How much water do you produce everyday from respiration?
Jun 15, 2020 · Similarly one may ask, where is the water produced in cellular respiration? The water molecules are produced in mitochondria, in the electron transport system, when the …
How would the lack of water affect cellular respiration?
May 21, 2020 · Water is formed when hydrogen and oxygen react to form H2O during the electron transport chain, which is the final stage of cellular respiration.
What role does cellular respiration play in the water cycle?
At the end of the electron transport chain, oxygen accepts electrons and takes up protons to form water. During cellular respiration, a glucose molecule is gradually broken down into carbon …
Where does the water go from cellular respiration?
Oct 17, 2010 · In the third stage of cellular respiration NADH is oxidised to NAD+ and water is produced by reduction of oxygen. In this stage energy and water are produced What 4 products …
Which cellular process produces water?
Can cellular respiration produce water?
At what point is water produced during cellular respiration quizlet?
What role does water play in cellular respiration?
What is cellular respiration, and why is it important?
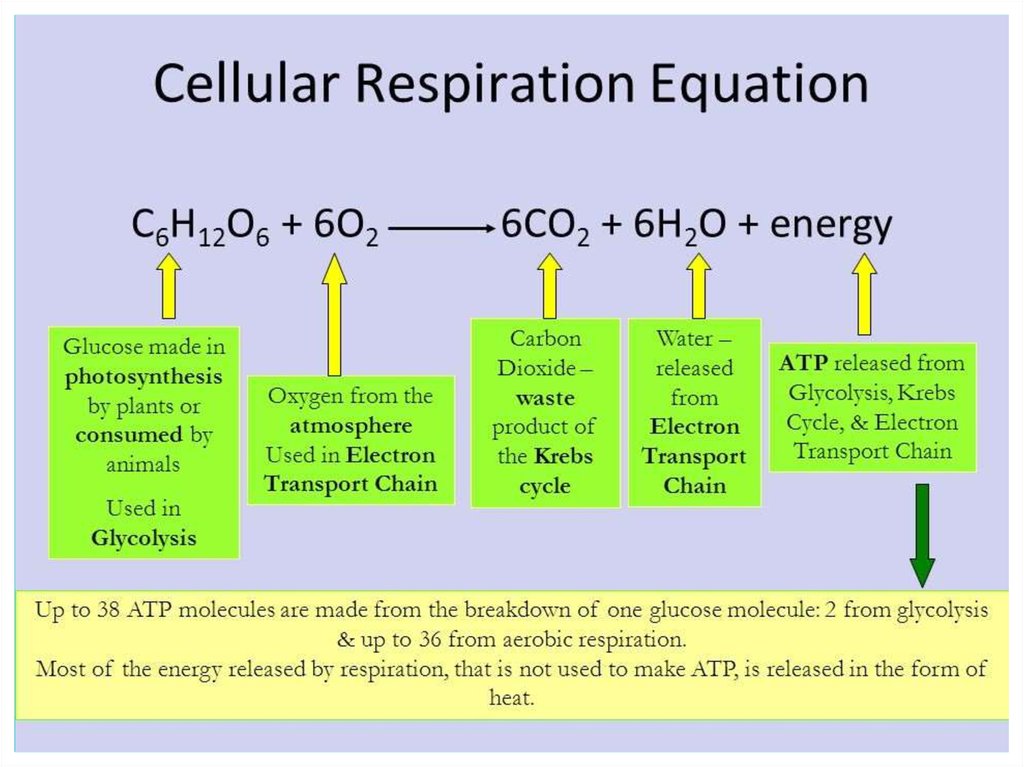
Cellular respiration involves a series of chemical reactions that break down organic compounds to produce energy in the form of ATP. This energy is...
What are the steps in aerobic respiration?
There are four main steps of aerobic respiration. They include glycolysis, transition reaction (this stage is also referred to as bridge reaction o...
What are aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration is a series of chemical reactions that involves breaking down food molecules to liberate the energy in them in the presence of...
What are the steps of cellular respiration?
The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
Is cellular respiration the most elegant metabolic pathway?
Cellular respiration is one of the most elegant, majestic, and fascinating metabolic pathways on earth. At the same time, it’s also one of the most complicated. When I learned about it for the first time, I felt like I had tripped and fallen into a can of organic-chemistry-flavored alphabet soup!
How is glucose converted into carbon dioxide?
To see how a glucose molecule is converted into carbon dioxide and how its energy is harvested as ATP and in one of your body's cells, let’s walk step by step through the four stages of cellular respiration. Glycolysis. In glycolysis, glucose—a six-carbon sugar—undergoes a series of chemical transformations. In the end, it gets converted ...
What happens to glucose in glycolysis?
In glycolysis, glucose—a six-carbon sugar—undergoes a series of chemical transformations. In the end, it gets converted into two molecules of pyruvate, a three-carbon organic molecule. In these reactions, ATP is made, and is converted to . Pyruvate oxidation.
What is the process of glycolysis?
In glycolysis, the beginning process of all types of cellular respiration, two molecules of ATP are used to attach 2 phosphate groups to a gluco se molecule, which is broken down into 2 separate 3-carbon PGAL molecules. PGAL releases electrons and hydrogen ions to the electron carrier molecule NADP+.
Where is NAD+ located?
NAD+ is an electron transport molecule inside the cristae of a cell's mitochondria. In glycolysis, the beginning process of all types of cellular respiration, two molecules of ATP are used to attach 2 phosphate groups to a glucose molecule, which is broken down into 2 separate 3-carbon PGAL molecules.
How does anaerobic respiration occur?
Anaerobic respiration in humans takes place when muscle undergoes extreme contraction as in vigorous exercise. When oxygen is limited, the oxidation of NADH to NAD+ by the electron transport chain is insufficient to maintain glycolysis. Under these conditions NAD+ is regenerated by the reduction of pyruvate to lactate.
Where are water molecules produced?
The water molecules are produced in mitochondria, in the electron transport system, when the electrons exit the final electron carrier of the respiratory chain in the inner mitochondri al membrane and are accepted by molecular oxygen, along with the binding of hydrogen ions (protons, H+) to form H2O.
Which enzyme transfers fatty acyl group from CoA to carnitine?
Another enzyme, known as Carnitine palmitoyltransferase I , which is present on the outer membrane of the mitochondria, transfers the fatty acyl group from CoA to carnitine. The new molecule called acylcarnitine is then transferred to the mitochondrial matrix via Carnitine acylcarnitine translocase protein.
What happens to glucose during glycolysis?
During glycolysis, glucose molecules (six-carbon molecules) are split into two pyruvates (three-carbon molecules) during a sequence of enzyme-controlled reactions. This is the same reaction as occurs in aerobic respiration. Without oxygen, pyruvate is converted to lactic acid in animals or ethanol in plants and yeast.
Where are fatty acids found?
It is found in the RER, Peroxisomes, and inside and on the outer membrane of mitochondria [1]. Oxidation of the fatty acids occurs in the mitochondrial matrix. Thus, free fatty acids need to be transported inside the mitochondria for its metabolism.