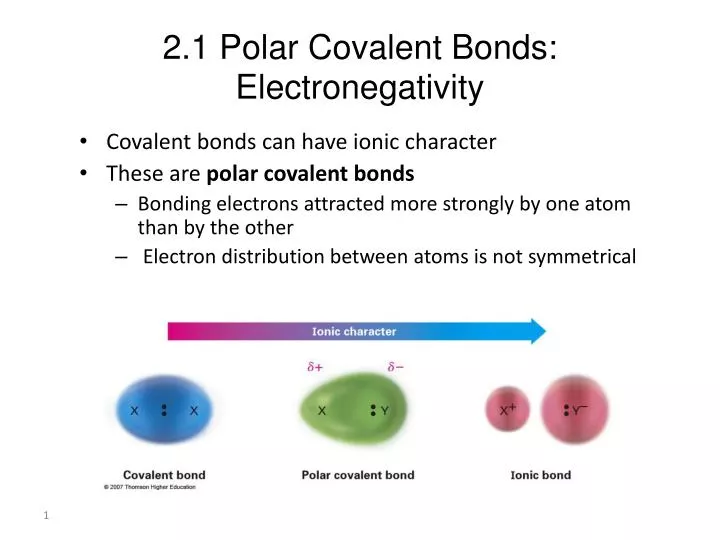
How do you determine polar and nonpolar bonds?
- Carbon has an electronegativity of 2.5, while the value for hydrogen is 2.1. The difference is 0.4, which is rather small. ...
- Both hydrogen atoms have the same electronegativity value—2.1. ...
- Sodium’s electronegativity is 0.9, while chlorine’s is 3.0. ...
- With 2.1 for hydrogen and 3.5 for oxygen, the electronegativity difference is 1.4. ...
What are some examples of polar and nonpolar bonds?
Polar molecules might be involved in hydrogen bonding between the charged poles of the bond. Nonpolar molecules usually have weaker intermolecular forces like van der Waal’s forces. Examples: Some examples of polar molecules are H 2 O, CHF 3, NH 3, etc. Some examples of nonpolar molecules are CO 2, H 2, benzene, etc.
What is the difference between polar and non - polar bonds?
Polar vs Nonpolar bonds: What is the Main Difference?
- Polar vs nonpolar bonds. E.N difference is greater than 0.4 E.N difference is less than 0.4
- Polar bond. Among many types of bonds, polar bonds are the bonds with atoms having a significant difference in their electronegativity values.
- Nonpolar bond. ...
- Geometrical non-polarity in molecules. ...
- Key Differences between polar and nonpolar bonds
- Concepts Berg. ...
What type of bond can be polar and non polar?
In simple terms, polar means oppositely charged, and non-polar means equally charged. Covalent bonds can be polar or non-polar. To understand the difference between polar and non-polar bonds, it is essential to comprehend electronegativity. What is meant by non polar?
What type of bond is a peptide bond?
covalent bondPeptide bond: A covalent bond joining the α-amino group of one amino acid to the carboxyl group of another with the loss of a water molecule.
How do you know if a peptide is polar?
Just a recap, if you have on the end a Hydroxyl group, so OH. You have an Amino group, like an NH2, or you have a Sulfhydryl group, like an SH group on the end, then that would tell you that you have a polar R-Group for that particular Amino acid.
Are peptide bond hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
hydrophobicThey are hydrophobic. About 5 amino acids have polar side chains, R-groups which do not ionize or become positively or negatively charged. These R-groups are neither strongly hydrophilic nor hydrophobic. Atoms in long molecules, such as polypeptides, are not rigidly fixed in space or position.
How do you identify a peptide bond?
A peptide bond is a chemical bond formed between two molecules when one molecule's carboxyl group interacts with the other molecule's amino group, releasing a water molecule (H2O). The resulting bond of CO-NH is considered a peptide bond, and an amide is the resulting molecule.
Is amino group polar or nonpolar?
Amino R-NH The amino group consists of a nitrogen atom attached by single bonds to hydrogen atoms. An organic compound that contains an amino group is called an amine. Like oxygen, nitrogen is also more electronegative than both carbon and hydrogen, which results in the amino group displaying some polar character.
Are amino acids polar or nonpolar?
Amino acids can also be characterised as polar or non-polar and these dictate the amino acid function. There are 10 non-polar amino acids found in protein core, and there are 10 polar amino acids.
Is a peptide bond a covalent bond?
Covalent bonds involve the equal sharing of an electron pair by two atoms. Examples of important covalent bonds are peptide (amide) and disulfide bonds between amino acids, and C-C, C-O, and C-N bonds within amino acids.
Is polar hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
To sum up, usually polar substances are not-hydrophobic (i.e they are hydrophilic), however some polar molecules such as nitriles, ketones and esters can be hydro-neutral (midway between hydrophobic and hydrophilic.
Is a peptide bond a hydrogen bond?
Hydrogen bonding between atoms in peptide bonds is a common theme in protein structure and forms the basis for all secondary structure. Figure 1 Amide hydrogen atoms carry a partial-positive charge. The nitrogen of the peptide bond carries a substantial amount of positive charge due to resonance.
How do you identify a peptide bond in larger molecules?
The carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid are involved in a peptide bond. How do you identify a peptide bond? Biuret test can be used to identify a peptide bond.
Which bond is a peptide bond quizlet?
What is a peptide bond? The covalent bond (C-N) formed by a condensation reaction between two amino acids; links the residues in peptides and proteins.
Are peptide bonds Ionic?
A peptide bond is a type of covalent bond between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid. Amino acids themselves are made of atoms joined together by covalent bonds.
Why do polar molecules have polar bonds?
Polar molecules must contain polar bonds due to a difference in electronegativity between the bonded atoms. A polar molecule with two or more polar bonds must have an asymmetric geometry so that the bond dipoles do not cancel each other.
What is the net dipole of a polar molecule?
A polar molecule has a net dipole as a result of the opposing charges (i.e. having partial positive and partial negative charges) from polar bonds arranged asymmetrically. (Wikipedia)
What is peptide bond?
A peptide bond joins together chains of amino acids, which are involved in the construction of proteins. Amino acids are comprised of several atoms like carbon, oxygen, nitrogen and hydrogen. {"error":true,"iframe":true}. You must c C reate an account to continue watching. Register to view this lesson.
What is nonpolar covalent bond?
Nonpolar covalent bonds are very strong bonds requiring a large amount of energy to break the bond. Nonpolar covalent bonds are extremely important in biology. They form the oxygen we breathe and help make up our living cells. One kind of nonpolar covalent bond that is very important in biology is called a peptide bond.
What type of bond is when two atoms share a pair of electrons with each other?
Nonpolar covalent bonds are a type of bond that occurs when two atoms share a pair of electrons with each other. These shared electrons glue two or more atoms together to form a molecule. Like children who share toys, atoms involved in a nonpolar covalent bond equally share electrons. An example of a nonpolar covalent bond is ...
How do you know if an atom has a chemical bond?
You may be wondering: How do you know what type of bond will occur between atoms? You can predict which type of bond will form by looking at the electronegativity of each atom involved in the bond. Electronegativity is how strongly an atom will attract electrons from another atom in a chemical bond. Some atoms have a higher electronegativity, while others have a lower electronegativity. Electronegativity is like a tug of war game between two atoms. If you have one person on the side of the rope that is stronger than the other person, then that stronger person will tug harder, pulling the other person in their direction. On the other hand, if you had two people of equal strength, then the rope would not shift in any one direction and would stay in the same place.
What happens to electrons in a nonpolar covalent bond?
In a nonpolar covalent bond, the atoms share electrons equally with one another.
Why does one atom have a stronger pull on electrons than the other?
This stronger pull causes electrons to be unequally shared and spend more time near the atom with the higher electronegativity.
How to remember polar covalent bonds?
To remember a polar covalent bond, instead say 'puller covalent,' and remember one atom has more 'pull' on electrons than the other atom. In a polar covalent bond, one atom spends more time with the electrons than the other. Your life actually depends on polar covalent bonding.
What Is a Polar Covalent Bond?
The periodic table is divided into two main sections, metals and non-metals. When two non-metals form a bond together, they form a covalent bond. These types of bonds rely on the sharing of a pair of electrons between the non-metals. Covalent bonds can be classified in one of two ways; polar covalent and nonpolar covalent.
What Is a Nonpolar Covalent Bond?
Nonpolar covalent bonds exist between two nonmetals which have little to no difference in the electronegativity of the two atoms. To classify for this label, the difference in electronegativity values needs to be less than 0.4 from the table shown in the first section.
Polar Covalent Bonds vs. Nonpolar Covalent Bonds
Polar covalent and nonpolar covalent bonds not only have different labels, but they also have a few key differences in properties due to the differences in bond types. The following chart outlines the similarities and differences in the properties of compounds that contain each type of bonds.
What Factors Determine Peptide Solubility?
Occasionally, one of the more difficult aspects of conducting research with synthetic peptides can be determining the most effective solvent in which to dissolve the peptide. Many peptides dissolve easily in aqueous solutions (sterile water), but some researchers may encounter problems related to low solubility or even insolubility, particularly when working with peptides that contain long sequences of hydrophobic amino acids. However, researchers can predict any one peptide’s solubility by studying the known characteristics of its individual amino acids.
How to predict peptide solubility?
To predict the solubility characteristics of a given peptide, the researcher must first evaluate the amino acid composition of the peptide, as the number and types of ionic charges in the peptide influence solubility.
What temperature should peptides be stored?
Once the peptide solution has been prepared, it should be aliquoted as necessary and stored at -20C (-4F). For those peptides containing cysteine, methionine, or tryptophan, prevent oxidation damage by storing them in an oxygen-free environment. ( Read more about Peptide Storage ).
How to dilute peptides?
Once the peptide has been successfully dissolved, dilute the peptide solution to the desired concentration by slowly adding the peptide solution into a buffered solution. Use gentle but constant agitation while combining to visually monitor and prevent localized concentration of the peptide in the aqueous solution. It is recommended to prepare the peptide stock solution at a higher concentration than is required by the experimental assay: the peptide stock solution can then be diluted further with the assay buffer.
Can peptides be solubilized?
Peptide Solubility Guidelines. Researchers should always test peptide solubility with a small amount of peptide in case ideal solubility is not initially achieved. Peptides should be allowed to warm to room temperature before attempting to dissolve them in solution.
Can peptides dissolve in water?
Many peptides dissolve easily in aqueous solutions (sterile water), but some researchers may encounter problems related to low solubility or even insolubility, particularly when working with peptides that contain long sequences of hydrophobic amino acids.
Do nonpolar amino acids dissolve in aqueous solutions?
Non-polar amino acids are hydrophobic (they do not dissolve in aqueous solutions). Peptides containing a relatively large number of non-polar amino acids or polar uncharged amino acids generally dissolve more effectively in organic solvents such as DMSO, propanol, isopropanol, methanol, or DMF.
Polar and Nonpolar Molecules
Such polar particles happen when two atoms do not take part in electrons equally in a covalent bond. A dipole type, with the particle’s position bringing a small favourable cost and the other part getting a small negative fee. This takes place when there is a variation in the Electronegativity of each atom.
B. Nonpolar Molecules
When particles share electrons uniformly in a covalent bond, there is no net electrical cost across the molecule. In a nonpolar covalent bond, the electrons are evenly dispersed. You can forewarn nonpolar molecules that will develop when atoms have the same or comparable Electronegativity.
Polar Covalent Bonds
Have you ever seen two kids play, and one kid appears challenging towards the various other children? The bully youngster shows up to invest even more time playing with the plaything than the other child. They are not consistently for sharing the toys.