...
| Forehead | |
|---|---|
| TA98 | A01.1.00.002 A02.1.00.013 |
| TA2 | 101 |
| FMA | 63864 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
What are the parts of skull?
The skull consists of three parts, of different embryological origin—the neurocranium, the sutures, and the facial skeleton (also called the membraneous viscerocranium). The neurocranium (or braincase) forms the protective cranial cavity that surrounds and houses the brain and brainstem.
What is the forehead of the skull called?
frontal boneThe frontal bone forms the forehead. The two parietal bones form the upper sides of the skull; the two temporal bones form the lower sides. The butterfly-shaped sphenoid bone is located at the base of the skull.
Is head and forehead same?
As nouns the difference between forehead and head is that forehead is the part of the face above the eyebrows and below the hairline while head is (label) the part of the body of an animal or human which contains the brain, mouth and main sense organs.
Where is the forehead located?
The forehead is the superior region of the upper face region. The superficial layer of the forehead is made up of skin. Deeper to the skin layer of the forehead is the fat pads. The central forehead fat pad is in the center of the forehead.Jun 18, 2021
Where is the frontal bone of the skull?
The frontal bone is located in front of the skull, above the nasal bones and in front of the parietal bones, which form the sides of the skull. The frontal bone is also surrounded by seven articulating bones to create joints.
Is there bones in your forehead?
Anatomy and function There are eight cranial bones, each with a unique shape: Frontal bone. This is the flat bone that makes up your forehead. It also forms the upper portion of your eye sockets.May 24, 2018
What is the side of your forehead called?
It is located on the side of the head behind the eye between the forehead and the ear....Temple (anatomy)TempleHuman skull. Temporal bone is orange, and the temple overlies the temporal bone as well as overlying the sphenoid bone.DetailsArterysuperficial temporal arteryVeinsuperficial temporal vein7 more rows
Is forehead part of the face?
The forehead constitutes the upper third of the face. It is delineated superiorly by the hairline and inferiorly by the glabella and frontonasal groove (centrally) and the eyebrows overlying the supraorbital ridges (laterally.)Jun 28, 2016
Why is forehead called forehead?
Fore means front, and your forehead is the front of your head.
What is the area above the eyebrow called?
The glabella, in humans, is the area of skin between the eyebrows and above the nose. The term also refers to the underlying bone that is slightly depressed, and joins the two brow ridges.
How thick is the skull at the forehead?
Skull bone thickness was measured in 4 anatomical compartments, and vertical dimension of the left and right frontal sinuses were measured. The mean thickness of frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital bones was 7.9 mm, 9.7 mm, 6 mm, and 10.1 mm for men; 8.7 mm, 10.2 mm, 6.1 mm, and 10.1 mm for women, respectively.
Where is the eyebrow located?
An eyebrow is an area of short hairs above each eye that follows the shape of the lower margin of the brow ridges of some mammals. In humans, eyebrows serve two main functions: first, communication through facial expression, and second, prevention of sweat, water, and other debris from falling down into the eye socket.
What is the forehead?
Anatomical terminology. In human anatomy, the forehead is an area of the head bounded by three features, two of the skull and one of the scalp. The top of the forehead is marked by the hairline, the edge of the area where hair on the scalp grows.
Why is the forehead important?
Society and culture. In physiognomy and phrenology, the shape of the forehead was taken to symbolise intellect and intelligence. "Animals, even the most intelligent of them,", wrote Samuel R. Wells in 1942, "can hardly be said to have any forehead at all, and in natural total idiots it is very diminished".
Why is the forehead shaped?
In physiognomy and phrenology, the shape of the forehead was taken to symbolise intellect and intelligence. "Animals, even the most intelligent of them,", wrote Samuel R. Wells in 1942, "can hardly be said to have any forehead at all, and in natural total idiots it is very diminished".
What muscles help with facial expressions?
Expression. The muscles of the forehead help to form facial expressions. There are four basic motions, which can occur individually or in combination to form different expressions. The occipitofrontalis muscles can raise the eyebrows, either together or individually, forming expressions of surprise and quizzicality.
What to do if you have a dent in your skull?
If you notice a change in your skull shape, you should make an appointment with your doctor. Take note of any other symptoms, like headaches, memory loss, and vision difficulties, that could be connected to a dent in your skull. Last medically reviewed on October 21, 2019.
What causes bone loss in the skull?
Gorham’s disease is a rare condition that leads your bone mass to be replaced by other kinds of tissue. Gorham’s disease can cause bone loss in your skull, leading to a visible dent in some cases.
Why do babies have indentions?
These indentations can be caused by the birth process or by the way the baby was positioned in their mother’s womb. If the bones in a baby’s skull fuse prematurely, the baby’s head may appear dented or misshapen — a condition called craniosynostosis.
What is a depressed fracture?
Car accidents, falls, or severe blows to the head can cause what’s called a depressed fracture in your skull. A depressed fracture means that a part of your skull has been crushed in toward your brain. This kind of injury requires emergency medical treatment.
What is the best medicine for bone dent?
If you have Paget’s disease of bone, Gorham’s disease, or another rare bone disease that’s causing your skull dent, your doctor may prescribe bisphosphonates — drugs that keep your body from absorbing your bone tissue. Alendronate (Fosamax) and ibandronate (Boniva ) are examples of these drugs.
Can skull depression cause cancer?
There are case reports of skull depressions that have led doctors to discover cancer in a person. These cases are rare#N#Trusted Source#N#, but “bone-destructive” cancers (such as multiple myeloma) can cause skull depressions and skull irregularities.
Overview
In human anatomy, the forehead is an area of the head bounded by three features, two of the skull and one of the scalp. The top of the forehead is marked by the hairline, the edge of the area where hair on the scalp grows. The bottom of the forehead is marked by the supraorbital ridge, the bone feature of the skull above the eyes. The two sides of the forehead are marked by the temporal ridge, …
Structure
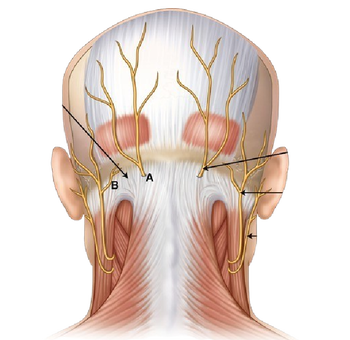
The bone of the forehead is the squamous part of the frontal bone. The overlying muscles are the occipitofrontalis, procerus, and corrugator supercilii muscles, all of which are controlled by the temporal branch of the facial nerve.
The sensory nerves of the forehead connect to the ophthalmic branch of the trigeminal nerve and to the cervical plexus, and lie within the subcutaneous fat. The motor nerves of the forehead con…
Function
The muscles of the forehead help to form facial expressions. There are four basic motions, which can occur individually or in combination to form different expressions. The occipitofrontalis muscles can raise the eyebrows, either together or individually, forming expressions of surprise and quizzicality. The corrugator supercilii muscles can pull the eyebrows inwards and down, forming a frown. The procerus muscles can pull down the centre portions of the eyebrows.
Society and culture
In physiognomy and phrenology, the shape of the forehead was taken to symbolise intellect and intelligence. "Animals, even the most intelligent of them,", wrote Samuel R. Wells in 1942, "can hardly be said to have any forehead at all, and in natural total idiots it is very diminished".
Pseudo-Aristotle, in Physiognomica, stated that the forehead is governed by Mars. A low and little forehead denoted magnanimity, boldness, and confidence; a fleshy and wrinkle-free forehead, liti…
See also
• Artificial cranial deformation
• Bindi
• Forehead lift
• Squamous part of the frontal bone
• Third eye
External links
• Media related to Foreheads at Wikimedia Commons