What enzymes are used in protein hydrolysis?
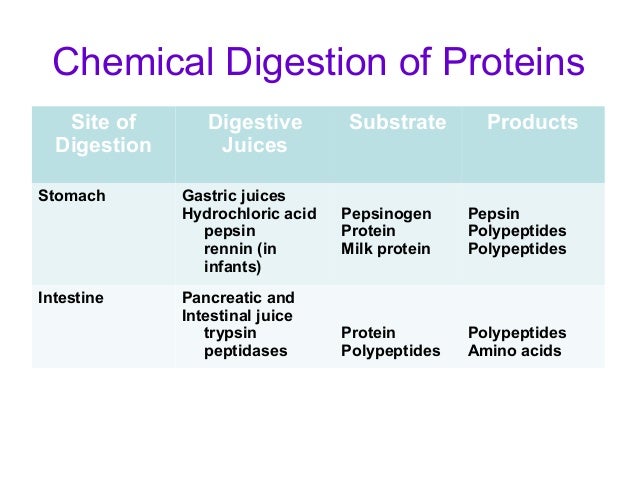
The proteolytic enzymes of the pancreas are responsible for the major portion of protein hydrolysis, which occurs within the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract. The pancreas secretes two types of peptidases. Trypsin, chymotrypsin, and elastase are endopeptidases that attack peptide bonds along the polypeptide chain to produce smaller peptides.
Which enzyme hydrolyzes starch in the stomach?
Carboxypeptidase Hydrolyzes starch, but is deactivated in the stomach Salivary amylase Brush-border enzyme that breaks down oligosaccharides
What is produced during the gastric phase of protein hydrolysis?
The gastric phase of protein hydrolysis involves the proteolytic action of pepsin, which is secreted by the chief cells of the stomach as an inactive precursor called pepsinogen. This zymogene is activated by the acidic pH in the stomach lumen and by the autocatalytic hydrolysis of the active form of pepsin.
What enzymes are used in digestion?
GI enzymes and Their Importance in Digestion 1 Ptyalin – Converts starch to simple soluble sugars 2 Amylase – Converts starch to soluble sugars 3 Betaine – Maintains cell fluid balance as osmolytes 4 Bromelain – Anti-inflammatory agent, tenderizes meat
What enzyme hydrolyzes proteins?
The hydrolysis of proteins can be achieved by a single enzyme (e.g., trypsin) or multiple enzymes (e.g., a mixture of proteases known as Pronase, pepsin and prolidase).
What hydrolyzes protein in the stomach?
The gastric phase of protein hydrolysis involves the proteolytic action of pepsin, which is secreted by the chief cells of the stomach as an inactive precursor called pepsinogen. This zymogene is activated by the acidic pH in the stomach lumen and by the autocatalytic hydrolysis of the active form of pepsin.
Does pepsin hydrolyze protein?
Pepsin is active in acidic pH like that in the gastric portion and can hydrolyze several proteins, except for mucins, spongins, conchiolin, keratin, or low molecular weight peptides (Sumner and Somers, 1947 apud Fange and Grove, 1979).
Which enzyme is used for hydrolyze the protein to amino acid?
Enzymes trypsin, pepsin and chymotrypsin hydrolyses proteins to α- amino acids. Pepsin and trypsin hydrolyzed proteins to produce a complex mixture of peptides called proteoses and peptones. Chymotrypsin cleaves peptide amide bonds and finally breaks proteins into amino acids which is easily absorbed by the body.
What hydrolyzes peptide bonds with pepsin?
Pepsinogen is an inactive form of pepsin; pepsin is the active form of the enzyme. Both enzymes catalyze the hydrolysis of peptide bonds. Chymotrypsin catalyzes the hydrolysis of peptide bonds following aromatic amino acids, while trypsin catalyzes the hydrolysis of peptide bonds following lysine and arginine.
What are the 3 types of enzymes that hydrolyse proteins?
Endopeptidases and exopeptidases are involved in the hydrolysis of proteins. Name the other type of enzyme required for the complete hydrolysis of proteins to amino acids. The other type of enzyme required is a dipeptidase.
Does trypsin break down protein?
Trypsin is a serine protease found in the digestive system of many vertebrates, where it hydrolyzes proteins at the carboxyl side of the amino acids lysine or arginine.
What is pepsin and trypsin?
Pepsin is an enzyme which acts only in acidic medium ,trypsine is an enzyme which acts in alkaline medium. pepsin is secreted by gastric juice, trypsin secreted by pancreatic juice. Pepsin is secreted in stomach, trypsin is secreted in small intestine.
What does the enzyme pepsin do?
An enzyme made in the stomach that breaks down proteins in food during digestion. Stomach acid changes a protein called pepsinogen into pepsin.
How are proteins hydrolyzed?
Protein hydrolysates are produced from purified protein sources by heating with acid or, preferably, addition of proteolytic enzymes, followed by purification procedures.
What is hydrolyzed protein made from?
Hydrolyzed vegetable protein (HVP) is produced by boiling foods such as soy, corn, or wheat in hydrochloric acid and then neutralizing the solution with sodium hydroxide. The acid breaks down the protein in vegetables into their component amino acids.
Which of the following is produced by hydrolysis of proteins?
Amino acids are produced on hydrolysis of proteins.
What causes hydrolysis of proteins?
Protein hydrolysis is carried out by chemical and enzymatic methods. Most of the enzymes used for protein hydrolysis are from animal sources (such as pancreatin and pepsin), plant sources (such as papain from papaya, ficin from fig, and bromelain from pineapple), and microbial sources (such as Alcalase).
What is hydrolyzed in digestion?
Chemical digestion, through a process called hydrolysis, uses water and digestive enzymes to break down the complex molecules. Digestive enzymes speed up the hydrolysis process, which is otherwise very slow.
How does hydrolysis break down proteins?
We can break the peptide bonds (amide links) joining the amino acid units together by using acidified water in an acid hydrolysis reaction. This disrupts the primary structure of the protein and the protein breaks down into smaller pieces, eventually resulting in many amino acids.
What is protein denaturation?
denaturation, in biology, process modifying the molecular structure of a protein. Denaturation involves the breaking of many of the weak linkages, or bonds (e.g., hydrogen bonds), within a protein molecule that are responsible for the highly ordered structure of the protein in its natural (native) state.
What is enzymatic hydrolysis?
New processes for production of oil based on enzymatic protein hydrolysis are being developed and applied in the industry. Enzymatic protein hydrolysis is based on the use of commercial proteases for proteolytical cleavage of peptide bonds, facilitating the degradation of fish tissue and release of oil. The advantages of using enzymatic hydrolysis compared to the wet rendering method could be a protein product with better biological, digestible, and functional properties. In addition, the use of lower cooking temperature (50–60 °C) compared to the wet rendering method (90–95 °C) can give an oil of higher quality (low oxidation status) and stability.
Which organ is responsible for the major portion of protein hydrolysis?
The proteolytic enzymes of the pancreas are responsible for the major portion of protein hydrolysis, which occurs within the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract. The pancreas secretes two types of peptidases.
What is the function of Ef-G?
Ef-G, an accessory protein, hydrolyses GTP to GDP in order to provide energy for the translocation of the ribosome. A second elongation factor (Ef-Tu) promotes binding of the aminoacyl-tRNA to the ribosomal A site, also with hydrolysis of GTP. The two elongation factors have overlapping binding sites on the ribosome.
What does salt do to proteins?
The addition of salt 13% w/v or higher results in a controlled protein hydrolysis that prevents putrefaction, prevents the development of food poisoning , such as botulism, and yields meaty savory amino acid–peptide sauces and pastes that provide very important condiments, particularly for those unable to afford much meat in their diets.
What is the simplest amino acid?
Glycine is the simplest amino acid and can be produced by protein hydrolysis. This sweet-tasting compound was first isolated from gelatin in 1820. This central nervous system inhibitory neurotransmitter is particularly important for its role in mediating atonia occurring during REM sleep.
What are the factors that influence hydrolysis?
Several factors can influence the hydrolysis process: substrate type and properties, enzyme type and properties, and processing conditions including temperature, pH, hydrolysis time, and amount of added water. These factors are important for product yield and quality and need to be controlled during processing.
What is the pH of gastric lipase?
Gastric lipase secreted by gastric mucosa begins to hydrolyze triglycerols, producing 1,2-diacylglycerols and fatty acids. The optimal pH of gastric lipase is about 4, but the enzyme is active up to pH 6 or 6.5.12 Several GI hormones, including gastrin, somatostatin, and ghrelin, are also produced by cells within the stomach.13.
What are the enzymes that help digest food?
Digestive enzymes help to breakdown polymeric macro-molecules into small building blocks, which are required by our body to maintain a healthy life. These enzymes are also present in the saliva, where they assist the first step of digestion. The enzymes are classified on the nature of substrates they work. Digestive enzymes are broadly classified into four groups. They are: 1 Proteolytic Enzyme: split proteins to amino acids 2 Lipolytic Enzyme: split fats to fatty acids and glycerol 3 Amylolytic Enzyme: split carbohydrate and starch to simple sugars 4 Nucleolytic Enzyme: split nucleic acids to nucleotides
What enzyme breaks down triglycerides?
Phospholipase- Hydrolyzes phospholipids into fatty acids. Trypsin- Converts proteins to basic amino acids. Steapsin- Breakdown of triglycerides to glycerol and fatty acids.
Why are enzymes important for digestion?
Digestive enzymes play a key role in regulating and maintaining the functions of the digestive system properly.
What enzyme converts maltose to glucose?
Maltase- Converts maltose to glucose. Lactase- Converts lactose to glucose and galactose. Isomaltase- Converts maltose to isomaltose. After knowing the types of digestive enzymes and their respective functions, I hope you understand how intricately the human digestive system works.
What is the main digestive gland of the body?
Pancreas is the main digestive gland of our body. The digestive enzymes of the pancreas breakdown carbohydrates and starch molecules to simple sugars. They also secrete a group of enzymes which help in degradation of nucleic acids. It functions both as an endocrine and exocrine gland.
What is the enzyme that kills bacteria and germs?
The enzymes released by the stomach are known as gastric enzymes. Stomach secretes hydrochloric acid which kills bacteria and germs and provides an acid environment for proper enzymatic activity of protease enzymes.
Where does enzyme digestion begin?
Enzymatic digestion begins in the mouth and extends to the intestine, where it gets converted to simpler particles and are then excreted by our body. These digestive enzymes act as catalysts for breakdown of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
What is partial protein hydrolysis?
Partial protein hydrolysis to enhance their emulsifying properties which had been used for milk and wheat proteins were applied for soy proteins. Acid modified glycinins present different degrees of deamidation, surface hydrophobicity, and molar mass. A slight enhancement of emulsifying stability at moderated deamidation degrees was observed (Wagner and Gueguen, 1999 ). Another study found that pH-shifting treatment, by holding SPI in acidic (pH 1.5–3.5) and alkaline (pH 10.0–12.0) pH for different times, followed by refolding (1 h at pH 7.0) resulted in a substantial structural modifications, which consequently led to markedly improved EAI and ES of SPI ( Jiang et al., 2009 ). Chen et al. (2013) reported that emulsions stabilized by moderately oxidized SPI had a smaller droplet size and better thermal stability in comparison with the control and over-oxidized SPI. Matemu et al. (2011) found that the EAI and ES of 7S and 11S were significantly improved upon acylation with saturated fatty acids. Water binding capacity and surface hydrophobicity of 7S were significantly improved by acylation while no changes were observed in the acylated 11S. In addition, when 90% of ε-amino groups in soy protein were succinylated, both emulsifying activity and emulsifying stability were improved by 30% and 21%, respectively ( Franzen and Kinsella, 1976 ). Achouri et al. (2010) prepared glycated CaCl 2 -11S using κ-carrageenan, and observed the improvement of EAI and foaming properties at a moderate degree of glycation.
What are the enzymes used in shellfish hydrolysis?
For the hydrolysis of shellfish proteins, enzymes from microbial sources such as Alcalase, Neutrase, Protamex, and Flavourzyme could be used.
What are the substrates for hydrolysate production?
Different protein substrates have been considered for hydrolysate production; however, those obtained from fish and by-products (e.g., myofibrillar protein collagen, gelatin) have gained the attention of the food, nutraceutical, and pharmaceutical industries due to their special characteristics.
What is the process of hydrolysis?
Protein hydrolysis is carried out by chemical and enzymatic methods. Most of the enzymes used for protein hydrolysis are from animal sources (such as pancreatin and pepsin), plant sources (such as papain from papaya, ficin from fig, and bromelain from pineapple), and microbial sources (such as Alcalase).
What are proteases from?
Proteases from microbial sources offer a wide variety of enzyme activities. Proteases from bacterial, algal, fungal, and yeast sources are produced on a large scale and usually only require simple purification steps, which can be used for an industrial application such as the production of peptone.
When was hydrolysis first used?
Hydrolysis. Most of the initial work on fish protein hydrolysis was performed in the 1960s. Emphasis was on fish protein concentrate as an inexpensive nutritious protein source for developing countries (Kristinsson and Rasco, 2000a ).
Which protein cleaves arginine, lysine, and phenylalanine?
Papain has a broad specificity, cleaving bonds at phenylalanine, arginine, and lysine. Pancreatin cleaves at tryptophan, arginine, tyrosine, leucine, phenylalanine, and lysine bonds. Proteins incubated with microbes lead to hydrolysis by fermentation, during which proteolytic enzymes are secreted.
What is hydrolyzed protein?
Hydrolyzed protein is a solution derived from the hydrolysis of a protein into its component amino acids and peptides. While many means of achieving this exist, most common is prolonged heating with hydrochloric acid, sometimes with an enzyme such as pancreatic protease to simulate the naturally occurring hydrolytic process.
What is hydrolysis in food?
Protein hydrolysis is a useful route to the isolation of individual amino acids. Examples include cystine from hydrolysis of hair, tryptophane from casein, histidine from red blood cells, and arginine from gelatin. Common hydrolyzed products used in food are hydrolyzed vegetable protein and yeast extract, which are used as flavor enhancers ...
Why is hydrolyzed protein good for cats?
The protein contents of the foods are split into peptides which reduces the likelihood for an animal's immune system recognizing an allergic threat. Hydrolyzed protein diets for cats are often recommended for felines with food allergies and certain types of digestive issues.
Why is beef protein powder used in formula?
Some hydrolyzed beef protein powders are used for specialized diets. Protein hydrolysis can be used to modify the allergenic properties of infant formula. Reducing the size of cow milk proteins in the formula makes it more suitable for consumption by babies suffering from milk protein intolerance.
Is hydrolyzed protein a hypoallergenic food?
Hydrolyzed protein is also used in certain specially formulated hypoallergenic pet foods, notably dog foods for dogs and puppies that suffer from allergies caused by certain protein types in standard commercial dog food brands.
What enzyme hydrolyzes phospholipids into fatty acids and lipophilic substances?
Phospholipase – Hydrolyzes phospholipids into fatty acids and lipophilic substances (List of Digestive Enzymes and Functions, n.d.). Now that all the enzymes has been addressed and their functions explained, one can truly understand how complex and fascinating the digestive system is and how it works.
What enzyme breaks down proteins into smaller peptide fragments?
1 Pepsin is the main gastric enzyme. It breaks proteins into smaller peptide fragments. 2 Gelatinase, degrades type I and type V gelatin and type IV and V collagen, which are proteoglycans in meat. 3 Gastric amylase degrades starch, but is of minor significance.
What enzyme converts maltose to glucose?
Maltase – Converts maltose to glucose. 5. Lactase – Converts lactose to glucose and galactose. 6. Isomaltase – Converts maltose to isomaltose (List of Digestive Enzymes and Functions, n.d.). We also need to remember other organs help aid in the digestion of food. The pancreas is one those organs.
What enzymes convert starch to soluble sugar?
LET THE DIGESTION BEGIN! Here are all the digestive enzymes in the mouth and their function. 1. Ptyalin – Converts starch to simple soluble sugars. 2. Amylase – Converts starch to soluble sugars. 3.
What enzymes are used to digest meat?
2. Amylase – Converts starch to soluble sugars. 3. Betaine – Maintains cell fluid balance as osmolytes. 4. Bromelain – Anti-inflammatory agent, tenderizes meat. So before you even swallow your bite of this meal, you begin digesting. (List of Digestive Enzymes and Functions, n.d.).
What are the functions of the pancreatic enzymes?
Here is a list of the pancreatic enzymes and their functions: 1. Pancreatic lipase – Degrades triglycerides into fatty acids and glycerol. 2. Chymotrypsin – Converts proteins to aromatic amino acids. 3. Carboxypeptidase – Degradation of proteins to amino acids. 4. Pancreatic amylase – Degradation of carbohydrates to simple sugars.
What is enzyme in biology?
Enzymes are substances produced by a living organism that acts as a catalyst to bring about a specific biochemical reaction (List of Digestive Enzymes and Functions, n.d.). There are enzymes in each part of your digestion system and all have a specific function.
What is the function of lipase?
Our body contains a chemical entity called lipase, which it uses to speed up the process of digestion. The forthcoming article provides in-depth information on gastric lipase functions. Our body contains a chemical entity called lipase, which it uses to speed up the process of digestion.
What are lipases made of?
Some Features Explained. • Lipases are enzymes made up of polypeptides and amino acids. They are involved in several biological processes, like digestion, communication between body cells, and coordination of cell activities.
What is the food that our gut categorizes?
Generally, we talk about food in terms of chicken, meat, vegetables, etc. However, our gut does not understand these terms. It categorizes food into triglycerides, fats, carbohydrates, and proteins, and digests them accordingly. Various types of lipases are involved in the human body chemistry.
Does pancreatic lipase cause cystic fibrosis?
In certain health conditions, such as pancreatitis or cystic fibrosis, a person suffers from pancreatic lipase deficiency. In such situations, gastric lipase along with lingual lipase (another acidic lipase) compensate for the lack of pancreatic lipase and do not hamper the process of digestion.
Does the body use gastric lipase?
According to one theory, the body may have used gastric lipase initially and later on through evolution it must have switched to the use of pancreatic lipase. Another theory states that may be the body needed a trump card to act as the second line of nourishment in case the pancreatic lipase fails to deliver.