What are the monoprotic and diprotic acids?
Monoprotic acids: 1. Hydrochloric acid, HCl 2. Nitric acid, HNO3 3. Acetic acid, CH3COOH Diprotic acids: 1. Sulphuric acid, H2SO4 2.
Is acetic acid a monoprotic or polyprotic?
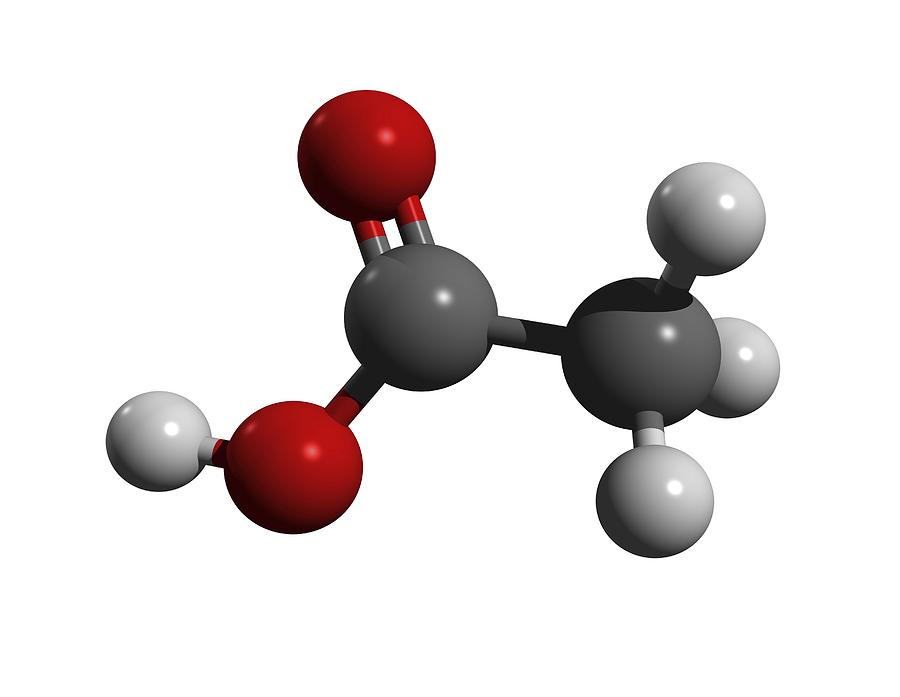
Although it contains more than one hydrogen atom, acetic acid (CH 3 COOH) is also a monoprotic acid as it dissociates to release only a single proton. The following examples are polyprotic acids that either fall under the category of diprotic or triprotic.
Is formic acid a diprotic acid?
No, formic acid only has a single C (O)OH group. To be diprotic, it would have to have two C (O)OH groups so it could lose 2 acidic protons. No, formic acid is not a diprotic acid. Instead, it is a monoprotic acid.
How do you know if an acid is monoprotic?
The electrical charge of a monoprotic acid jumps one level higher before it gives away its proton. Any acid that contains just one hydrogen atom in its formula is monoprotic, but some acids that contain more than one hydrogen atom are also monoprotic.
Is Ethanoic acid is a monoprotic acid?
Recall that acetic acid is a weak carboxylic acid, meaning that it dissociates only partially in water, hence the double arrow in the equation above. Since acetic acid is capable of releasing only one hydrogen proton, it is classified as a monoprotic acid.
Why is Ethanoic acid a monoprotic acid?
Even though it contains four hydrogen atoms, acetic acid, CH3CO2H, is also monoprotic because only the hydrogen atom from the carboxyl group (COOH) reacts with bases: Similarly, monoprotic bases are bases that will accept a single proton.
What type of acid is Ethanoic acid?
carboxylic acidsacetic acid (CH3COOH), also called ethanoic acid, the most important of the carboxylic acids. A dilute (approximately 5 percent by volume) solution of acetic acid produced by fermentation and oxidation of natural carbohydrates is called vinegar; a salt, ester, or acylal of acetic acid is called acetate.
How can you tell if an acid is monoprotic or Diprotic?
1:185:27So basic city of of an acid is the number of hydrogen ions which can be produced by one molecule ofMoreSo basic city of of an acid is the number of hydrogen ions which can be produced by one molecule of the acid. So basicity of a Nessy is the number of hydrogen ion which can be produced by one
Is ch3cooh a diprotic acid?
Monoprotic acids are acids that can release only one proton per molecule and have one equivalence point....Monoprotic Acids.NameFormulaKaKaNitric acid (strong)HNO32.4 x 101Acetic acid (weak)CH3COOH1.74 x 10-51 more row•Aug 15, 2020
What is an example of a monoprotic acid?
Hydrochloric acid (HCl), acetic acid (CH3CO2H or HOAc), nitric acid (HNO3), and benzoic acid (C6H5CO2H) are all monoprotic acids.
Is ethanoic acid monobasic?
Acetic acid is monobasic because it has one dissociable hydrogen ion and combines with one hydroxyl ion of the base to give a single salt and water.
Is ethanoic acid dibasic?
Example, in ethanoic acid. When 1 mole of hydrogen ions is furnished from 1 mole of an acid, the acid is monobasic; it is dibasic when 2 moles of hydrogen ions are furnished, and tribasic when 3 moles of hydrogen ions are furnished from 1 mole of its solution.
Why is ethanoic acid a acid?
They imply that the hydrogen ion is actually attached to a water molecule. The pH depends on both the concentration of the acid and how easily it loses hydrogen ions from the -COOH group. Ethanoic acid is typical of the acids where the -COOH group is attached to a simple alkyl group.
How do you identify a monoprotic?
In a titration curve, identification of a single equivalence point will determine that the acid is monoprotic. Because a monoprotic acid is only able to donate one proton, the molecular formula for this type of acid will have one proton present in its structure.
What acids are Diprotic?
Diprotic acids, such as sulfuric acid (H2SO4), carbonic acid (H2CO3), hydrogen sulfide (H2S), chromic acid (H2CrO4), and oxalic acid (H2C2O4) have two acidic hydrogen atoms.
Which of the following is not a diprotic acid?
H2O is not a diprotic acid.
What is a monobasic acid?
Monobasic Acids likewise know as monoprotic acids. These are acids which yield one free hydrogen particle in answer for every atom of corrosive ionized. A case of a monobasic corrosive is hydrochloric corrosive (HCl).
How many pH jumps does a monoprotic acid have?
In a titration of a weak acid a monoprotic acid yields one pH jump, a diprotic acid two pH jumps. You could expect that a triprotic acid gives three pH jumps but this last jump is not so well visible. 77 views. ·.
What is a protic solvent?
protic solvent is a solvent that has a hydrogen atom bound to an oxygen (as in a hydroxyl group) or a nitrogen (as in an amine group). In general terms, any solvent that contains labile H+ is called a protic solvent. The molecules of such solvents readily donate protons (H+) to reagents. 12.7K views. ·.
What are some examples of acidic compounds?
The best examples would be sulfur dioxide, sulfur trioxide, nitrogen dioxide and carbon dioxide. All these dissolve in water to form, respectively, sulfurous acid, sulfuric acid, nitric acid and carbonic acid. The last one is quite safe to consume.
Which acid produces two moles of hydrogen?
Diprotic acids are those that produces two moles of Hydrogen (di=2) when they ionize. Example. H2SO4==>2H^+ and SO4^2-. Triprotic acids are those acids which produces 3 Hydrogen ions (protons) when they ionized (tri=3) Example is. H3PO4==>3H^+ and PO4^-. 10.5K views.
Why is the pH of a monoprotic acid predictable?
Because only one hydrogen is released , the pH calculation for a monoprotic acid is fairly straightforward and predictable. A monoprotic base will only accept a single hydrogen atom. See below for examples of acids that donate only one proton or hydrogen in solution and their chemical formulas.
What is a polyprotic acid?
This is in contrast to acids capable of donating more than one proton/hydrogen, which are called polyprotic acids. Polyprotic acids may be further categorized according to how many protons they can donate (diprotic = 2, triprotic = 3, etc.). The electrical charge of a monoprotic acid jumps one level higher before it gives away its proton.
Is a single hydrogen atom monoprotic?
Any acid that contains just one hydrogen atom in its formula is monoprotic, but some acids that contain more than one hydrogen atom are also monoprotic. In other words, all single-hydrogen acids are monoprotic but not all monoprotic acids contain only a single hydrogen.
Is HCl a monoprotic acid?
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) and nitric acid (HNO 3) are common monoprotic acids. Although it contains more than one hydrogen atom, acetic acid (CH 3 COOH) is also a monoprotic acid as it dissociates to release only a single proton.