The wave front expanding out from an explosion is possibly the most dynamic example of a compressional wave. And a pulse of compressed air can transfer a LOT of energy. Vibrations in gases. Oscillations in spring. Sound waves. Internal water waves. Seismic primary wave.
What is an example of a compression wave?
03/06/2020 · The wave front expanding out from an explosion is possibly the most dynamic example of a compressional wave. And a pulse of compressed air can transfer a LOT of energy. Few examples of Compressible waves are : Vibrations in gases. Oscillations in spring. Sound waves. Internal water waves. Seismic primary wave.
What is compression and rarefaction in longitudinal waves?
15/04/2020 · One example of a compressional wave is a sound wave – which travels through air, an elastic medium, with the help of pressure. The speed with which a sound wave travels through air depends on the characteristics of the air. Another example of a compressional wave is seismic P-waves, or primary waves – these are created during an earthquake. These fast waves travel …
What is an example of a mechanical longitudinal wave?
19/01/2022 · Some examples of compressional waves include sound and P-waves, which are from earthquakes.
Which of the following is an example of sound waves in longitudinal?
What are some examples of compressional waves?
A compressional wave is made up of compressions and rarefactions that flow through the medium of the wave. A wavelength is the distance from one compression to another compression, or rarefaction to another rarefaction. Some examples of compressional waves include sound and P-waves, which are from earthquakes.19-Jan-2022
What are 2 examples of longitudinal compressional waves?
This type of motion in which particles move along the direction of the wave back and forth is a longitudinal motion....7 Real Life Examples Of Longitudinal WavesSpeaking on the mic. ... Clapping. ... Vibrating Drumheads. ... Tsunami Waves. ... Earthquake (Seismic-P wave) ... Vibration in Window Panels after a Thunder.More items...
Which of the following is compressional wave?
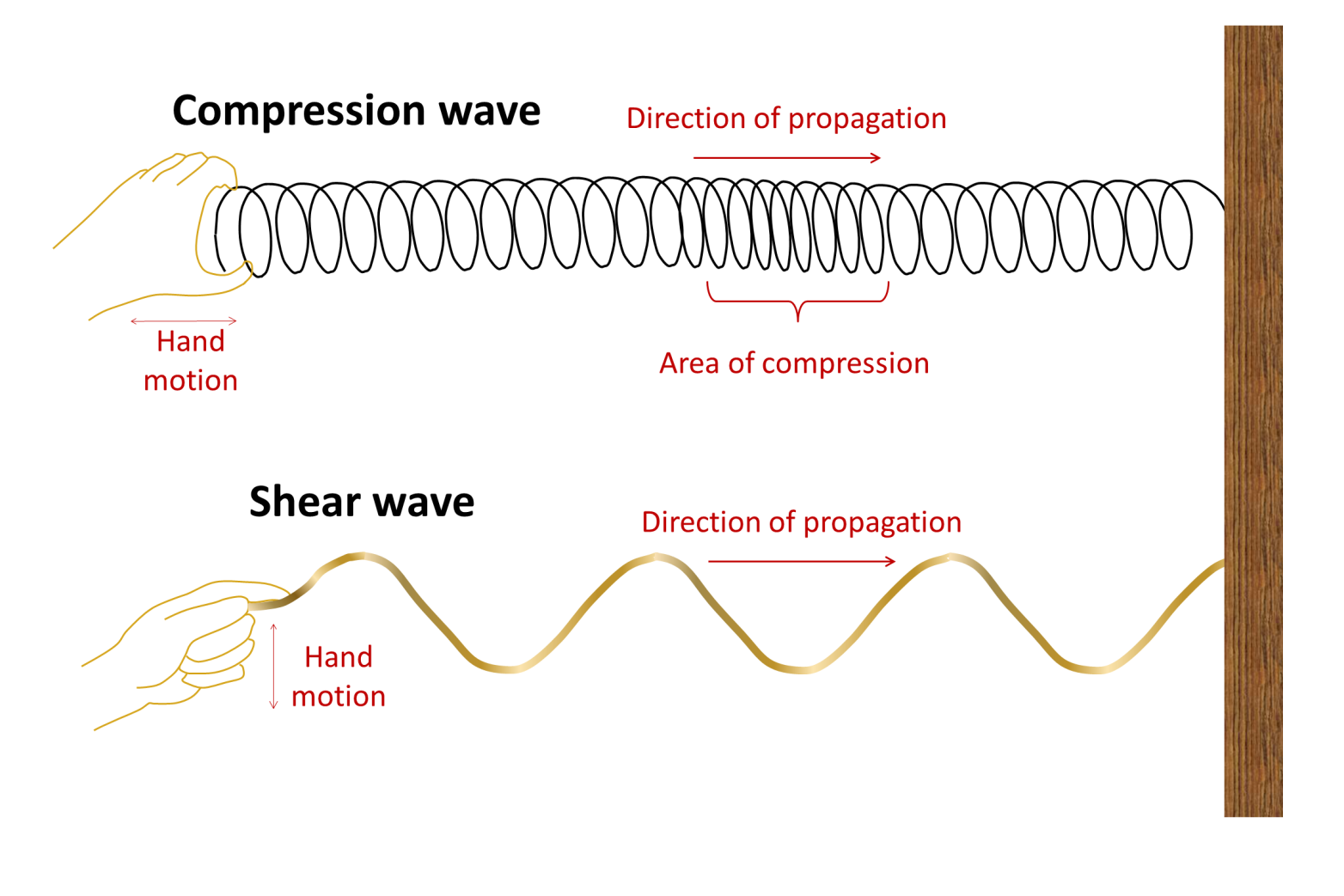
longitudinal wavesCompressional waves are also known as a longitudinal waves because of the way in which they travel through a medium. Compressions and rarefactions occur in the direction of travel, which is often visualized as the snapping of a slinky (see figure below).05-Jan-2017
What are the two types of compressional waves?
There are two basic types of wave motion for mechanical waves: longitudinal waves and transverse waves.
What are 10 examples of longitudinal waves?
Examples of Longitudinal WavesSound waves in air.The primary waves of an earthquake.Ultrasound.The vibration in a spring.The fluctuations in a gas.The tsunami waves.
What are 3 examples of a longitudinal wave?
Examples of longitudinal waves include:sound waves.ultrasound waves.seismic P-waves.
What is the most common example of a compressional wave?
A simple example of such waves is compressions moving along a slinky. One can generate a longitudinal wave by pushing and pulling the slinky horizontally. When traveling through a medium, these waves create compression and rarefaction. Compressions are high-pressure regions where wave particles are close together.12-Sept-2020
Is a shock wave a compression wave?
A compression wave is a wave in which the pressure increases gradually over some distance, whereas for a shock wave, the pressure jumps essentially at at once at the same place.
What is wave compression?
A compression is a region in a longitudinal wave where the particles are closest together. ... The region where the medium is compressed is known as a compression and the region where the medium is spread out is known as a rarefaction.
What is the difference between a compressional wave and a transverse wave?
A longitudinal wave is a wave that moves in the direction that it was started. It has a compression (increased intensity) of the medium particles and a rarefaction (a reduction of intensity). ... A transverse wave is wave that travels perpendicular or at right angles to the direction it was started.
What is compressional wave velocity?
Compressional wave velocity is a measure of the velocity with which sound waves pass through soil and rock strata. It varies with porosity, lithology, degree of fracturing and bulk density of the earth material.31-May-2019
What is meant by compressions and rarefactions?
compressions are regions of high pressure due to particles being close together. rarefactions are regions of low pressure due to particles being spread further apart.
How do compressional waves move?
Compressional waves move longitudinally. The motion is in the same, or parallel direction as that of the flow of energy of the wave.
What are compression and transverse waves?
A compression wave is a where the movement of the medium, or the vibration/disturbance within the medium, is in the same, or parallel, direction as...
What causes compression waves?
Compression waves are caused by a disturbance or a vibration in a medium. Disturbances could include a stick hitting the head of a drum or a vibrat...
What are 3 examples of longitudinal waves?
Three examples of longitudinal waves include sound waves, ultrasound and seismic P-waves. Ultrasound waves are used in many medical imaging techniq...
What are some examples of compressional waves?
What Is an Example of a Compressional Wave? An example of a mechanical longitudinal wave, or a compressional wave, is a sound wave. Another example is primary waves of an earthquake. Both travel through their respective medium, either air and Earth, while the particles constituting these mediums move in the direction parallel to the wave.
Do particles move along with a wave?
The particles of which that matter consists, however, do not move along with the wave. They are displaced in the direction parallel to that in which the wave propagates. To visualize a compressional wave in a nonwave example, picture a slinky toy.