- crabgrass
- corn (maize)
- sugarcane
- sorghum
What are the different types of CAM plants?
- Aizoaceae (Caryophyllales)
- Apiaceae (Apiales)
- Apocynaceae (Gentianales)
- Asteraceae (Asterales)
- Cactaceae (Caryophyllales)
- Celastraceae (Rosids)
- Clusiaceae (Malpighiales)
- Convolvulaceae (Solanales)
- Crassulaceae (Saxifragales)
- Cucurbitaceae (Cucurbitales)
What are some examples of a CAM plant?
- Pickleweed. Sarcopenia Pacifica ( the scientific name is usually less than a foot and 1/2 tall, very widespread in marshes and crimsons when it tries to get rid of salt.
- Alkali Health. A low-growing plant, abundant in riverine marshes. ...
- Cattail. Long, perennial plants that have brown flowers on top.
- Saltgrass. The plant Grows in desert habita
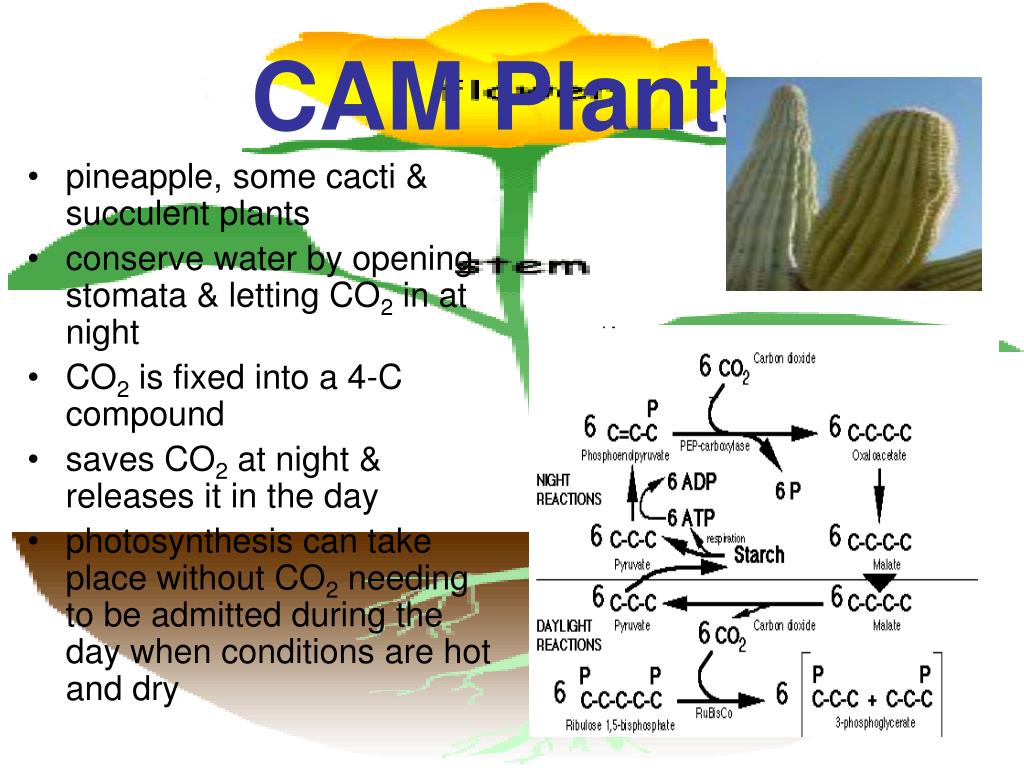
What are CAM plants and what is their advantage?
What are CAM plants and what is their advantage? Crassulacean Acid Metabolism ( CAM ) has the advantage of essentially eliminating evapotranspiration through a plants stomata (water loss through gas exchange) during the day, allowing CAM plants to survive in inhospitable climates where water loss is a major limiting factor to plant growth.
What types of plants are C4 and Cam?
C4 plants include corn, sugar cane, millet, sorghum, pineapple, daisies and cabbage. The image above shows the C4 carbon fixation pathway. CAM Plants. Plants that use crassulacean acid metabolism, also known as CAM plants, are succulents that are efficient at storing water due to the dry and arid climates they live in.
What are the examples of CAM plants?
CAM Plants Examples Carbon dioxide supply is limited due to slower diffusion in water. Aquatic CAM plants absorb CO2 at night when there is less competition from other photosynthetic plants. Orchids, Cacti, Aloe, Pineapple, Agave, Moringa, Some species of Euphorbia and Bromelioideae, etc.
What is CAM plant give its example?
CAM plants are therefore highly adapted to arid conditions. Examples of CAM plants include orchids, cactus, jade plant, etc. Compare: C3 plant, C4 plant. See also: Crassulacean acid metabolism, Calvin cycle.
What are CAM plants name three examples?
Examples of CAM plants, besides the aforementioned cactus (family Cactaceae), are pineapple (family Bromeliaceae), agave (family Agavaceae), and even some species of Pelargonium (the geraniums). Many orchids are epiphytes and also CAM plants, as they rely on their aerial roots for water absorption.
What are examples of C3 C4 and CAM plants?
Difference Between C3, C4 and CAM pathwayC3C4CAMExampleBeans, Spinach, Sunflower, Rice, CottonMaize, Sorghum, SugarcaneOrchids, Cacti, euphorbiasCarboxylating enzymeIn C3, RuBP carboxylasePEP carboxylase – mesophyll RuBP carboxylase – bundle sheathRuBP carboxylase – day time PEP carboxylase – night time26 more rows
Which one is an example of CAM?
Sedum, Kalanchoe, Pineapple, Opuntia, Snake plant are the examples of CAM plants. These plants also perform double carbon dioxide fixation. The carbon dioxide acceptor in CAM plants is Phosphoenol pyruvic acid (PEP) during the night and Ribulose bisphosphate is carbon dioxide acceptor during the daytime.
Is a cactus a CAM plant?
Cacti utilize CAM photosynthesis, a process unique to succulents. In CAM photosynthesis, stomata open only at night when the plant is relatively cool, so less moisture is lost through transpiration.
Is a pineapple a CAM plant?
Pineapple (Ananas comosus (L.) Merr.) is the most economically valuable crop possessing crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM), a photosynthetic carbon assimilation pathway with high water-use efficiency, and the second most important tropical fruit.
Is aloe vera a CAM plant?
Introduction. Aloe vera is a succulent CAM plant recently domesticated in Mexico. This plant is different from other CAM species because it is a native of the semitropical regions of South Africa (Cowling, 1982).
Is Bryophyllum a CAM plant?
Plant materials and growth conditions. Bryophyllum pinnatum (Linnaeus f.) Oken is a CAM plant native to Africa and has been cultivated widely in China.
Is cactus a C4 or CAM?
Some plants that are adapted to dry environments, such as cacti and pineapples, use the crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) pathway to minimize photorespiration.
Are succulents CAM plants?
Succulent plants store water in their leaves and stems and therefore can withstand long periods without water. This is described as Crassulacean Acid Metabolism (CAM). Crassulacean Acid Metabolism is a carbon fixing pathway that has evolved in some plants as an adaptation to arid conditions.
What is a C4 plant examples?
Examples of C4 plants include corn, sorghum, sugarcane, millet, and switchgrass. However, the C4 anatomical and biochemical adaptations require additional plant energy and resources than C3 photosynthesis, and so in cooler environments, C3 plants are typically more photosynthetically efficient and productive.
List of Families in the Angiosperms Having at Least One Cam Member: (From Simpson 2010)
In parentheses are the orders (ending ‘ales’) to which the respective families belong.
Examples of CAM Plants
Specific examples of CAM plants are the jade plant ( Crassula argentea ), Aeonium , Echeveria , Kalanchoe, and Sedum of the family Crassulaceae, pineapple ( Ananas comosus ), Spanish moss ( Tillandsia usneoides ), cacti, orchids, Agave, and wax plant ( Hoya carnosa, family Apocynaceae).
What is a CAM plant?
CAM plants are the plants, which fix carbon dioxide by CAM pathway or Crassulacean acid metabolism. It was first discovered in the plants of the Crassulaceae family. They are present in dry and arid environments. The CAM pathway is adapted to minimise water loss and photorespiration. Examples of CAM plants include cactus, pineapple, etc.
Why do aquatic plants have CAM pathways?
In aquatic plants, the CAM pathway occurs due to scarcity of CO 2. Carbon dioxide supply is limited due to slower diffusion in water. Aquatic CAM plants absorb CO 2 at night when there is less competition from other photosynthetic plants.
Why do CAM plants absorb carbon dioxide?
In CAM plants stomata are open at night and they absorb carbon dioxide at night to reduce water loss during the daytime. The process has the following steps: The first step in carbon dioxide fixation is the combination of CO 2 with PEP (phosphoenolpyruvate) to form 4 carbon oxaloacetate (same as C 4 plants) in the chloroplast of mesophyll cells.