sarcomere and whether they change during contraction 5 Explain the sliding filament process of muscle contraction
How many sarcomeres are in a muscle fiber?
Because myofibrils are only approximately 1.2 μm in diameter, hundreds to thousands (each with thousands of sarcomeres) can be found inside one muscle fiber.
What is the layer of collagen and reticular fibers called?
Inside each fascicle, each muscle fiber is encased in a thin connective tissue layer of collagen and reticular fibers called the endomysium. The endomysium surrounds the extracellular matrix of the cells and plays a role in transferring force produced by the muscle fibers to the tendons. In skeletal muscles that work with tendons to pull on bones, ...
How many layers of connective tissue are there in skeletal muscle?
Each skeletal muscle has three layers of connective tissue that enclose it, provide structure to the muscle, and compartmentalize the muscle fibers within the muscle ( Figure 10.2.1 ). Each muscle is wrapped in a sheath of dense, irregular connective tissue called the epimysium, which allows a muscle to contract and move powerfully ...
Why do skeletal muscle fibers have many nuclei?
Having many nuclei allows for production of the large amounts of proteins and enzymes needed for maintaining normal function of these large protein dense cells. In addition to nuclei, skeletal muscle fibers also contain cellular organelles found in other cells, such as mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum.
What is the structure of skeletal muscle?
Each organ or muscle consists of skeletal muscle tissue, connective tissue, nerve tissue, and blood or vascular tissue. Skeletal muscles vary considerably in size, shape, and arrangement of fibers.
What are the skeletal muscles?
Skeletal muscles vary considerably in size, shape, and arrangement of fibers. They range from extremely tiny strands such as the stapedium muscle of the middle ear to large masses such as the muscles of the thigh. Some skeletal muscles are broad in shape and some narrow.
What is the term for the thick ropelike tendon?
Commonly, the epimysium, perimysium, and endomysium extend beyond the fleshy part of the muscle, the belly or gaster, to form a thick ropelike tendon or a broad, flat sheet-like aponeurosis. The tendon and aponeurosis form indirect attachments from muscles to the periosteum of bones or to the connective tissue of other muscles.
What is the connective tissue sheath called?
Each muscle is surrounded by a connective tissue sheath called the epimysium. Fascia, connective tissue outside the epimysium, surrounds and separates the muscles. Portions of the epimysium project inward to divide the muscle into compartments. Each compartment contains a bundle of muscle fibers. Each bundle of muscle fiber is called ...
What is the fiber of a skeletal muscle called?
Each skeletal muscle fiber is a single cylindrical muscle cell. An individual skeletal muscle may be made up of hundreds, or even thousands, of muscle fibers bundled together and wrapped in a connective tissue covering. Each muscle is surrounded by a connective tissue sheath called the epimysium. Fascia, connective tissue outside the epimysium, surrounds and separates the muscles. Portions of the epimysium project inward to divide the muscle into compartments. Each compartment contains a bundle of muscle fibers. Each bundle of muscle fiber is called a fasciculus and is surrounded by a layer of connective tissue called the perimysium. Within the fasciculus, each individual muscle cell, called a muscle fiber, is surrounded by connective tissue called the endomysium.
What is the layer of connective tissue that surrounds the fasciculus?
Each bundle of muscle fiber is called a fasciculus and is surrounded by a layer of connective tissue called the perimysium. Within the fasciculus, each individual muscle cell, called a muscle fiber, is surrounded by connective tissue called the endomysium.
How are skeletal muscles attached to bones?
Typically a muscle spans a joint and is attached to bones by tendons at both ends. One of the bones remains relatively fixed or stable while the other end moves as a result of muscle contraction. Skeletal muscles have an abundant supply of blood vessels and nerves. This is directly related to the primary function of skeletal muscle, contraction.
What is the structure of skeletal muscle?
Structure Of Skeletal Muscle. This muscle is attached to the bones by an elastic tissue or collagen fibres called tendons. These tendons are comprised of connective tissues. The skeletal muscles consist of a bundle of muscle fibres namely fascicule.
What are the properties of skeletal muscles?
The skeletal muscles have the following properties: Extensibility: It is the ability of the muscles to extend when it is stretched. Elasticity: It is the ability of the muscles to return to its original structure when released. Excitability: It is the ability of the muscle to respond to a stimulus.
What is the membrane of muscle?
Each muscle fibre is lined by plasma membrane namely sarcolemma reticulum. It encloses a cytoplasm called sarcoplasm which has the endoplasmic reticulum. The muscle fibres consist of myofibrils, which have two important proteins, namely actin and myosin in it. The fascicule is enclosed by perimysium and the endomysium is the connective tissue that encloses the muscle fibres.
What is the term for the muscle that is attached to bones?
Skeletal muscle is a muscle tissue that is attached to the bones and is involved in the functioning of different parts of the body. These muscles are also called voluntary muscles as they come under the control of the nervous system in the body.
Which muscle is responsible for extending the arm?
The skeletal muscles are responsible for body movements such as typing, breathing, extending the arm, writing, etc. The muscles contract which pulls the tendons on the bones and causes movement. The body posture is maintained by the skeletal muscles . The gluteal muscle is responsible for the erect posture of the body.
What is smooth muscle?
Smooth muscle is a type of muscle tissue that is utilized by different systems for the application of pressure to organs and vessels. It is an involuntary muscle, which shows no cross stripes even when examined under a microscope.
Where are cardiac muscles located?
One of the three types of muscles, the cardiac muscles is a muscle tissue found in the heart, wherein it is performing and bringing about coordinated contractions, which enable the heart to pump blood throughout the body through the circulatory system.
Which muscle has small motor units?
Muscles that require fine motor control and coordinated movements, such as the extraocular muscles, have small motor units.
Which muscle fiber is more susceptible to injury?
Type II muscle fibers are more susceptible to injury than type I fibers.
What are the proteins in the filaments?
Thin filaments consist of three proteins (actin, tropomyosin, and troponin), which form the I band of a myofibril (see Fig. 26-2 ).
What is the mechanism of muscle contraction?
Muscle contraction is initiated by the release of ionic calcium into the sarcoplasm.
What is the point of contact of each muscle fiber?
Each nerve cell axon branches many times, providing each muscle fiber with a point of contact called the motor endplate.
What is the membrane that covers muscle fibers?
Below the layer of endomysium that covers each muscle fiber sits a plasma membrane called the sarcolemma ( Fig. 26-2 and Table 26-2 ).
Where do tears occur in a muscle strain?
Contused muscle tears at the point of impact, whereas muscle strains usually result in tears at the myotendinous junction.
What is the smallest unit of muscle fiber?
Myofibrils are assembled of repeated structures called sarcomeres – the smallest functional unit of muscle fiber. Each sarcomere is formed of actin (called thin) and myosin (called thick) filaments arranged in a precise order and of protein complexes which support the filament structures.
Which connective tissue layer surrounds muscle fiber?
List the 5 connective tissue components in order from most superficial to most deep. Endomysium-inner most layer that surrounds muscle fiber. Perimysium- surrounds individual fascicles, contain blood vessels and nerves.