What are the dangers of carbonic acid?
Carbonic acid is not considered to be toxic or dangerous to human health since it is present naturally in the human body. However, it is important to note that exposure to high concentrations of H2CO3 can irritate the respiratory tract and the eyes.
Is carbonic acid by itself a good buffer?
The Carbonic-Acid-Bicarbonate Buffer in the Blood By far the most important buffer for maintaining acid-base balance in the blood is the carbonic acid-bicarbonate buffer. The dissolved carbon dioxide and bicarbonate ion are at equilibrium (Eq. 10).
What is carbonic acid and how does it effect rock?
What is carbonic acid and how does it affect rock? It forms when water combines with carbon dioxide. It can dissolve rocks, such as limestone and marble.
Is carbonic acid the same as CO2?
These are two entirely different things. Carbonic acid is simply a solution of Carbon dioxide on water; CO2 + H2O — > H2CO3. It would be impossible to get this “pure" meaning 100% acid since the solubility of CO2 in water is limited.
Is carbonic acid a liquid or gas?
gasCarbonic acid is a heavy gas —it extinguishes fire and destroys all animal life.
Is carbonic acid a water?
Carbonic acid (ancient name acid of air or aerial acid) is a weak acid with the formula H2CO3. It is formed in small amounts when carbon dioxide is dissolved in water, and it is usually found only in solution....Carbonic acidSolubility in waterexists only in solutionAcidity (pKa)6.36 (see text) 10.2510 more rows
Is carbonic acid aqueous or liquid?
Aqueous carbonic acid (H2CO3) decomposes into a carbon dioxide gas and liquid water.
What is called carbonic acid?
carbonic acid, (H2CO3), a compound of the elements hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen. It is formed in small amounts when its anhydride, carbon dioxide (CO2), dissolves in water.
Can you drink carbonic acid?
The decomposition of carbonic acid produces the characteristic soda fizz. Despite its acidic properties, there's no evidence to suggest that carbonic acid in beverages does you any harm.
Is carbonic acid the same as carbon dioxide?
Carbonic acid is a type of weak acid formed from the dissolving of carbon dioxide in water. The chemical formula of carbonic acid is H2CO3. Its structure consists of a carboxyl group with two hydroxyl groups connected. As a weak acid, it partially ionizes, dissociates or rather, breaks apart, in a solution.
What state of matter is carbonic acid?
gaseous stateCarbonic acid is often described as a respiratory acid since it is the only acid that is exhaled in the gaseous state by the human lungs. It is a weak acid and it forms carbonate and bicarbonate salts.
Why carbonic acid is a mineral acid?
Carbonic acids are considered as mineral acid instead of contains hydrogen and carbon because it has ionic bounds while on the other hand some acids containg hydrogen and carbon are considered as organic acid because it has covalent bounds.
Is carbonic acid soluble in water?
WaterCarbonic acid / Soluble inWater is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms. It is vital for all known forms of life, even though it provides neither food, energy, nor organic micronutrients. Wikipedia
What is another name for carbonic acid?
Carbonic acidNamesIUPAC name Carbonic acidOther names Hydroxyformic acid Hydroxymethanoic acid DihydroxycarbonylIdentifiersCAS Number463-79-622 more rows
What has carbonic acid?
Carbonic acid is present in blood in the human body. It is formed in the human body when water gets dissolved with carbon dioxide. It is also present in rainwater, calcite, fermentation, coal, groundwater, meteors, volcanoes, amino acids, proteins, oceans, plants, erythrocytes, sulphur deposits, salts, and caves.
Is carbon dioxide an acid?
CO2 is not an acid itself, since it does not contain ions of hydrogen (H+). CO2 becomes carbonic acid in water. Carbonic acid (H2CO3) is a weak, H+-splitting acid. Carbonic acid, a weak acid that acidifies the solution, is formed when some of the carbon dioxide dissolves in the water.
Where is carbonic acid found?
The fact that the carbonic acid may form by irradiating a solid H 2 O + CO 2 mixture or even by proton-implantation of dry ice alone has given rise to suggestions that H 2 CO 3 might be found in outer space or on Mars, where frozen ices of H 2 O and CO 2 are found, as well as cosmic rays.
What is the pH of carbonic acid?
Since pK a1 has a value of ca. 6.8 , at equilibrium carbonic acid will be almost 50% dissociated in the extracellular fluid ( cytosol) which has a pH of ca.7.2. Note that dissolved carbon dioxide in extracellular fluid is often called as "carbonic acid" in biochemistry literature, for historical reasons. The reaction in which it is produced.
What temperature does carbonic acid decompose?
The pure compound decomposes at temperatures greater than ca. −80 °C. In biochemistry, the name "carbonic acid" is often applied to aqueous solutions of carbon dioxide, which play an important role in the bicarbonate buffer system, used to maintain acid–base homeostasis.
Is carbon dioxide converted to carbonic acid?
Hence, the majority of the carbon dioxide is not converted into carbonic acid, remaining as CO 2 molecules. In the absence of a catalyst, the equilibrium is reached quite slowly. The rate constants are 0.039 s −1 for the forward reaction and 23 s −1 for the reverse reaction. In nature, limestone may react with rainwater, ...
Is carbonic acid a dibasic acid?
In aqueous solution carbonic acid behaves as a dibasic acid. The Bjerrum plot shows typical equilibrium concentrations,in solution, in seawater, of carbon dioxide and the various species derived from it, as a function of pH. The acidification of natural waters is caused by the increasing concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, ...
Is carbonic acid anhydrous or anhydrous?
Pure carbonic acid. Carbonic acid, H 2 CO 3, is stable at ambient temperatures in strictly anhydrous conditions. It decomposes to form carbon dioxide in the presence of any water molecules. Carbonic acid forms as a by-product of CO 2 /H 2 O irradiation, in addition to carbon monoxide and radical species (HCO and CO 3 ).
What is carbonic acid?
Carbonic acid, (H 2 CO 3 ), a compound of the elements hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen. It is formed in small amounts when its anhydride, ...
How is carbonic acid formed?
Carbonic acid (H2CO3) is formed in small amounts when its anhydride, carbon dioxide (CO2),... CO 2 + H 2 O ⇌ H 2 CO 3 The predominant species are simply loosely hydrated CO 2 molecules. Carbonic acid can be considered to be a diprotic acid from which two series of salts can be formed—namely, hydrogen carbonates, containing HCO 3−, and carbonates, ...
How does carbonic acid transport carbon dioxide?
Carbonic acid is important in the transport of carbon dioxide in the blood. Carbon dioxide enters blood in the tissues because its local partial pressure is greater than its partial pressure in blood flowing through the tissues. As carbon dioxide enters the blood, it combines with water to form carbonic acid, which dissociates into hydrogen ions(H+) and bicarbonate ions (HCO3-). Blood acidity is minimally affected by the released hydrogen ions because blood proteins, especially hemoglobin, are effective buffering agents. (A buffersolution resists change in acidity by combining with added hydrogen ions and, essentially, inactivating them.) The natural conversion of carbon dioxide to carbonic acid is a relatively slow process; however, carbonic anhydrase, a protein enzyme present inside the red blood cell, catalyzes this reaction with sufficient rapidity that it is accomplished in only a fraction of a second. Because the enzyme is present only inside the red blood cell, bicarbonate accumulates to a much greater extent within the red cell than in the plasma. The capacity of blood to carry carbon dioxide as bicarbonate is enhancedby an ion transport system inside the red blood cell membrane that simultaneously moves a bicarbonate ion out of the cell and into the plasma in exchange for a chloride ion. The simultaneous exchange of these two ions, known as the chloride shift, permits the plasma to be used as a storage site for bicarbonate without changing the electrical chargeof either the plasma or the red blood cell. Only 26 percent of the total carbon dioxide content of blood exists as bicarbonate inside the red blood cell, while 62 percent exists as bicarbonate in plasma; however, the bulk of bicarbonate ions is first produced inside the cell, then transported to the plasma. A reverse sequence of reactions occurs when blood reaches the lung, where the partial pressure of carbon dioxide is lower than in the blood.
Why is carbonic acid important?
Carbonic acid is important in the transport of carbon dioxide in the blood. Carbon dioxide enters blood in the tissues because its local partial pressure is greater than its partial pressure in blood flowing through the tissues. As carbon dioxide enters the blood, it combines with water to form carbonic acid, which dissociates into hydrogen ions ...
What percentage of carbon dioxide is in blood?
Only 26 percent of the total carbon dioxide content of blood exists as bicarbonate inside the red blood cell, while 62 percent exists as bicarbonate in plasma; however, the bulk of bicarbonate ions is first produced inside the cell, then transported to the plasma.
What is the compound of hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen?
Carbonic acid, (H 2 CO 3 ), a compound of the elements hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen. It is formed in small amounts when its anhydride, carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), dissolves in water. Carbonic acid (H2CO3) is formed in small amounts when its anhydride, carbon dioxide (CO2),...
How does blood carry carbon dioxide?
The capacity of blood to carry carbon dioxide as bicarbonate is enhanced by an ion transport system inside the red blood cell membrane that simultaneously moves a bicarbonate ion out of the cell and into the plasma in exchange for a chloride ion.
What is the hypothetical acid of carbon dioxide and water?
Carbonic acid ( H2C03). The hypothetical acid of carbon dioxide and water. It exists only in the form of its salts (carbonates), acid salts (hydrogen carbonates), amines (carbamic acid), and acid chlorides (carbonyl chloride).
What is soda ash?
Soda ash is the trade name for sodium carbonate, a chemical refined from the mineral trona or sodium-carbonate -bearing brines (both referred to as "natural soda ash") or manufactured from one of several chemical processes (referred to as "synthetic soda ash").
Where does carbon dioxide come from?
In various parts of the world—notably in Italy, Java, and Yellowstone National Park in the United States—carbon dioxide is formed underground and issues from fissures in the earth. Natural mineral waters such as Vichy water sparkle (effervesce) because excess carbon dioxide that dissolved in them under pressure collects in bubbles and escapes when the pressure is released. The chokedamp (see damp damp,
What is the temperature of carbon dioxide?
Carbon dioxide is a colorless gas with a faintly pungent odor and acid taste; it has a density of 0.0019 g/cm3 (at 0°C and 0.1 meganewtons per sq m [MN/m2]), a melting point of -56.6°C, a boiling point of -78.5°C, a critical temperature of 31°C, and a critical pressure of 7.62 MN/m2, or 76.2 kilograms-force per sq cm (kgf/cm2 ). At atmospheric pressure and a temperature of -78.5°C, carbon dioxide hardens into a white, snowlike mass known as dry ice, thus bypassing the liquid state. Liquid carbon dioxide exists at room temperature only when the pressure exceeds 5.85 MN/m2 (58.5 kgf/cm2 ). The density of liquid CO 2 is 0.771 g/cm3 at 20°C, while that of the solid form is 1.512 g/cm3. In the gaseous phase, the carbon dioxide molecule has the symmetrical form O=C=O, with a distance between the carbon and oxygen atoms of 1.162 angstroms (Å). Solid CO 2 crystallizes in a face-centered cubic lattice, with a = 5.62 Å.
How is carbon dioxide used in agriculture?
In agriculture, carbon dioxide is used as a fertilizer. An insufficiency of carbon dioxide in the air, which frequently occurs when the ground is shielded, as is especially the case with hydroponic cultivation, lowers the rate of photosynthesis and the crop yield. Gaseous carbon dioxide (from cylinders) or purified products (containing up to 15 percent CO 2) of the catalytic combustion of natural gas and solid fuel are introduced during the daytime into hothouses and greenhouses to improve the carbon supply to plants. Solid carbon dioxide (dry ice) can be used as a source of gaseous carbon dioxide; here, pieces of the solid are distributed about an area. Organic and mineral fertilizers that liberate carbon dioxide upon decomposition may also be used as sources. The efficiency of carbon dioxide fertilizers depends on the mineral supply available to plants, the illumination, and the temperature of the soil and air.
How does carbon dioxide affect the blood?
In humans and animals, carbon dioxide, together with bicar-bonates, forms an important buffer system of the blood. An increase in the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the blood strengthens the bond of oxygen to hemoglobin. By acting, both directly and indirectly, on the centers of the medulla oblongata, carbon dioxide figures in the regulation of respiration and blood circulation. A mixture of 95 percent oxygen and 5 percent carbon dioxide (Carbogen) is used in medicine in the case of toxic dosages of narcotics and carbon monoxide poisoning. In high concentrations, carbon dioxide is toxic, inducing hypoxia. Breathing carbon dioxide for a period of several days, even in concentrations of 1.5–3 percent, causes headache, vertigo, and nausea. At concentrations greater than 6 percent (critical level), a person becomes drowsy and unable to work, and there is a weakening of respiratory and cardiac activity, posing a threat to life. An accumulation of carbon dioxide in the air with a concomitant decrease in the oxygen content is seen in enclosed, poorly ventilated spaces, for example, areas in mines and sewers, and in places, such as breweries, where fermentation is occurring. First aid calls for removing the victim into the fresh air and applying artificial respiration. Carbon dioxide does not reach critical levels in the air in residential and public buildings. The concentration of carbon dioxide serves as an environmental indicator of air purity.
Examples of carbonic acid gas in a Sentence
Recent Examples on the Web The primitive atmosphere of the earth was greatly richer in carbonic acid gas [carbon dioxide] than the present, and therefore unfit for the respiration of the warm-blooded animals. — Daniel C. Schlenoff, Scientific American, 1 May 2018
Medical Definition of carbonic acid gas
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!
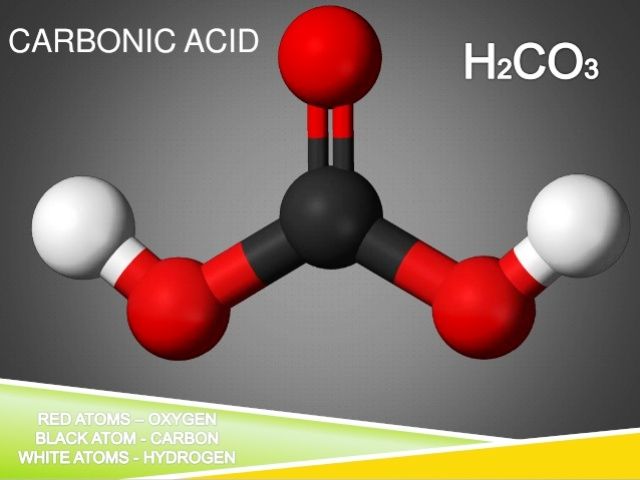
Overview
Chemical equilibria
In aqueous solution carbonic acid behaves as a dibasic acid. The Bjerrum plot shows typical equilibrium concentrations, in solution, in seawater, of carbon dioxide and the various species derived from it, as a function of pH. The acidification of natural waters is caused by the increasing concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, which is caused by the burning of increasin…
Use of the term carbonic acid
Strictly speaking the term "carbonic acid" refers to the chemical compound with the formula .
Since pKa1 has a value of ca. 6.8 , at equilibrium carbonic acid will be almost 50% dissociated in the extracellular fluid (cytosol) which has a pH of ca.7.2. Note that dissolved carbon dioxide in extracellular fluid is often called as "carbonic …
Pure carbonic acid
Carbonic acid, H2CO3, is stable at ambient temperatures in strictly anhydrous conditions. It decomposes to form carbon dioxide in the presence of any water molecules.
Carbonic acid forms as a by-product of CO2/H2O irradiation, in addition to carbon monoxide and radical species (HCO and CO3). Another route to form carbonic acid is protonation of bicarbonates (HCO3 ) with aqueous HCl or HBr. This has to be done at cryogenic conditions to av…
Further reading
• "Climate and Carbonic Acid" in Popular Science Monthly Volume 59, July 1901
• Welch, M. J.; Lifton, J. F.; Seck, J. A. (1969). "Tracer studies with radioactive oxygen-15. Exchange between carbon dioxide and water". J. Phys. Chem. 73 (335): 3351. doi:10.1021/j100844a033.
• Jolly, W. L. (1991). Modern Inorganic Chemistry (2nd Edn.). New York: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-112651-9.
External links
• Carbonic acid/bicarbonate/carbonate equilibrium in water: pH of solutions, buffer capacity, titration and species distribution vs. pH computed with a free spreadsheet
• How to calculate concentration of Carbonic Acid in Water