Echidna
Echidnas, sometimes known as spiny anteaters, belong to the family Tachyglossidae in the monotreme order of egg-laying mammals. The four extant species of Echidnas and the platypus are the only living mammals that lay eggs and the only surviving members of the order Monotremat…
How do echidnas adapt to their environment?
Adaptations of the echidna include: A long tongue with sticky saliva, with which it eats termites and ants. A long snout which makes it easy for the echidna to burrow for ants, termites and worms. During breeding season, the female echidna develops a pouch, where she lays and incubates her egg.
What is the behaviour of a short-beaked echidna?
Behavioural: When the short-beaked echidna is disturbed, it will dig straight down into the ground at a high speed, and cover themselves with dirt.
What is the lifespan of an echidna?
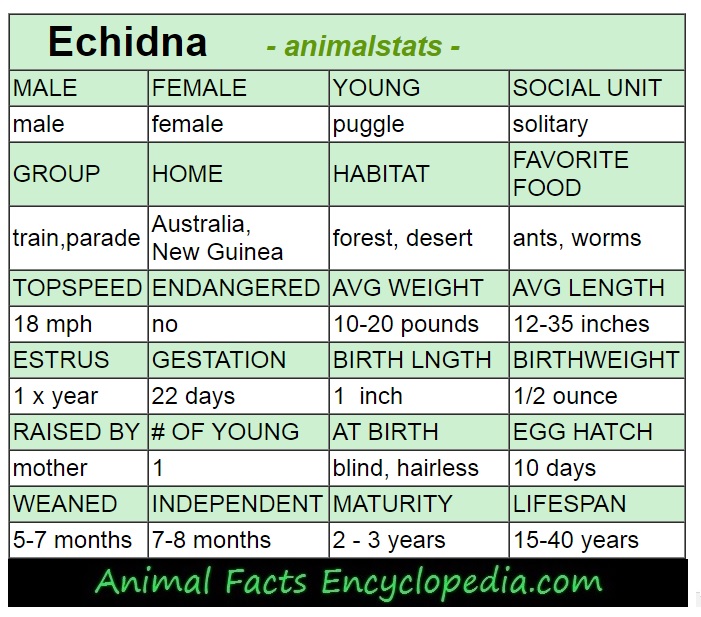
When grown, echidnas measure 30–53 cm long with males weighing about 6 kg and females about 4.5 kg. Echidnas have been known to live for as long as 16 years in the wild, but generally their life span is thought to be under 10 years (Rismiller & Seymour 1991).
What do Echidnas use their feet for?
This allows the animal to feed easily, especially when suckling. The short, stout limbs of echidnas are well suited for scratching and digging the soil. The front feet have five flattened claws which are used to dig forest litter, burrow, and tear open logs and termite mounds.
What are echidnas Behaviour?
Habits. Echidnas are very solitary animals, but they are not territorial and are willing to share their home range with others of their kind. They are active during the day, but in warmer months they will often become nocturnal to avoid the heat.
What are two adaptations of a echidna?
ADAPTATIONS FOR THIS DIET Echidnas have short muscular legs, with very long forefeet and very long sharp claws. These are used for burrowing into ant nests and termite mounds, and for turning over leaf litter and digging into rotten logs. The mouth and nose are elongated to form a tubular snout.
What are Behavioural adaptations?
Behavioral adaptation: something an animal does usually in response to some type of external stimulus in order to survive. Hibernating during winter is an example of a behavioral adaptation.
What adaptations can an echidna find and eat?
Echidna are found in the deserts of Australia and also have unique adaptations. Their long nose helps them locate food by sensing the electrical movements created by ants and termites. Then they use their long tongues to get into ant and termite mounds.
What Behavioural adaptations do echidnas have to survive bushfires?
Instead of fleeing from fire, echidnas burrow underground and hibernate while waiting for the fire to pass them. "They dig into a burrow or the soil and slow down their metabolism and make a buffer from them and the fire," Dr Palmer said.
What Behavioural adaptations do echidnas have to survive cold winters?
Behavioural: In order for echidnas to keep cool in hot climates they find shelter. They use fallen wood, bushes, rocks, small caves and burrows to take cover from the heat.
What are 3 behavioral adaptations?
Behavioral Adaptation: Actions animals take to survive in their environments. Examples are hibernation, migration, and instincts.
What are 5 examples of behavioural adaptations?
A Behavioral Adaptation is something an animal does - how it acts - usually in response to some type of external stimulus. Examples of some Behavioral Adaptions: What an animal is able to eat....Overview of Physical and Behavioral Adaptations:Webbed feet.Sharp Claws.Large beaks.Wings/Flying.Feathers.Fur.Scales.
What are 2 types of behavioral adaptation?
There are two different types of behavioral adaptations: instinct and learned behavior. When an animal is born knowing how to behave or do something this is called instinct.
Why do echidnas have 4 heads?
But in short-beaked echidnas, the cavernosum was merged while the spongiosum remained separate. This separate spongiosum tissue is what allows echidnas to erect each half, or pair of heads, independently from the other, the researchers said.
What are structural and behavioral adaptations?
Structural adaptations are physical features of an organism like the bill on a bird or the fur on a bear. Other adaptations are behavioral. Behavioral adaptations are the things organisms do to survive. For example, bird calls and migration are behavioral adaptations. Adaptations are the result of evolution.
How many echidnas are left in the world 2021?
Although there are estimated to be as many as 10,000 mature individuals, the population is decreasing, and this species is extinct in some parts of its former range.
What are behavioural adaptations?
If you're wondering what a behavioural adaptation is, they are things that are organisms or living things do to survive for example an echidna would roll into a ball to survive from predators
Caring for their Children
When the baby echidna also known as a puggle is born it doesn't have any spikes on it's back. The mother carry's the puggle around for about 45-55 days until the bay starts to grow spikes. The mother will then put the puggle into a burrow for the next 6 months.
Reacting to danger
When an echidna is in danger it can roll in a ball so it doesn't get eaten on it's belly, or it can use it's sharp claw to burrow into the dirt.
What is an echidna's behavior?
Behavioural Adaptations: Echidna’s use their forepaws to dig into ants nests to find food and use their fast tongues to trap them.
Why do echidnas have long, fast moving tongues?
They have long, fast moving tongues to trap and eat ants, termites and other insects in their nests.
Where do echidnas hibernate?
Echidna hibernation takes place in all climate zones, not just cold regions (Augee et al. 2006) Echidnas in cold climates enter deep hibernation; those in milder climates only enter hibernation for short periods (Morrow et al. 2009) Eastern Australia: long periods of hibernation.
What is the best position for an echidna to sleep?
Sleep: resting position with spines down. Defense: body round, with head tucked in and spines raised. Upside-down belly scratch: echidna rolls over on its back and scratches its belly with its claws. Earth-roll: echidna rolls over in a depression in the ground to dust bathe.
What is the purpose of torpor in echidnas?
Echidnas experience torpor (Nowack et al. 2016) An animal in torpor lowers its body temperature, heart rate, and metabolism to greatly reduce its energy needs. Torpor is an adaptation used to survive periods of low food availability, temperature challenges, natural disasters, and population bottlenecks.
Do echidnas communicate?
Echidnas are solitary; use scent and smell to communicate ‘at a distance’ (Nicol 2015a) Breeding season. Males are attracted to the scent of females and other mating echidnas (Nicol 2015a) A male’s spur secretions change during the mating season (Nicol 2015a) May be used by females to assess a mate.
Does echidna use energy?
Metabolism slows; short-beaked echidna is able to conserve energy, especially in the coldest parts of its range (Morrow and Nicol 2009) May use less than 12% of the energy typically used when not hibernating (Augee et al. 2006)
What are echidna behavioral adaptations?
ADAPTATIONS: Behavioral Adaptations: -Echidna’s use their front paws to dig into ants nests to find food and use their fast tongues to trap them. -Echidna’s young are pushed out of their pouch whilst still young so their growing spikes do not penetrate and hurt the mother.
When do short beaked echidna change their pattern of activity?
RHYTHMIC PATTERNS: Short beaked echidna are usually active in the daytime; however during the warmer months the short beaked echidna change their pattern of activity, becoming nocturnal (active at night) or crepuscular (active at dawn or dusk).
What is the shape of an echidna's tongue?
The tongue is so flexible that is can bend in a U-turn shape and catch insects that make an attempt to escape. The short beaked echidnas tongue also has the ability to avoid picking up splinters while scavenging in logs and other woods. The short beaked echidna’s snout shape is like a double wedge.
What is the tongue of an echidna?
The tongue is the single means of the echidna catching its prey. . The short beaked echidnas tongue is coated in glycoprotein-rich mucus, which makes the tongue sticky. This mucus on the tongue lubricates movement in and out of the snout and helps to catch ants and termites.
What does a short beaked echidna pouch protect?
This pouch protects her babies from predators such as goannas. Short beaked echidnas have a long tongue with sticky saliva, with which they eats termites and ants. They also have a long snout which makes it easy for food. Short beaked echidnas have numerous structural adaptations to aid their lifestyle. The short beaked echidna has short limbs and ...
Why do short beaked echidna dig?
This is useful when bush fires occur as there is a low level of oxygen. The short beaked echidna can dig up to a metre into the ground to retrieve ants, termites or worms or avoid predators. The short beaked echidna can also dive under water when flash floods occur.
Why do echidna have a short beaked claw?
Due to the fact that the short beaked echidna has one of the shortest spinal cords of any mammal (extending as far as the thorax) this is believed to allow its flexibility to wrap into a ball. The claws located on the back feet are lengthened and curved backward to enable cleaning and grooming between the spines.