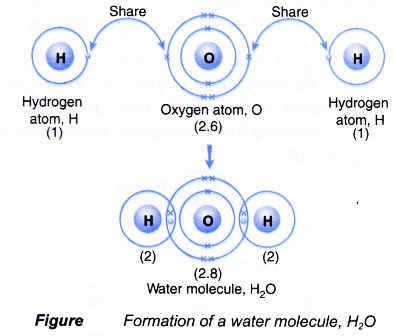
A covalent bond consists of the mutual sharing of one or more pairs of electrons between two atoms. These electrons are simultaneously attracted by the two atomic nuclei. A covalent bond forms when the difference between the electronegativities of two atoms is too small for an electron transfer to occur to form ions.
How do atoms form covalent bonds?
Covalent bonding occurs when pairs of electrons are shared by atoms. By sharing their outer most (valence) electrons, atoms can fill up their outer electron shell and gain stability. Subsequently, question is, how bonds are formed?
What type of bond is formed by sharing of electrons?
Covalent Bond A covalent bond is formed by equal sharing of electrons from both the participating atoms. The pair of electrons participating in this type of bonding is called shared pair or bonding pair. The covalent bonds are also termed as molecular bonds.
What is a shared pair in a covalent bond?
A covalent bond is formed by equal sharing of electrons from both the participating atoms. The pair of electrons participating in this type of bonding is called shared pair or bonding pair.
How do you classify a covalent bond?
Depending upon the number of shared electron pairs, the covalent bond can be classified into: A single bond is formed when only one pair of the electron is shared between the two participating atoms. It is represented by one dash (-).
Properties of Covalent Bond
If sharing a single electron pair between atoms does not satisfy an atom’s normal valence, the atoms may share more than one electron pair between them. Covalent bonds have the following properties:
Octet Rule
Except for noble gases, all atoms have fewer than eight electrons in their valence shell. In other words, these atoms’ valence shells do not have stable configurations. As a result, they combine with one another or with other atoms to form stable electronic configurations.
Types of Covalent Bonds
Depending upon the number of shared electron pairs, the covalent bond can be classified into Single Double and Triple Covalent Bond.
Sample Questions
Atoms with eight electrons in their final orbit are stable and do not react. Atoms with fewer than eight electrons react with other atoms to gain eight electrons in their outermost orbit and thus become stable. Atoms with slightly more than eight electrons may lose them to atoms with fewer than eight.