What vegetables should diabetics avoid?
Winters bring various seasonal fruit and vegetables, but many of them are loaded with ... Here, we are telling you 7 foods that a diabetic patient should avoid during the winter season and should be consumed in the right quantity only after consulting ...
Are there still good snacks for diabetics?
The 21 Best Snack Ideas If You Have Diabetes
- Hard-Boiled Eggs. Hard-boiled eggs are a super healthy snack for people with diabetes. ...
- Yogurt with Berries. Yogurt with berries is an excellent diabetes-friendly snack for a variety of reasons. ...
- Handful of Almonds. ...
- Veggies and Hummus. ...
- Avocado. ...
- Sliced Apples with Peanut Butter. ...
- Beef Sticks. ...
- Roasted Chickpeas. ...
- Turkey Roll-Up. ...
- Cottage Cheese. ...
Are parsnips high in carbs?
Parsnips are not keto-friendly because they are high in carbs. They may kick you out of ketosis even with a small serving size. Too Much Carbs! Parsnips should be avoided on keto because they are very high in net carbs (13.41g of net carbs per 100g serving). It is important to limit your net carb consumption to 20g - 30g per day to stay in ketosis.
Which flour is best for a diabetic?
The 5 Best Flour Options for Diabetes
- Almond flour. Almond flour is made from finely ground almonds and a great gluten-free alternative to regular flour.
- Coconut flour. Coconut flour is a type of flour made from coconut meat that has been dried and ground. ...
- Chickpea flour. ...
- Oat flour. ...
- Spelt flour. ...
Are parsnips diabetic friendly?
Vegetables like artichokes, celery root, sweet potatoes, parsnips, turnips, acorn squash, potatoes with skins, Brussels sprouts, cabbage, broccoli, carrots, cauliflower, asparagus, and beets are good sources of fiber as well.
Which vegetables should diabetics avoid?
The Worst Vegetables for People With DiabetesPotatoes. Both sweet potatoes and regular potatoes are considered a starchy vegetable, meaning they contain a higher amount of carbohydrates than most veggies. ... Corn. ... Peas. ... Butternut Squash. ... Vegetable Juice.
Are parsnips high in carbs?
Parsnips are great for a low-carb diet since a whole cup only provides you with 24 grams of carbs. According to the Mayo Clinic, a low-carb diet is up to 57 grams of carbs.
What root vegetables are good for diabetics?
Root vegetables such as potatoes, carrots, beets, radishes, turnips, rutabagas, celery root and jicama are particularly ideal if you are have diabetes and are trying to lose weight.
What is the one food that kills diabetes?
It is also known that bitter melon contains a lectin that reduces blood glucose concentrations by acting on peripheral tissues and suppressing appetite – similar to the effects of insulin in the brain. This lectin is thought to be a major factor behind the hypoglycemic effect that develops after eating bitter melon.
Is cabbage good for diabetes?
Broccoli, spinach, and cabbage are three diabetes-friendly veggies because they are low in starch. Filling up with vegetables is a great way to keep your blood sugar levels in check.
Is parsnip high in sugar?
Per 100-gram serving, these root vegetables contain upwards of 3.8 grams of sugar: parsnips, carrots, radishes, rutabaga, turnips and beets. Chicory root claims the highest value among root vegetables at 8.7 grams of sugar.
Which is healthier potato or parsnip?
Parsnip is an underrated and overlooked vegetable richer in fibers, phosphorus, zinc, copper, and magnesium, and vitamins B1, B5, K, folate, and E. On the other hand, potatoes are richer in potassium, iron, and vitamins B3, B6, and C. Potatoes have a lower glycemic index.
Which is healthier carrots or parsnips?
Parsnip is richer in iron, potassium, magnesium, copper, zinc, and phosphorus. Parsnips contain 85.5% less sodium compared to carrots. Both food items are equal in their calcium content.
Are parsnips starchy?
While starchy vegetables are concentrated sources of starch, they are less starchy than grains. Other root vegetables like carrots, beets, parsnips, turnips, and rutabagas are classified as non-starchy vegetables. Together, starchy and non-starchy vegetables provide excellent sources of fiber, vitamins, and nutrients.
Are parsnips good for you?
Along with vitamin C, parsnips are rich in potassium, a mineral that helps your heart function, balances your blood pressure, and lowers your risk for kidney stones. One serving of parsnips provides about 10 percent of your DRI of potassium.
Do carrots raise blood sugar?
Diabetics can opt for carrots in their daily diet despite its sweet flavour as it can help manage blood glucose levels. Carrot juice may still contain sugar and carbohydrates, it won't spike the blood sugar levels.
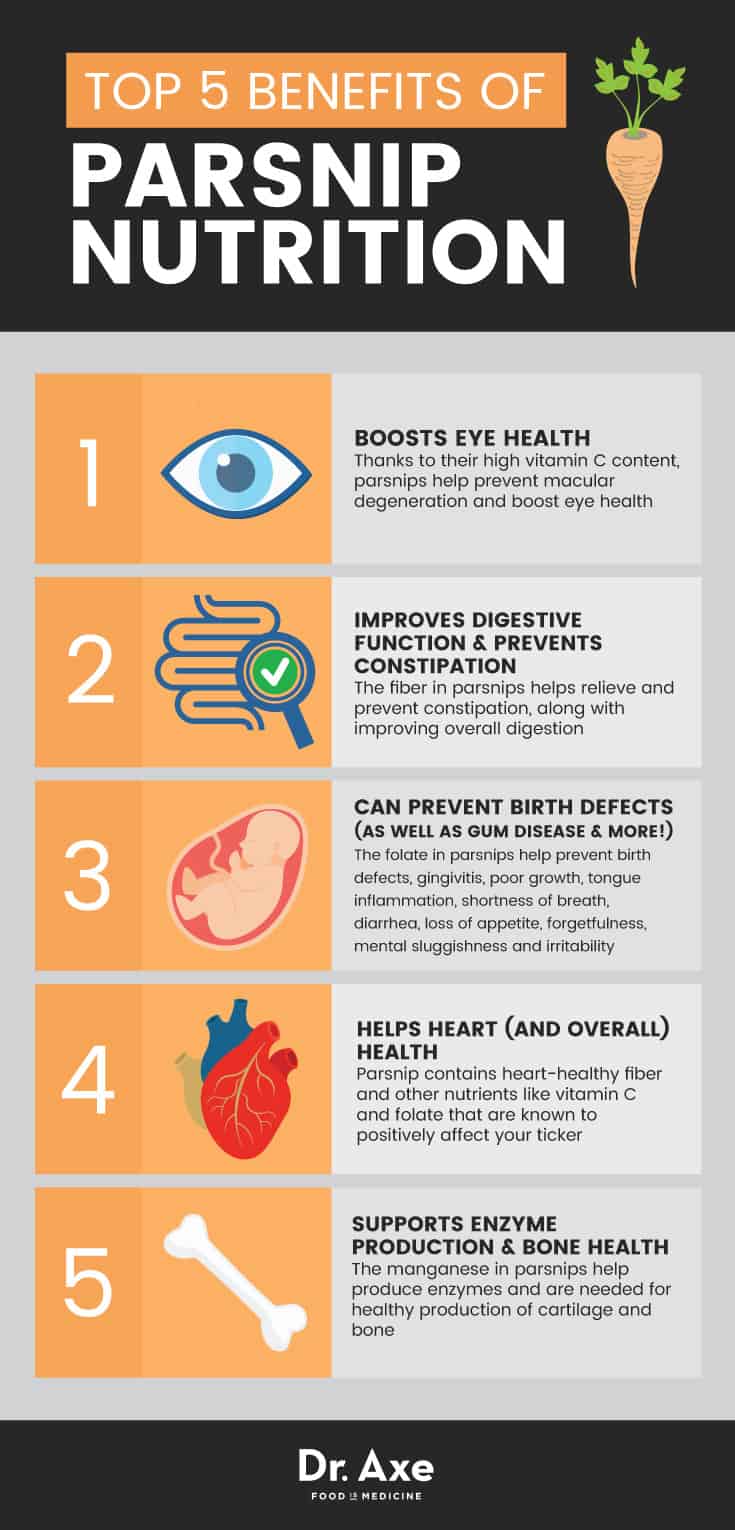
What are the benefits of eating parsnips?
11 Impressive Health Benefits of Parsnips 11 Impressive Health Benefits of Parsnips Parsnips health benefits includes boosting heart health, preventing digestive issues, enhancing vision, supporting a healthy pregnancy, strengthening bones and managing diabetes. Other benefits includes boosting brain health, supporting immune system, supporting weight loss and treating respiratory illness such as asthma. Parsnip is a vegetable used in food since ancient times. It is widely known for its use in the European Nations and is a famous ingredient in their dishes. Parsnips are considered to be very close to carrots and parsley. However, both the vegetables are known to have significant differences regarding taste. This vegetable has some nutritional benefits that make parsnips a healthy and tasty addition to different kinds of foods. Parsnips are rich in Potassium , Zinc , Magnesium , Phosphorus , Manganese , and Iron . It also contains many Vitamins and fiber along with certain amounts of protein and folate. The folate found in this vegetable is known to be very important in fighting chronic illnesses. Due to the vegetable containing all the above mentioned important nutrients, it is highly beneficial to add the use of parsnips in our diet. In this article, we will be discussing eleven health benefits derived from using this vegetable. 11 Impressive Health Benefits of Parsnips The fiber found in parsnips helps the heart by reducing the cholesterol and its negative effects. Also, since parsnips are rich in potassium that helps in lowering the blood pressure and saves the heart from ill effects of hypertension. In addition to that, parsnips are also known to have low levels of sodium which makes them a perfect choice for people suffering from hypertension. Parsnips are also ri Continue reading >>
What are parsnips used for?
People used to believe (falsely) that eating parsnips could relieve a toothache or tired feet. Half a cup of sliced, cooked parsnips has 3 grams of fiber and only 55 calories. They are a good source of vitamin C (11% of the recommended daily allowance), folate (11%), and manganese (10%). It's no coincidence that the parsnip resembles the carrot. The two veggies are close relatives. But it's not related to the "cow parsnip," which is a member of the parsley family. The parsnip's unique flavor comes when its starches change to sugar. This happens after the first frost, when the vegetable is still in the ground. In Europe, parsnips were used to sweeten jams and cakes before sugar was widely available. 2 cups (about 2 large) thinly sliced leeks 1 pound Yukon Gold potatoes, thinly sliced 1 pound parsnips, peeled and thinly sliced 1 cup, plus 2 Tbsp, nonfat, low-sodium chicken broth 1. Preheat oven to 350degrees F. Spray and heat a large nonstick skillet over medium heat. Saute leeks until caramelized, about 7 minutes. Add garlic, and continue cooking 2 to 3 minutes. 2. Coat an 8- by 12-inch glass baking dish with cooking spray. Arrange half the potatoes in the dish, overlapping slightly. Top with half the sauteed leeks, garlic, and parsnips, and season with half the salt, pepper, nutmeg, and thyme. Repeat layering, using remaining vegetables and seasonings. Pour broth over and around vegetables. Cover pan tightly with foil and bake 1 hour. 3. Increase oven temperature to 375 F. Remove foil and pour cream over vegetables. Sprinkle cheese and breadcrumbs and continue baking, uncovered, 30 minutes or until golden brown. Per serving: 195 calories, 5 g protein, 33 g carbohydrate, 6 g Continue reading >>
How does glycemic index affect blood sugar?
The index measures how quickly the carbohydrates in a specific food impact your blood sugar. They are rated low, medium, or high, depending on how quickly they raise your blood sugar level, compared to either glucose or white bread (these foods have a glycemic index rating of 100). By choosing low glycemic index foods, you can minimize dramatic increases in your blood sugar. Additionally, if you eat a high glycemic index food, you can expect that it will increase your blood sugar more significantly. It may also cause a higher post-meal blood sugar reading. Many factors can change the glycemic index of a food. These factors include its composition and how the food is cooked. The glycemic index of food also changes when it is mixed together. The glycemic index of food is not based on a normal serving of a particular food. For example, carrots have a high glycemic index, but to get the amount measured for carrot’s glycemic index you would have to eat a pound and a half. A different measure, called glycemic load, is also available. This measure takes into account both the speed of digestion and the amount present in a normal serving of a food. It may be a better way to measure the impact a carbohydrate food has on blood sugar. To assign a GI number, foods are assigned to one of three categories: low, medium, or high. low GI foods: have a GI of 55 or less medium GI foods: between 56 and 69 high GI foods: 70 or higher For glycemic load, under 10 is considered low, 10 to 20 is considered medium, and over 20 is consider high. Several factors are taken into account when assigning a food a glycemic rating. These factors include: Acidity Foods that are highly acidi Continue reading >>
Why are root vegetables and tubers bad for diabetics?
This can be problematic for diabetics because they can produce a large glycemic response in situations when they are not combined with high fiber foods.
What vegetables should diabetics eat?
Vegetables are a vital component of a healthy diet and this is particularly true for diabetics. Most fruits and vegetables are high in fiber and nutrient dense but low in calories making them ideal for diabetics who often need to watch their calorie intake. The general rule of thumb for diabetics is that root vegetables should be eaten in moderation (no more than 1 serving a day), while green and red vegetables are great choices and should be consumed in high amounts, preferably 3-5 servings a day. There are exceptions to this rule that we will discuss in more detail below. Root Vegetables & Tubers Root vegetables and tubers are relatively concentrated sources of sugars and starches and tend to contain only small amounts of fiber. This can be problematic for diabetics because they can produce a large glycemic response in situations when they are not combined with high fiber foods. The glycemic index of root vegetables and tubers range from moderate (40-60) to very high (80+). The lowest GI vegetables are yams, carrots and sweet potatoes with GI values of 38, 47 and 55 respectively. High GI root vegetables include potatoes (GI of 60-90), parsnip (97), rutabaga (71), and beets (65). If you like these vegetables, try and limit your intake to one serving (approx. 200g) a day. Cooking method also has a significant impact on the GI value of the vegetable. In general, boiling rather than baking or mashing a root vegetable will result in a lower GI. Boiled potatoes for example have a GI of around 70 compared to 80-90 for mashing or baking. Cooking root vegetables converts some of the starch into simple sugars which are more readily absorbed by the body, increasing their GI values. A raw carrot for example has a GI of just 15, while over-cooking a carrot until it turns to mush c Continue reading >>
How much fiber is in a parsnip?
Parsnip is an excellent source of fiber. A one-cup serving of parsnip contains 7 grams of dietary fiber. The daily recommended dietary fiber intake for men and women are 38 grams and 25 grams, respectively.
What vegetables have the lowest GI?
The lowest GI vegetables are yams, carrots and sweet potatoes with GI values of 38, 47 and 55 respectively. High GI root vegetables include potatoes (GI of 60-90), parsnip (97), rutabaga (71), and beets (65). If you like these vegetables, try and limit your intake to one serving (approx. 200g) a day.
What are the benefits of parsnips?
Here are 6 nutrition and health benefits of parsnips. Share on Pinterest. 1. Packed With Important Nutrients. Parsnips are an excellent source of many important nutrients, packing a hearty dose of fiber, vitamins, and minerals into each ser ving. In particular, parsnips are a great source of vitamin C, vitamin K, and folate, ...
What is the flavor of parsnips?
Closely related to other vegetables like carrots and parsley roots, parsnips have long, cream-colored tuberous roots with a sweet, slightly nutty flavor. In addition to bringing a unique taste to your dishes, ...
How many grams of parsnips are in a cup?
In particular, parsnips are a great source of vitamin C, vitamin K, and folate, as well as several other important micronutrients. One cup (133 grams) of parsnips provides the following ( 1. Trusted Source. ):
What to do with parsnips in a shepherd's pie?
Combine parsnips with mushrooms and lentils for a vegetarian shepherd’s pie. Mash parsnips and mix with lemon and herbs. Prepare a parsnip gratin with ingredients like feta, turmeric, and cumin. Bake sliced parsnips in the oven to make vegetable crisps. Toss with olive oil and spices and roast alongside carrots.
What is the most important vitamin for RDI?
Vitamin K: 25% of the RDI. Folate: 22% of the RDI. Vitamin E: 13% of the RDI. Magnesium: 10% of the RDI. Thiamine: 10% of the RDI. Phosphorus : 8% of the RDI. Zinc : 7% of the RDI. Vitamin B6: 7% of the RDI. In addition to the nutrients listed above, parsnips contain a small amount of calcium, iron, and riboflavin.
What does parsnip taste like?
Parsnips have a sweet taste similar to carrots, but with a nutty, earthy undertone. They can be mashed, roasted, sautéed, boiled, baked, grilled, or fried and add a rich flavor to many dishes, working especially well in soups, stews, casseroles, gratins, and purees.
Is parsnip good for cancer?
Trusted Source. ). In particular, parsnips are high in ascorbic acid (vitamin C) — a water-soluble vitamin that doubles as a powerful antioxidant ( 1. Trusted Source.
What are the benefits of eating parsnips?
Parsnip contains a number of essential vitamins and minerals which have quite a few beneficial effects on our health. Parnips are rich in potassium which help to keep the heart in good shape . The dietary fibers in this vegetable help to improve digestion and prevent ailments related to digestion .
Why are parsnips good for you?
Parsnips are rich in soluble fiber that helps to reduce cholesterol levels and also lowers the chances of developing diabetes. Dietary fiber also helps to add bulk to the stool and thus facilitates the smooth movement of bowel through the digestive system. This helps to prevent constipation and gastrointestinal disorders.
What are the nutrients in parsnips?
It contains minerals like phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, manganese, zinc and iron. Parsnip is rich in folate and also has vitamins like Vitamin B, C, E and K which are very beneficial for our health.
What is the difference between parsnip and carrot?
Parsnip or Pastinaca sativa is a biennial plant belonging to the Apaiaceae family. It resembles a carrot so much that many may confuse the two. However, the skin and flesh of parsnip are white to cream-coloured while the carrot’s skin is orange in colour. This vegetable has a nutty, sweet taste.
What are parsnips rich in?
Parsnips are rich in anti-oxidants and other organic compounds which protect us from various diseases. Foremost among these are Vitamin C and Vitamin E which neutralize the disease causing free radicals and prevent them from causing any harm.
What is edible parsnip?
Cultivation of Parsnips. Parsnips have a long history but edible parsnips were actually the result of continuous cultivation. Besides being used as a staple food, this vegetable was also used as a natural sweetener for breads, cakes and jams.
Why do we need parsnips?
You can include parsnips in your diet if you want your bones and teeth to be healthy and strong. This is because this vegetable is not only rich in calcium but also contains magnesium which helps in the proper absorption of calcium.
What are some foods that help with diabetes?
Beets also contain nitrates, which research shows has blood pressure lowering effects. Carrots and pumpkin contain carotenoids, along with vitamin A, E, and C.
What vegetables have the lowest glycemic index?
This can be problematic for diabetics because they can produce a large glycemic response in situations when they are not combined with high fiber foods…The lowest GI vegetables are yams, carrots and sweet potatoes with GI values of 38, 47 and 55 respectively. High GI root vegetables include potatoes (GI of 60-90), parsnip (97), rutabaga (71), ...
What vegetables have high GI?
High GI root vegetables include potatoes (GI of 60-90), parsnip (97), rutabaga (71), and beets (65).”. As you can see, yams and carrots are really your best 2 options here, followed by a small amount of sweet potato on the odd occasion. BUT, that’s only when it comes to GI levels – you still have to keep the amount of carbs in mind.