Proactivity
| Control Proactivity | Behavioral control | Outcome control |
| Feedforward control | Organizational culture | Market demand or economic forecasts |
| Concurrent control | Hands-on management supervision during a ... | The real-time speed of a production line |
| Feedback control | Qualitative measures of customer satisfa ... | Financial measures such as profitability ... |
What are the 4 levels of organization in order?
Philosophical Accounts of Levels of Organization
- 2.1 The Layer-Cake Account. In the classic paper “The Unity of Science as a Working Hypothesis” (1958; see also the entry the unity of science ), Oppenheim and Putnam (hereafter ...
- 2.2 Levels of Mechanisms. ...
- 2.3 Wimsatt’s “Local Maxima” Account. ...
- 2.4 Levels Skepticism and Deflationary Accounts. ...
What are the different types of organizational controls?
Organizational control is important to know how well the organization is performing, identifying areas of concern, and then taking an appropriate action. There are three basic types of control systems available to executives: (1) output control, (2) behavioral control, and (3) clan control. Different companies opt different types of control ...
What are the 4 levels of organization in an organism?
What are the four levels of organization in the body? The major levels of organization in the body, from the simplest to the most complex are: atoms, molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and the human organism.See below Figure 1.1.
What are the 4 levels of organization in living things?
Levels of organization found in living things imp. 1. Cells 2. Tissues – groups of cells 3. Organs – groups of tissues 4. Organ systems – groups of organs Digestive system Respiratory system Nervous system Circulatory system Excretory system Muscular system Reproductive system 5. Organism ANALOGY Bricks cells Brick wall tissues Room organ ...
What are the 4 types of controls?
The four types of control systems are belief systems, boundary systems, diagnostic systems, and interactive system.
What are the types of organizational controls?
Organizational control systems allow executives to track how well the organization is performing, identify areas of concern, and then take action to address the concerns. Three basic types of control systems are available to executives: (1) output control, (2) behavioral control, and (3) clan control.
Which of the 4 steps in the control process is the most important?
Take Corrective Action If there is an issue, this becomes the most important step because you want to fix the problem as quickly as possible.
What are the four phases of management control?
Process for operating activities has four phases: programming, budget preparation, execution, and evaluation.
What are the three levels of control?
In management, there are varying levels of control: strategic (highest level), operational (mid-level), and tactical (low level).
What do you mean by organizational control?
Organizational control is defined as any process by which managers direct attention, motivate, and encourage organizational members to act in desired ways to meet the firm's objectives.
Why the four steps involved in the control function are important?
These steps are important because they allow control in order to ensure everyone stays aligned with the organization's goals.
What are the four characteristics of effective control?
Characteristics Of Effective Control SystemsAccurate. Information on performance must be accurate. ... Timely. ... Objective and Comprehensible. ... Focused on Strategic Control Points. ... Economically Realistic. ... Organizational Realistic. ... Coordinated with the Organization's Work Flow. ... Flexible.More items...
What is the fourth step in quality planning and control?
Step 4. Determine whether the product or service satisfies realistic quality standards by analysing them. This is the control step.
What are the 4 basic model of strategic management?
This type of business model in strategic management is a macro-level plan that helps organizations assess future changes based on four factors—Political, Economic, Social and Technological.
What are the four phases of management control quizlet?
Step 1 — establish objectives and standards. Step 2 — measure actual performance. Step 3 — compare results with objectives and standards. Step 4 — take corrective action as needed.
What are the 4 steps in the strategic analysis process?
The 4 Steps of Strategic Planning ProcessEnvironmental Scanning. Environmental scanning is the process of gathering, organizing and analyzing information. ... Strategy Formulation. ... Strategy Implementation. ... Strategy Evaluation.
What are the levels of control?
Two Levels of Control: Strategic and Operational. Imagine that you are the captain of a ship. The strategic controls make sure that your ship is going in the right direction; management and operating controls make sure that the ship is in good condition before, during, and after the voyage. With that analogy in mind, strategic control is concerned ...
What is operational control?
Where operational controls are imposed, they function within the framework established by the strategy.
What is the difference between behavioral and outcome control?
Within these types of strategy, controls can vary in terms of proactivity, where feedback controls were the least proactive. Outcome controls are judged by the result of the organization’s activities, while behavioral controls involve monitoring how the organization’s members behave on a daily basis.
What is feedback control?
Finally, feedback controls involve gathering information about a completed activity, evaluating that information, and taking steps to improve the similar activities in the future. This is the least proactive of controls and is generally a basis for reactions.
When are outcome controls preferable?
Outcome controls are generally preferable when just one or two performance measures (say, return on investment or return on assets) are good gauges of a business’s health.
Is financial control a behavioral control?
While we often think of financial controls as a form of outcome control, they can also be used as a behavioral control. For instance, if managers must request approval for expenditures over a budgeted amount, then the financial control also provides a behavioral control mechanism as well.
How do organizational controls work?
Organizational controls can take many forms. Strategic controls help managers know whether a chosen strategy is working , while operating controls contribute to successful execution of the current strategy. Within these types of strategy, controls can vary in terms of proactivity, where feedback controls were the least proactive. Outcome controls are judged by the result of the organization’s activities, while behavioral controls involve monitoring how the organization’s members behave on a daily basis. Financial controls are executed by monitoring costs and expenditure in relation to the organization’s budget, and nonfinancial controls complement financial controls by monitoring intangibles like customer satisfaction and employee morale.
How do strategic controls work?
Imagine that you are the captain of a ship. The strategic controls make sure that your ship is going in the right direction; management and operating controls make sure that the ship is in good condition before, during, and after the voyage. With that analogy in mind, strategic control is concerned with tracking the strategy as it is being implemented, detecting any problem areas or potential problem areas suggesting that the strategy is incorrect, and making any necessary adjustments (Venkataraman & Saravathy, 2001). Strategic controls allow you to step back and look at the big picture and make sure all the pieces of the picture are correctly aligned.
What is feedback control?
Finally, feedback controls involve gathering information about a completed activity, evaluating that information, and taking steps to improve the similar activities in the future. This is the least proactive of controls and is generally a basis for reactions. Feedback controls permit managers to use information on past performance to bring future performance in line with planned objectives.
What is concurrent control?
The process of monitoring and adjusting ongoing activities and processes is known as concurrent control. Such controls are not necessarily proactive, but they can prevent problems from becoming worse. For this reason, we often describe concurrent control as real-time control because it deals with the present. An example of concurrent control might be adjusting the water temperature of the water while taking a shower.
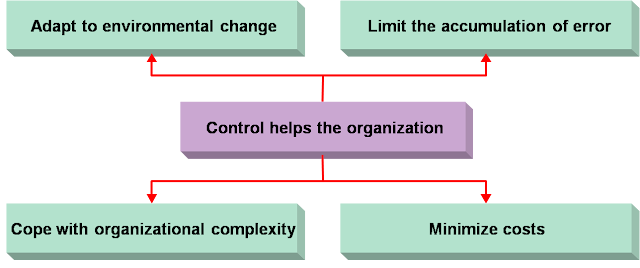
What are the benefits of organizational controls?
When they are well designed and implemented, they provide at least five possible areas of benefits, including (1) improved cost and productivity control, (2) improved quality control, (3) opportunity recognition, (4) better ability to manage uncertainty and complexity, and (5) better ability to decentralize decision making. Let’s look at each one of these benefits in turn.
Why are organizational controls important?
Organizational controls provide significant benefits, particularly when they help the firm stay on track with respect to its strategy. External stakeholders, too, such as government, investors, and public interest groups have an interest in seeing certain types or levels of control are in place.
What is the third potential cost of having controls?
The third potential cost of having controls is that they can afford less organizational flexibility and responsiveness.
How can productivity be controlled?
Similarly, productivity can be controlled by comparing how much each person can produce, in terms of service or products. For instance, you can imagine that the productivity of a fast-food restaurant like McDonald’s depends on the speed of its order takers and meal preparers.
How do good controls help an organization?
First, good controls help the organization to be efficient and effective by helping managers to control costs and productivity levels. Cost can be controlled using budgets, where managers compare actual expenses to forecasted ones.
What is Google's organizational structure?
Google has implemented an effective organizational structure that focuses on flatness in order to be innovative. Their matrix structure and the organizational culture that it supports emphasizes change and direct social links within the firm. These elements of structure and culture support the firm’s strategic interest for excellence in innovation and are in support of Google’s corporate mission and vision.
Why are controls put in place?
Typically, controls are put in place to prevent problems, but controls can also create problems. For instance, the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) is responsible for helping people and business cope with the consequences of natural disasters, such as hurricanes.
What are the benefits of organizational controls?
When they are well designed and implemented, they provide at least five possible areas of benefits, including (1) improved cost and productivity control, (2) improved quality control, (3) opportunity recognition, (4) better ability to manage uncertainty and complexity, and (5) better ability to decentralize decision making. Let’s look at each one of these benefits in turn.
Why are organizational controls important?
Organizational controls provide significant benefits, particularly when they help the firm stay on track with respect to its strategy. External stakeholders, too, such as government, investors, and public interest groups have an interest in seeing certain types or levels of control are in place. However, controls also come at a cost. It is useful to know that there are trade-offs between having and not having organizational controls, and even among the different forms of control. Let’s look at some of the predominant costs and benefits of organizational controls, which are summarized in the following figure.
What is the critical limiting factor of an organizational form?
(1974). Organization design: An information processing view. Interfaces, 4, 28–36. Galbraith believes that “the greater the uncertainty of the task, the greater the amount of information that must be processed between decision makers during the execution of the task to get a given level of performance.” Firms can reduce uncertainty through better planning and coordination, often by rules, hierarchy, or goals. Galbraith states that “the critical limiting factor of an organizational form is the ability to handle the non-routine events that cannot be anticipated or planned for.”