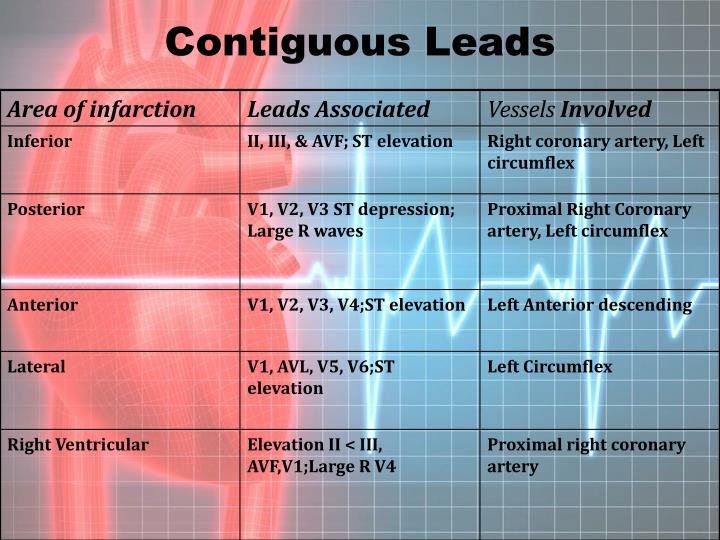
What are contiguous leads on ECG?
| Leads with ST segment elevations | Affected myocardial area | Occluded coronary artery (cuprit) |
| V1–V2 | Septal | Proximal LAD. |
| V3–V4 | Anterior | LAD. |
| V5–V6 | Apical | Distal LAD, LCx or RCA. |
| I, aVL | Lateral | LCx. |
What are contiguous leads in cardiology?
4 rows · Jun 20, 2020 · Contiguous leads are next to one another anatomically speaking. They view the same general area ...
How many leads are there in ECG?
Jan 27, 2020 · What are contiguous leads in ECG? Contiguous leads are next to one another anatomically speaking. They view the same general area of the heart (specifically the left ventricle). For example, these states in the upper-midwest are contiguous, because they are all touching and in the same region of the country. Click to see full answer.
What is an example of a contiguous lead?
May 26, 2019 · You should know what contiguous leads are before attempting to interpret a 12-Lead ECG.
What is a 12 lead EKG?
Contiguous leads Picture EKG Lead Lateral I, aVL, V5, V6 Inferior II, III, aVF Septal V1, V2 Anterior V3, V4 Inverted waves aVR Axis Deviation Look at lead I and aVF I- If deflects up its left aVF- If deflects up its down Normal Axis Deviation I- Up aVF- Up Left Axis Deviation I- Up aVF- Down Right Axis Deviation I- Down aVF- Up
Are leads II and aVL contiguous?
1:259:44What are contiguous leads? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo all of those leads are considered contiguous to each other it leads one AVL will be 5 and b6.MoreSo all of those leads are considered contiguous to each other it leads one AVL will be 5 and b6.
What are the two types of ECG leads?
Electrocardiogram LeadsLimb Leads (Bipolar)Augmented Limb Leads (Unipolar)Chest Leads (Unipolar)
What are reciprocal ECG leads?
Reciprocal change is a very important ECG finding, not only supporting the diagnosis of STEMI but also indicating a high-risk patient. Reciprocal change is defined as ST-segment depression occurring on an ECG which also has ST-segment elevation in at least 2 leads in a single anatomic segment.Jun 20, 2014
Why multiple leads are used in ECG?
To a certain extent, the more points that are recorded, the more accurate the representation of the heart's electrical activity. The importance of multiple leads is illustrated in the diagnosis of myocardial infarction (MI).
What is aVR AVL aVF in ECG?
aVR means augmented Vector Right; the positive electrode is on the right shoulder. aVL means augmented Vector Left; the positive electrode is on the left shoulder. aVF means augmented Vector Foot; the positive electrode is on the foot.
What is aVR lead?
In pericarditis, lead aVR is most often the only lead which shows reciprocal ST depression where as in Acute Infarction, usually a group of leads shows reciprocal depression. In the presence of persistent ST elevation in anterior chest leads, the R in aVR is suggestive of left ventricular aneurysm (Goldburger's sign).
Are V2 and V3 contiguous leads?
For example, leads V3 and V4 are contiguous; V1 and V2 are also contiguous; aVL and I are also contiguous; V3 and V5 are not contiguous, because lead V4 is placed between these leads.
Which leads are anterior?
The arrangement of the leads produces the following anatomical relationships: leads II, III, and aVF view the inferior surface of the heart; leads V1 to V4 view the anterior surface; leads I, aVL, V5, and V6 view the lateral surface; and leads V1 and aVR look through the right atrium directly into the cavity of the ...
Why is ST elevation in MI?
ST-segment elevation MI (STEMI) is most commonly caused by acute rupture of atherosclerotic plaque and thrombosis of the involved coronary arteries. For this diagnosis to be made, the ECG must show ST-segment elevation of at least 0.1 mV (1 mm) in two consecutive leads.
What are frontal plane leads?
Six leads view the heart in the frontal plane (I, II, III, aVR, aVL, aVF) and six leads (V1 through V6) view the heart in the horizontal plane. The three standard leads (I, II, III) are bipolar leads; each lead records the potential difference between two limbs (Fig. 8-2).
Why it is called 12 lead ECG?
The 12-lead ECG displays, as the name implies, 12 leads which are derived by means of 10 electrodes. Three of these leads are easy to understand, since they are simply the result of comparing electrical potentials recorded by two electrodes; one electrode is exploring, while the other is a reference electrode.
What is unipolar limb leads?
In addition to the three bipolar limb leads, there are three augmented unipolar limb leads. These are termed unipolar leads because there is a single positive electrode that is referenced against a combination of the other limb electrodes.
What is an ECG lead?
An ECG lead is a graphical description of the electrical activity of the heart and it is created by analysing several electrodes.
How many electrodes are needed for a 12 lead ECG?
In general, lead systems with less than 10 electrodes can still be used to compute the all standard leads in the 12-lead ECG. Such calculated ECG waveforms are very similar to the original 12-lead ECG waveforms, with some minor differences that may affect amplitudes and intervals.
What is Mason Likar's lead system?
Mason-Likar’s lead system simply implies that the limb electrodes have been relocated to the trunk. This is used in all types of ECG monitoring (arrhythmias, ischemia etc). It is also used for exercise stress testing (as it avoids muscle disturbances from the limbs).
Where are the left and right arm electrodes located?
The left and right arm electrodes are moved to the trunk, 2 cm beneath the clavicle, in the infraclavicular fossa ( Figure 24 A ). The left leg electrode is placed in the anterior axillary line between the iliac crest and the last rib. The right leg electrode can be placed above the iliac crest on the right side. Placement of the chest leads is not changed.
Can 12 lead ECG be missed?
There are conditions that may be missed when utili zing the 12-lead ECG. Fortunately, researchers have validated the use of additional leads to improve diagnostics of such conditions. These are now discussed.
What is the most used ECG system?
Numerous ECG lead systems and constellations of leads have been tested but the standard 12-lead ECG is still the most used and the most important lead system to master. The 12-lead ECG offers outstanding possibilities to diagnose abnormalities.
Is EASI a good ECG?
EASI provides a good approximation to the conventional 12-lead ECG. However, EASI may also generate ECG waveforms with amplitudes and durations that differ from the 12-lead ECG. This lead system is generated by using electrodes I, E and A from Frank’s leads, and by adding electrode S on the manubrium.
fiznat
We had a bit of a disagreement in medic class today about contiguous leads, I thought some of you folks here might be able to help out.
JCicco345
I just took my cardiology portion last semester and we learner that V2, V3 are contiguous leads as are V4, V5. For the reason you said. V2 and V3 would be anteroseptal, and V4 and V5 would be anterolateral. Atleast thats the way i remember it. I could be wrong.