How are the male urethra different than female's?
Key Differences
- Male urethra is longer than female urethra in length
- Both are important parts of body useful for excretion.
- In females, the path which urine takes getting from the bladder to the external world is more direct.
- In males, the path which urine takes getting from the bladder to the external world is more curving.
Why is the male urethra larger than the female?
Why is the female urethra shorter than male? Glands within the urethra produce mucus. This mucus helps protect the epithelium against damage from corrosive urine. The female urethra is significantly shorter than the male urethra. This means that females often have a higher risk of developing urinary tract infections (UTIs).
What are differences between male and female urethra?
Male Urinary System vs Female Urinary System
- The male urinary system shares a common pathway with the male reproductive system, the penis. ...
- The major difference between the male and female urinary system is the urethra. ...
- Aside from function, there is also a difference in length. ...
- Since the male urethra is longer, it passes through more organs and muscles. ...
Is female urethra longer than the male?
The main difference between Male Urethra and Female Urethra is in length. In males urethra is 8 inches long, and in females urethra is only 2 inches long. Male urethra has differentiated into four parts while female urethra has no differentiation. Male Urethra vs. Female Urethra. Word “urethra” has derived from the Greek language.
What is the diameter of the male and female urethra?
Diameter. Male Urethra: The diameter of the male urethra is 8-9 mm. Female Urethra: The diameter of the female urethra is 6 mm.Dec 10, 2017
How wide is the female urethra?
about 6 mmIts diameter when undilated is about 6 mm. It perforates the fasciæ of the urogenital diaphragm, and its external orifice is situated directly in front of the vaginal opening and about 2.5 cm.
Is a female urethra bigger than a males?
The female urethra is much shorter than that of the male, being only 4 cm (1.5 inches) long. It begins at the bladder neck and opens to the outside just after passing through the urethral sphincter.
How does the female urethra differ from the male?
4. The Female Urethra Is Shorter Than the Male Urethra. Urine produced in the kidneys passes through the ureters, collects in the bladder, and is then excreted through the urethra. In females, the urethra is narrow and about 4 cm long, significantly shorter than in males.
How wide is male urethra?
The male urethra is 8 - 9 mm in diameter. The external meatus is 8 mm in size, but normally appears as a vertical slit. The portion of the urethra immediately behind it, in the glans, is 10 — 11 mm in diameter.
How far can you stretch your urethra?
According to him, the adult male external urethral meatal size on an average is 0.35 inches. as a vertical slit, if converted into the French scale, becomes 29.6 Fr. In our study, the maximum stretchable male external urethral meatus size on an average is 28.49 Fr.Jul 4, 2012
What is a woman's pee hole called?
urethral openingThere are two openings in the vulva — the vaginal opening and the opening to the urethra (the hole you pee out of). The urethral opening is the tiny hole that you pee out of, located just below your clitoris.Oct 28, 2019
How big is a male pee hole?
In the human male, the urethra is on average 18 to 20 centimetres (7.1 to 7.9 in) long and opens at the end of the external urethral meatus. This is the intramural part of the urethra surrounded by the internal urethral sphincter and varies between 0.5 and 1.5 cm in length depending on the fullness of the bladder.
How long can a girl hold their pee?
A healthy bladder can hold about 2 cups of urine before it's considered full. It takes your body 9 to 10 hours to produce 2 cups of urine....Pee table.AgeAverage bladder sizeTime to fill bladderChild (4–12 years)7–14 ounces2–4 hoursAdult16–24 ounces8–9 hours (2 ounces per hour)2 more rows•Jul 30, 2019
How do you know if you have a narrow urethra?
Incomplete bladder emptying. Spraying of the urine stream. Difficulty, straining or pain when urinating. Increased urge to urinate or more-frequent urination.Oct 20, 2020
What is the difference between a male and female urethra?
The male urethra is larger in length than female urethra. Another difference would be th path the urine takes getting from the bladder to the external world. In males the path is more curving and in females the path is more direct. This curved path makes catheterization of males more difficult. Due to the short length of the urethra in females, infection can be a problem.
When does the female urethra develop?
Female urethra develops in the 12 th gestational week. The female urethra is relatively a simple tubular structure that has the only purpose of urination. It is a short organ without complex investing structure. It is a richly vascular spongy cylinder and is designed to provide continence.
What is the fourth part of the penis?
Its fourth part is spongy urethra which runs along the length of the penis on its ventral surface. It is almost 15 to 16 cm in length and travels through the corpus spongiosun. The duct from the urethral gland enters here. The opening parts of the bulbourethral glands are also located here.
What is the third part of the urethra?
The third part of the male urethra is membranous urethra which is a small portion passing through the external urethral sphincter and almost 1 to 2 cm in length. This is the smallest in diameter part of the urethra. It is present in the deep perineal pouch. The bulbourethral glands and found posterior to this region but open in the spongy urethra.
What is the purpose of the urethra?
Males use their urethra for two purposes, urination and ejaculation . The external sphincter of male urethra is a striated muscle that allows voluntary control over urination and this additional internal urethral sphincter muscle is present only in males. Semen travels through the urethra during intercourse in males.
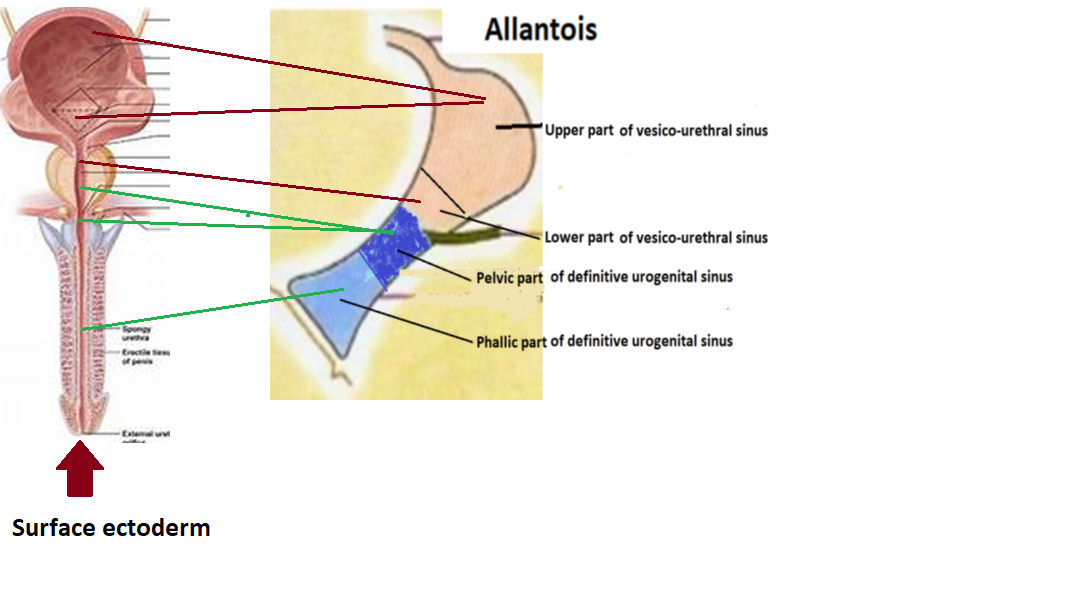
What part of the urethra is the paramesonephretic tubercle?
It has developed from the endoderm and the splanchnic mesoderm of the urogenital sinus. The paramesonephretic tubercle divides the urogenital sinus into pelvic which will later become a vesicourethral unit and a phallic portion which later becomes a vagina. Female urethra develops in the 12 th gestational week.
What is the first part of the bladder?
First part is pre-prostatic urethra which is intramural part of this organ and about 0.5 to 1.5 cm in length depending on the fullness of the bladder. Its second part is prostatic urethra which crosses through the prostate gland.
What is the difference between a male and female urethra?
The core difference between male and female urethra is that the male urethra belongs to both the reproductive and urinary system while the female urethra belongs to the urinary system alone.
What is the length of a male urine urethra?
Female Urethra. Meaning. It is a canal through which urine and semen pass through in males. It is the canal through which urine passes through in females. Length. Measure about 20 cm. Measure about 4 cm.
Why is the female urethra called the urinary system?
The female urethra is termed as a urinary system due to its core function. The short size of the female urethra makes it be highly susceptible to bacterial infection. The bacterial infection can spread to the bladder and it is recommended to be cautious.
What are the parts of the male urethra?
The main parts of the male urethra are the pre-prostatic urethra, prostatic urethra, membranous urethra, and penile urethra. Penile urethra runs through the penis while prostatic urethra runs through the prostate gland. The pre-prostatic urethra runs through the front of the prostate.
What is the function of the urethra?
Both the male and female reproductive systems have urethra. The core function of urethra is to pass urine from the bladder to the external opening in the perineum. However, male urethra and female urethra tend to have some slight differences.
What are the similarities between a male and female urinary system?
Similarities between Male and Female Urethra. Both are the final part of the urinary system. Both originate from the bladder. Both are the passage of urine out of the body. Both have transitional epithelium in the lining.
Which part of the urinary system allows the passage of urine and semen?
The male urethra is the canal that allows movement of both urine and semen while female urethra allows passage of urine alone. The male urethra is part of both reproductive and urinary system while female urethra is part of the urinary system. The male urethra is longer than female urethra.
How long is the urethra?
In the human male, the urethra is on average 18 to 20 centimetres (7.1 to 7.9 in) long and opens at the end of the external urethral meatus. The urethra is divided into four parts in men, named after the location: Region. Description. Epithelium.
Where does the urethra come from?
The cells lining the urethra (the epithelium) come from endoderm, whereas the connective tissue and smooth muscle parts are derived from mesoderm. After the third month, urethra also contributes to the development of associated structures depending on the biological sex of the embryo.
What is the proximal third of the urethra lined with?
The proximal two-thirds of the urethra is lined by transitional epithelial cells, while the distal third is lined by stratified squamous epithelial cells. Between the superior and inferior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm, the female urethra is surrounded by the urethral sphincter .
How does the urethra re-establish muscle tone?
Following this, the urethra re-establishes muscle tone by contracting the smooth muscle layer, and the bladder returns to a relaxed, quiescent state. Urethral smooth muscle cells are mechanically coupled to each other to coordinate mechanical force and electrical signaling in an organized, unitary fashion.
What is the clinical significance of a micrograph of urethral cancer?
Clinical significance. Micrograph of urethral cancer ( urothelial cell carcinoma ), a rare problem of the urethra. Infection of the urethra is urethritis, which often causes purulent urethral discharge.
What is the function of the urethra?
The urethra transports urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. This image shows (a) a female urethra and (b) a male urethra. The urethra (from Greek οὐρήθρα – ourḗthrā) is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males.
Where does the urethra go in a marsupial?
In human females and other primates, the urethra connects to the urinary meatus above the vagina, whereas in marsupials, the female's urethra empties into the urogenital sinus. Females use their urethra only for urinating, but males use their urethra for both urination and ejaculation.
Why is the female urethra shorter than the male?
The female urethra is significantly shorter than the male urethra. This means that females often have a higher risk of developing urinary tract infections (UTIs).
What is the urethra?
The urethra transports urine that’s stored in the bladder out of the body. The urethra is closely linked with the reproductive organs, so the anatomy of the urethra is different between males and females.
What is a benign mass in the urethra?
A urethral caruncle is a benign mass found in the urethra, usually occurring after menopause. It usually doesn’t cause any symptoms. However, some people might notice pain when urinating or bleeding from the urethra.
Why do males have stricture?
This is known as urethral stricture. Males are more likely to develop urethral stricture because of their longer urethras, but it can affect females as well.
What are the symptoms of urethral syndrome?
The main symptom of urethral syndrome is chronic pain in the pelvis and urinary tract. In some cases, the pain is constant. In others, certain things, including exercise, allergies, or exposure to irritants, can trigger it. Other common symptoms include an increased need to urinate and pain while urinating.
Where is the urethra located?
Anatomy and function of the female urethra. The female urethra begins at the bottom of the bladder, known as the neck. It extends downward, through the muscular area of the pelvic floor. Before reaching the urethral opening, urine passes through the urethral sphincter. This is a muscular structure in the urethra that helps hold urine inside ...
Can chlamydia cause urethritis?
chlamydia. herpes simplex virus. If a surgery or catheter placement is causing urethritis, it usually resolves on its own over time. However, urethritis due to an infection requires treatment with antibiotics or antiviral medication.
Urethra
James C. Brown, in Textbook of Veterinary Diagnostic Radiology (Seventh Edition), 2018
Urethra
Embryologically the female urethra is formed from an elongation between the bladder and the urogenital sinus. The urethra is positioned between the pelvic floor and the vagina and it empties into a groove on the ventral floor of the vestibule at the external urethral orifice.
Urethra
Harold C. SchottII, J. Brett Woodie, in Equine Surgery (Fourth Edition), 2012
The Urinary System
The urethra in the male is about 20 cm long ( Fig. 13.11 ). It arises from the trigone of the bladder and consists of three segments: the prostatic, membranous, and penile urethra. Within the short (3–4 cm) prostatic segment, the male urethra receives the ejaculatory ducts as well as many small ducts leading form the prostate gland.
Organ-Specific Toxicologic Pathology
Samuel M. Cohen, ... Shoji Fukushima, in Handbook of Toxicologic Pathology (Second Edition), 2002
Systems Toxicologic Pathology
Samuel M. Cohen, in Haschek and Rousseaux's Handbook of Toxicologic Pathology (Third Edition), 2013
Normative Histology of Organs
The urethra connects the urinary bladder to the body surface. In males the urethra is divided into the membraneous and the penile parts. The membranous urethra contains the colliculus seminalis and receives there the openings of vas deferens, prostate, seminal vesicles and ampullary glands.
Overview
The urethra (from Greek οὐρήθρα – ourḗthrā) is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males. In human females and other primates, the urethra connects to the urinary meatus above the vagina, whereas in marsupials, the female's urethra empties into the urogenital sinus.
Structure
The urethra is a fibrous and muscular tube which connects the urinary bladder to the external urethral meatus. Its length differs between the sexes, because it passes through the penis in males.
In the human male, the urethra is on average 18 to 20 centimeters (7.1 to 7.9 inches) long and opens at the end of the external urethral meatus.
Development
In the developing embryo, at the hind end lies a cloaca. This, over the fourth to the seventh week, divides into a urogenital sinus and the beginnings of the anal canal, with a wall forming between these two inpouchings called the urorectal septum. The urogenital sinus divides into three parts, with the middle part forming the urethra; the upper part is largest and becomes the urinary bladder, and the lower part then changes depending on the biological sex of the embryo. The cells lining t…
Function
The urethra is the vessel through which urine passes after leaving the bladder. During urination, the smooth muscle lining the urethra relaxes in concert with bladder contraction(s) to forcefully expel the urine in a pressurized stream. Following this, the urethra re-establishes muscle tone by contracting the smooth muscle layer, and the bladder returns to a relaxed, quiescent state. Urethral smooth muscle cells are mechanically coupled to each other to coordinate mechanical …
Clinical significance
Infection of the urethra is urethritis, which often causes purulent urethral discharge. It is most often due to a sexually transmitted infection such as gonorrhoea or chlamydia, and less commonly due to other bacteria such as ureaplasma or mycoplasma; trichomonas vaginalis; or the viruses herpes simplex virus and adenovirus. Investigations such as a gram stain of the discharge migh…
History
The word "urethra" comes from the Ancient Greek stem "uro" relating to urination, with the structure described as early as the time of Hippocrates. Confusingly however, at the time it was called "ureter". Thereafter, terms "ureter" and "urethra" were variably used to refer to each other thereafter for more than a millennia. It was only in the 1550s that anatomists such as Bartolomeo Eustacchio and Jacques Dubois began to use the terms to specifically and consistently refer to w…
See also
• Perineal urethra
• Vulvovaginal health
• Urethral glands
• Urethral sponge
• Sexual stimulation: Urethral sounding and Urethral intercourse
External links
• Histology at KUMC epithel-epith07 "Male Urethra"