Preliminary analytical procedures are used to identify material misstatements in financial statements. In this article, I explain how to create planning analytics and how to use them to identify potential misstatements. I also provide documentation tips.
What are some examples of analytical procedures?
- Obtain an understanding of the firm’s products or services.
- Obtain an understanding of the company’s revenue-recognition policies and related internal controls.
- Assess the risks of misstatements related to all relevant assertions then perform tests addressed to the related balance sheet accounts.
What are the types of analytical procedures?
Types of Analytical Procedures Trend analysis and ratios analysis are the two most commonly used analytical procedures in the audit. Auditors usually use trend and ratio analysis by comparing the amount or balances they obtain from client’s accounts or records to their expectations that were built by using the knowledge obtained in previous ...
What are substantive analytical procedures?
Substantive analytical procedures. It refers to the process of examining logical links between data, both financial and non-financial data. When the potential threat of material misstatement is low, and there are suitable control procedures in place, substantive analytical procedures are typically done. Auditors typically execute substantive analytical procedures by forming expectations and comparing them to the client’s experience.
What are analytical review procedures?
Analytical review procedures are one of two types of substantive audit procedures. They evaluate the relationship among financial data to determine if financial statement information is materially correct. Analytical review assumes these financial relationships are stable from period to period.
What are some examples of analytical procedures?
Examples of Analytical ProceduresCompare the days sales outstanding metric to the amount for prior years. ... Review the current ratio over several reporting periods. ... Compare the ending balances in the compensation expense account for several years. ... Examine a trend line of bad debt expenses.More items...•
What is the purpose of performing preliminary analytical procedures in audit planning?
Well-designed preliminary analytical review procedures are based on appropriate expectations of plausible relationships can be very effective in identifying risks of material misstatement (RMM) during the risk assessment process in audit planning.
What is a preliminary analytical review?
Preliminary analytical review (PAR) is a key procedure in the planning of an audit in helping to assess risk. This should not simply be a schedule that includes statements such as “trade debtors have increased because sales have increased” or “creditors have increased by 20% compared to last year – to be investigated”.
What are the key issues an auditor needs to follow to perform preliminary analytical procedures in auditing?
Performing analytical procedures generally follows this four-step process:Form an expectation. Here, the auditor develops an expectation of an account balance or financial relationship. ... Identify differences between expected and reported amounts. ... Investigate the reason. ... Evaluate differences.
Which of the following are two frequently used preliminary analytical procedures?
d. Two frequently used analytical procedures during risk assessment include trend analysis and ratio analysis.
What are the five major types of analytical procedures in auditing?
Those five audit procedures include Analytical review, inquiry, observation, inspection, and recalculation.
When Must analytical procedures be performed?
Analytical procedures are used for the following purposes: To assist the auditor in planning the nature, timing, and extent of other auditing procedures. As a substantive test to obtain evidential matter about particular assertions related to account balances or classes of transactions.
What is the purpose of analytical procedures?
The purpose of analytical procedures is to assist in planning the nature, timing and extend of other audit procedures. Next, it will be also applied as substantive procedures when their use is more effective or efficient than tests of details.
In which stages are analytical procedures required?
In which stages are analytical procedures required? Analytical procedures are required at the planning and overall review stages of the engagement.
What is analytical procedure?
Analytical procedures consist of ‘evaluations of financial information through analysis of plausible relationships among both financial and non-financial data’. They also encompass ‘such investigation as is necessary of identified fluctuations or relationships that are inconsistent with other relevant information or that differ from expected values by a significant amount’ (ISA 520). A basic premise underlying the application of analytical procedures is that plausible relationships among data may reasonably be expected to exist and continue in the absence of conditions to the contrary.
Why should auditors perform substantive analytical procedures before other substantive tests?
To derive the most benefit from substantive analytical procedures, the auditor should perform substantive analytical procedures before other substantive tests because results of substantive analytical procedures often impact the nature and extent of detailed testing.
Is there a correlation between the predictability of the data and the quality of the expectation derived from the data
Generally, the more precise an expectation is for an analytical procedure, the greater will be the potential reliability of that procedure.
1. Efficiency ratio analysis
One type of ratio analysis involves comparing line items on a financial statement to assess them for concerns such as liquidity, profitability and efficiency. Auditors calculate ratios and map them over an extended period.
2. Industry comparison ratio analysis
Auditors also use another type of ratio analysis, called industry comparison, to examine these ratios. This process involves the calculation of the same ratios for companies in the same industry to ensure their client's values are similar or higher than other companies.
4. Revenue and cost trend analysis
Auditors can use trend analysis using revenue and cost analysis. They use this process internally to create a trend line that reveals whether the company's revenue and costs have remained consistent. Depending on the distribution of the data points, auditors can identify potential problems and help their clients resolve them.
5. Investment trend analysis
The other type of trend analysis, called investment analysis, is more a part of investment strategy than an auditing method, but it can still affect a company's financial decisions. Investment analysis tracks the company's stock prices to see if investors can determine a cause for increases and decreases in the cost.
6. Reasonableness test
Auditors conduct reasonableness tests to confirm the validity of a company's transactions, balances and other financial events. They determine reasonableness based on the information provided on two or more sources of data. If the auditor notices possible inaccuracies, they address them with the client.
7. Regression analysis
Auditors use regression analysis to determine how two sets of variables relate to each other. This type of analysis requires the dependence of one variable on the other. Using this, auditors can determine how one variable affects the other over an established time period.
What is analytical procedure?
Analytical procedures are the processes of evaluating financial information through trend, ratio or reasonableness of data in relation to other financial and non-financial data. In this case, auditors perform data analysis to examine whether it is consistent with other relevant information and whether the fluctuation is within their ...
What is the purpose of analytical procedures in audit?
Auditors are required to perform analytical procedures at the planning stage of audit and at the completion stage of audit to perform an overall review of the financial statements before issuing the audit report.
Why do auditors use analytical procedures?
Analytical Procedures at planning stage. Auditors need to use analytical procedures as risk assessment procedures at the planning stage to obtain an understanding of the client and its business environment.
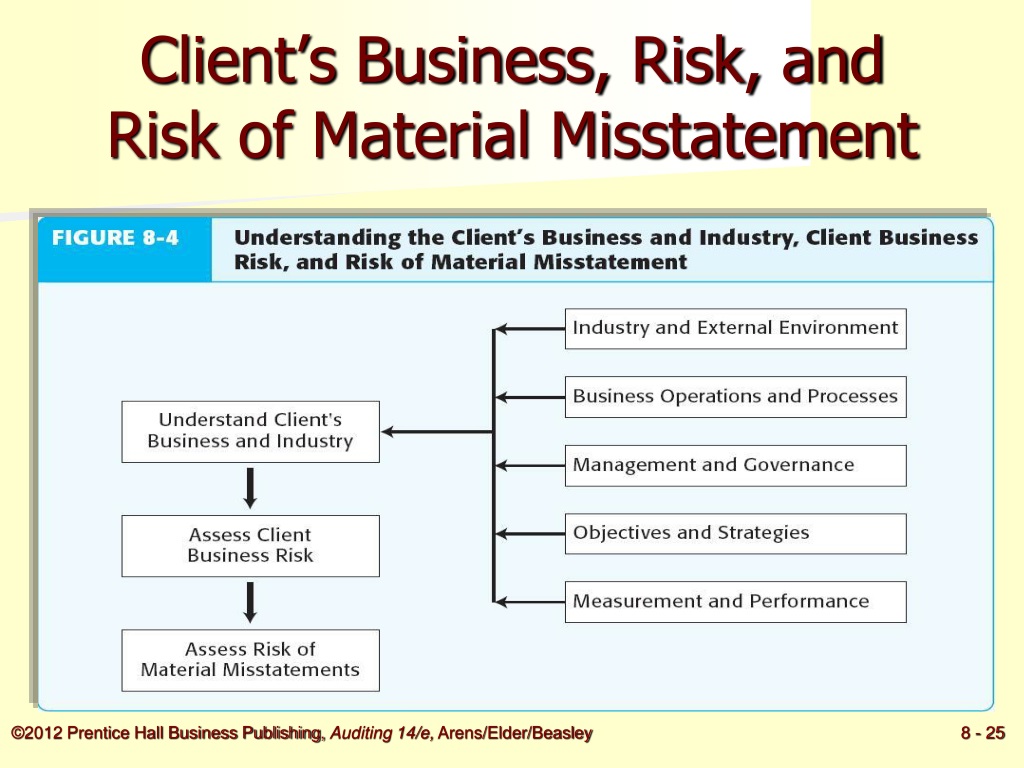
Definition of Analytical Procedures
Purposes of Analytical Procedures
- Analytical procedures are used throughout the audit process and are conducted for three primary purposes: 1. Preliminary analytical review – risk assessment (required by ISA 315) Preliminary analytical reviews are performed to obtain an understanding of the business and its environment (eg financial performance relative to prior years and relevant ...
Use of Substantive Analytical Procedures
- One of the objectives of ISA 520 is that relevant and reliable audit evidence is obtained when using substantive analytical procedures. The primary purpose of substantive analytical procedures is to obtain assurance, in combination with other audit testing (such as tests of controls and substantive tests of details), with respect to financial statement assertions for one …
Key Factors Affecting The Precision of Analytical Procedures
- There are four key factors that affect the precision of analytical procedures: 1 Disaggregation The more detailed the level at which analytical procedures are performed, the greater the potential precision of the procedures. Analytical procedures performed at a high level may mask significant, but offsetting, differences that are more likely to come to the auditor’s attention whe…