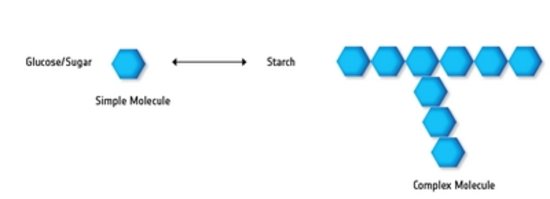
What are the differences between starch and glucose?
What are the Similarities Between Glucose and Starch?
- Glucose and starch are two types of carbohydrates.
- Both molecules consist of elements like carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O).
- These molecules are extremely important for humans that are taken through the diet.
- Both molecules have the same stoichiometric formula; (CH 2 O)n.
- They are both made up of monomers called monosaccharides.
Why starch must be digested to glucose?
glucose, galactose, fructose)
- Foods that contain glucose like grapes, dried apricots, honey and soft drinks.
- Foods that contain galactose like celery, beetroot, basil, spinach, kiwi fruit and plums.
- Foods that contain fructose like most fruit, soft drinks, sports drinks, cakes, confectionery and chocolate.
Why is starch needed to store glucose?
- Starch-Based Vegan Diets And Diabetes: The Science-Backed Truth No One Wants You To Know
- Scientists Identify 28,000 Medicinal Plants That Treat Ailments from Cancer to Diabetes
- 18 MEDICINAL PLANTS FOR TREATING DIABETES
How does starch turn into glucose?
When the stomach digests food, the carbohydrate (sugars and starches) in the food breaks down into another type of sugar, called glucose. The stomach and small intestines absorb the glucose and then release it into the bloodstream. Once in the bloodstream, glucose can be used immediately for energy or stored in our bodies, to be used later.
Is there a glucose in starch?
Starch is a chain of glucose molecules which are bound together, to form a bigger molecule, which is called a polysaccharide. There are two types of polysaccharide in starch: Amylose – a linear chain of glucose. Amylopectin – a highly branched chain of glucose.
How many units of glucose are in starch?
Amylopectin has 12-20 glucose units between the branches. Natural starches are mixtures of amylose and amylopectin. In glycogen, the branches occur at intervals of 8-10 glucose units, while in amylopectin the branches are separated by 10-12 glucose units.
What glucose is starch made of?
Starch is made from glucose, a sugar molecule made up of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) with a basic chemical formula C6H12O6. Since it is only made of glucose, starch is considered a homosaccharaide, a chain of sugars made of one type of molecule.
What is starch made up of?
Starch consists of the two glucose polymers amylopectin and amylose, which together form insoluble, semi-crystalline starch granules (Fig. 1; see [12] for a comprehensive review). Both polymers are made of α-1,4-linked glucan chains connected with α-1,6-branch points, but their structure and biosynthesis are distinct.
How is glucose produced from starch?
Commercially, glucose is obtained on a large scale by hydrolysis of starch, by boiling at 393 K with dilute sulphuric acid under pressure. Excess sulphuric acid is neutralized by adding chalk powder. Activated charcoal is used for the removal of coloured impurities.
What is glucose made of?
This molecule of the sugar glucose consists of 6 carbon atoms bonded together as a chain with additional atoms of oxygen and hydrogen.
What is the chemical formula of starch?
(2R,3S,4S,5R,6R)-2-(hydroxymethyl)-6-[(2R,3S,4R,5R,6S)-4,5,6-trihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-3-yl]oxy-oxane-3,4,5-triolStarch / IUPAC ID
Where is glucose found?
glucose, also called dextrose, one of a group of carbohydrates known as simple sugars (monosaccharides). Glucose (from Greek glykys; “sweet”) has the molecular formula C6H12O6. It is found in fruits and honey and is the major free sugar circulating in the blood of higher animals.
Where is starch found?
Starch is a complex carbohydrate that is found in potatoes, whole grains and cereal grains, which consists of numerous glucose strands. Eventually, all complex carbohydrates -- with the exception of fiber -- are digested into glucose. Starch is a simple sugar, which is the smallest form of carbohydrate, and is the main source ...
What happens when you chew on a starch?
As you chew, the glands in your mouth secrete saliva. Some of the enzymes in your saliva pull off those glucose branches from the starches before the enzymes send them down to your small intestine. Additional enzymes in your small intestine finish the conversion process, fully turning the starches into glucose.
How does glucose get into the bloodstream?
Glucose absorbs through intestinal walls and enters your bloodstream rather quickly. Whole foods, such as fresh produce, also contain fiber, which delays glucose absorption. Whole foods also minimize the chance that a spike in blood sugar will occur.
Is starch a carbohydrate?
Starch is a simple sugar, which is the smallest form of carbohydrate, and is the main source of energy for all cells. While both starch and glucose are considered carbohydrates, they have different effects in your body.
Which foods have the highest starch content?
These 5 foods contain high starch content: Whole-grain Pasta. Whole-grain pasta has a higher ratio of fiber to starch than refined pasta, making it a better choice if you are looking to eat less starch. Russets. To reduce your starch intake when eating potatoes, choose a low-starch variety like Russet.
What is starch in food?
Starch is a carbohydrate commonly found in nature and one of the primary sources of food energy for human beings. It is regularly eaten in the form of wheat, rice, potatoes, and other staple foods cultivated throughout the world.
How much starch is in a potato?
A single, medium-sized potato has about 31 g of starch. They are also simple carbohydrates, so they won’t keep you satiated for long. Potatoes are often consumed with unhealthy additives such as butter, sour cream, salt, and bacon bits. Popular potato dishes can be high in carbohydrates and fat leading to weight gain.
Why is starch bad for diabetes?
Because starch is a complex carbohydrate, eating less of it is believed to help people with diabetes manage their blood sugar levels. In one study of 28 participants who ate a low carbohydrate diet, 17 were able to reduce their use of blood sugar medication, and some even discontinued their use of medication entirely.
Which has more starch, white bread or whole wheat?
Whole wheat bread retains an intact bran, germ, and endosperm, whereas white bread only has the endosperm. The additional bran and germ in whole wheat gives you less starch and more fiber than white bread. Brown Rice. A cup of brown rice has 40 g of starch.
How much starch is in white rice?
A cup of white rice that has 44 g of starch. The processing process of white rice removes its bran and germ which contain the majority of nutrients. However, rice in the United States is often enriched with some nutrients such as iron, and B vitamins. Corn. Corn is one of the starchiest of staple foods.
How many carbs are in spaghetti?
A cup of cooked spaghetti has 43 grams (g) of carbohydrates, 36 of which come from starch. Pasta is a simple carbohydrate which means your body breaks it down into glucose (energy) quickly which causes a spike in your blood sugar.
What are the best sources of starch?
Some excellent sources of healthy starch include: vegetables, legumes, beans and whole grains. Healthy starches contain minerals and vitamins, natural sugar, and dietary fiber [2]. These nutrients are instrumental in maintaining a healthy diet as they can help protect from certain diseases like heart disease, help to control weight (and can even help with weight loss), and provide you with a source of long-lasting energy. That being said, we also have to keep in mind that a number of starch choices contain not only carbs, but protein and fat as well—making them one of the most complex components of our dietary intake.
What are some good foods to eat to get rid of starch?
Some things to consider when making starch choices: Eat more legumes. Peas, beans and lentils. They are usually low in fat and contain some necessary vitamins and minerals.
How many carbs are in a diabetic's food list?
All of the foods listed contain- 15 grams of carb, 1 gram of fat, 3 grams of protein and are 80 calories [3]. This list can serve as a guide when evaluating the amount of starch (carbohydrates from starch) that you ingest daily.
What to eat to lower glycemic index?
Choose whole grains. “Whole” wheat pasta, “whole” grain pita bread and crackers are a couple of choices. These foods also contain vitamins, minerals and fiber, and tend to have a lower glycemic index than their refined starch counterparts. So go forth without fear and consume starches wisely.
What are the three main types of carbohydrates?
There are 3 main types of carbohydrates: fiber, sugar and starch. Some examples of starchy foods include grains and pasta (including whole grains and whole wheat pasta), white rice and brown rice, breads and crackers, starchy vegetables like white potatoes, sweet potatoes, and other root vegetables, beans (such as kidney beans and black beans), ...
Is starch a bad thing?
For most of us, it is the bane of our existence. Starches are a large part of the dietary intake of most Americans. When we think about starches the one that immediately comes to mind for most of us is bread, followed by rice and potatoes. For most people with diabetes, starches are considered the forbidden food.
Do starches raise blood sugar?
Generally, starches (complex carbohydrates) will cause blood sugar levels to rise if you have diabetes. But, starches should not be seen as the enemy. They have health benefits and are necessary for our bodies to function properly on a balanced diet [1].
How many grams of starch are in a potato?
Potato Starch and Glucose. Of the 64.46 grams of carbohydrates in a potato, 56.97 grams exist in the form of starch. Starch is a complex carbohydrate that consists of multiple glucose molecules attached together. Because the body converts the carbohydrates it consumes into glucose, potatoes are easily digested and have a high glycemic index, ...
What are carbohydrates made of?
Carbohydrate Basics. All carbohydrates are composed of one or more sugar molecules. Complex carbohydrates, or starches, are composed of more than two sugar molecules, while simple carbohydrates, or sugars, are composed of two or less. When the body consumes carbohydrates, they are converted to natural sugar, glucose, where they are used for energy.
Why do potatoes have a high glycemic index?
Because the body converts the carbohydrates it consumes into glucose, potatoes are easily digested and have a high glycemic index, or the rate at which carbohydrates cause a rise in blood glucose levels after you eat something. Advertisement.
Why is russet potato glycemic?
The glycemic load was created to provide a better reflection of a particular food's effect on blood sugar and nutritional value. While a russet potato has a high glycemic index, it has a much lower glycemic load, with a measure of 23. Advertisement.
What is the glycemic index of potatoes?
Glycemic Index of Potatoes. A glycemic index of 70 or above is considered high, and potatoes have glycemic indexes ranging from about 58 to 111, depending on the variety and how they are cooked. For example, a russet potato has a glycemic index of 76. Foods that have a high glycemic index often face scrutiny in the weight-loss community because ...
Why do carbohydrates take longer to digest?
Because of their more complex chemical structure, complex carbohydrates take longer to be absorbed and have a more gradual effect on blood glucose levels, while simple sugars are digested quickly and provide quick energy. Advertisement.
How many carbs are in a potato?
Carbohydrates in Potatoes. One large potato with both the flesh and the skin, weighing 369 grams, contains 64.46 grams of carbohydrates, according to the USDA Nutrient Database. An adult who consumes a 2,000-calorie diet generally needs about 225 to 325 grams of carbohydrates each day.
Energy
Starch is the most important energy source for humans. The body digests starch by metabolizing it into glucose, which passes into the bloodstream and circulates the body. Glucose fuels virtually every cell, tissue, and organ in the body. If there is excess glucose, the liver stores it as glycogen.
Fiber
Dietary fiber is a nondigestible carbohydrate that only exists in plant-based foods. Foods rich in starch, such as corn, beets, potatoes, beans, fruits, and whole grains, are abundant fiber sources. Although the body does not digest fiber, this carb is an essential part of a nutritious diet.
Fullness
Eating starchy foods may help increase satiety, which is the feeling of being full, after eating.
What is the difference between cellulose and starch?
There is only one difference. In starch, all the glucose repeat units are oriented in the same direction. But in cellulose, each succesive glucose unit is rotated 180 degrees around the axis of the polymer backbone chain, relative to the last repeat unit. When bigshot scientists are talking bigshot scientist talk they say that the glucose units in starch are connected by alpha linkages, and that the glucose units in cellulose are connected by beta linkages. Does this make any difference? It makes a lot of difference! The most important difference in the way the two polymers behave is this: You can eat starch, but you can't digest cellulose. Your body contains enzymes that will break starch down into glucose to fuel your body. But we humans don't have enzymes that can break down cellulose. Some animals do, like termites, who eat wood, or cattle, who eat grass, and break down cellulose in their four-chambered stomachs. So unless you're a termite or a cow, don't try to nourish yourself on woodchips. Cellulose is a lot stronger than starch. Starch is practically useless as a material, but celluose is strong enough to make fibers from, and hence rope, clothing, etc. Cellulose doesn't dissolve in water the way starch will, and doesn't break down as easily. Breaking down or dissolving in water just would be a little too inconvenient for something we use to make clothes. Not to mention, a good soaking rain would wash away all the woo Continue reading >>
How are starch and cellulose made?
Did you know that the polymers starch and cellulose are both made by plants? In fact, plants make both starch and cellulose by connecting glucose molecules together. Every time they add a glucose to make the chain longer, a water molecule pops out! Add a glucose, out pops H2O! Add a glucose, out pops H2O! And so on and so on until the chains are really long. A starch chain can have 500 to 2 million glucose units. Cellulose can have 2,000 - 14,000 glucoses. That's a lot of sweetness! Glucose is a funny little molecule. Glucose likes to be in a ring, but sometimes the ring opens up. (Why? Why not? You can stand up, you can sit down. So sometimes you stand up!) When the ring closes again, the -OH can be pointed down, or it can be pointed out. Either way, it's still glucose! The -OH is pointed down instead of out. (We didn't draw in the C and H atoms that just hang out. See? The -OH is pointed outward instead of down. Look at the blue H atoms. They've moved around, but they're still there. (By the way, here in science land we call these molecules isomers, because they're made up of the same atoms that are put together differently.) Compare this guy to the other open chain form on the left. It's almost the same, but one of the bonds turned around, making the red O point up instead of down. Yep, it's allowed to do that! It's like swinging your arm around. Energy or Strength? Starch to store energy Plants really know how to use glucose. To make starch, they use α-glucose, with the -OH pointed down. That -OH is right where the next glucose will go. Since that one -OH is pointing down, it gives the chain a built-in curve. That curve is what makes starch so good for storing glucose. The starch polymer curls around and makes a nice little package. Many starch polymers have a lot Continue reading >>
What is the most common storage carbohydrate in plants?
Starch is the commonest storage carbohydrate in plants. It is used by the plants themselves, by microbes and by higher organisms so there is a great diversity of enzymes able to catalyse its hydrolysis. Starch from all plant sources occurs in the form of granules which differ markedly in size and physical characteristics from species to species. Chemical differences are less marked. The major difference is the ratio of amylose to amylopectin; e.g. corn starch from waxy maize contains only 2% amylose but that from amylomaize is about 80% amylose. Some starches, for instance from potato, contain covalently bound phosphate in small amounts (0.2% approximately), which has significant effects on the physical properties of the starch but does not interfere with its hydrolysis. Acid hydrolysis of starch has had widespread use in the past. It is now largely replaced by enzymic processes, as it required the use of corrosion resistant materials, gave rise to high colour and saltash content (after neutralisation), needed more energy for heating and was relatively difficult to control. Figure 4.2. The use of enzymes in processing starch.Typical conditions are given. Of the two components of starch, amylopectin presents thegreat challenge to hydrolytic enzyme systems. This is due to the residuesinvolved in a-1,6-glycosidic branch points which constitute about4 - 6% of theglucose present. Most hydrolytic enzymes are specific for a-1,4-glucosidic linksyet the a-1,6-glucosidic links must also be cleaved for complete hydrolysis ofamylopectin to glucose. Some of the most impressive recent exercises in thedevelopment of new enzymes have concerned debranching enzymes. It is necessary to hydrolyse starch in a wide variety ofprocesses which m be condensed into two basic classes: processes i Continue reading >>
What is sugar converted to?
Sugar is converted to ethanol, carbon dioxide and yeast/bacterial biomass as well as much smaller quantities of minor end products such as glycerol, fusel oils, aldehydes and ketones (Laopaiboon et al ., 2007; Jacques et al ., 1999). In the distillation section, alcohol from fermented mash is concentrated up to 95% v/v. This is further concentrated to produce ethanol with 99.6% v/v (minimum) concentration. The treatment of vinasse generated in the distillation section can be done using the following option: concentration of part of vinasse to 20 to 25% solids followed by composting using press mud available and concentration of the rest of the vinasse to 55% solids and can be used as liquid fertilizer. The schematic representation of ethanol fermentation from sweet sorghum stalk is given in Figure 2. The ethan ol production processing from sweet sorghum grain and bagasse is similar to other starchy crops like corn and cassava (Quintero et al ., 2008). Chemically starch is a polymer of glucose (Peterson, 1995). Yeast cannot use starch directly for ethanol production. Therefore, grain starch has to be completely broken down to glucose by a combination of two enzymes, viz., amylase and amyloglucosidase, before it is fermented by yeast to produce ethanol (Figures 2 and 3). After washing, crushing and milling the sweet sorghum grains, the starch is gelatinized, liquefied and saccharified using -amylase and amyloglucosidase. Fermentation, distillation and dehydration processing of grain sorghum are similar to the sweet sorghum stalk. However, the by-products of grain are not similar to the stalk because DDGS (dried distillers grains with solubles) as a co-product of the ethanol production process from grain is a high nutrient valued feed which is used by the livestock industr Continue reading >>
What are the three elements that make up carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates (also called saccharides) are molecular compounds made from just three elements: carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Monosaccharides (e.g. glucose) and disaccharides (e.g. sucrose) are relatively small molecules. They are often called sugars. Other carbohydrate molecules are very large (polysaccharides such as starch and cellulose). Carbohydrates are: a source of energy for the body e.g. glucose and a store of energy, e.g. starch in plants building blocks for polysaccharides (giant carbohydrates), e.g. cellulose in plants and glycogen in the human body components of other molecules eg DNA, RNA, glycolipids, glycoproteins, ATP Monosaccharides Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrates and are often called single sugars. They are the building blocks from which all bigger carbohydrates are made. Monosaccharides have the general molecular formula (CH2O)n, where n can be 3, 5 or 6. They can be classified according to the number of carbon atoms in a molecule: n = 3 trioses, e.g. glyceraldehyde n = 5 pentoses, e.g. ribose and deoxyribose ('pent' indicates 5) n = 6 hexoses, e.g. fructose, glucose and galactose ('hex' indicates 6) There is more than one molecule with the molecular formula C5H10O5 and more than one with the molecular formula C6H12O6. Molecules that have the same molecular formula but different structural formulae are called structural isomers. Glyceraldehyde's molecular formula is C3H6O3. Its structural formula shows it contains an aldehyde group (-CHO) and two hydroxyl groups (-OH). The presence of an aldehyde group means that glyceraldehyde can also be classified as an aldose. It is a reducing sugar and gives a positive test with Benedict's reagent. CH2OHCH (OH)CHO is oxidised by Benedict's reagent to CH2OHCH (OH)COOH; the aldehyde group is oxidised to Continue reading >>
How much carbohydrate should I eat a day?
The objective was to achieve a healthier lifestyle.1 The latest guidelines from the Institute of Medicine recommend a daily carbohydrate intake of up to 65% of daily food intake.2 The catastrophic result has been an epidemic of life-threatening obesity, type II diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and other diseases.2 The reason is simple. Starch is one of the largest dietary sources of blood sugar and dangerous after-meal blood glucose spikes.3,4 Even if you eat so-called “healthy grains” such as whole wheat and brown rice, these all convert into sugar during digestion.5 Fortunately, researchers have uncovered a dual-action enzyme known as transglucosidase (pronounced trans-gluco-side-ace) that blocks the conversion of starch into sugar and tranforms it into beneficial fiber.6 While you can’t eliminate all starch from your diet, you can neutralize its negative impact on your body. Transglucosidase represents a novel mechanism for protecting against the harmful effects of dietary starch. Impressive laboratory studies have shown that when transglucosidase comes in contact with starchy foods and natural enzymes in the digestive tract, there’s a 31% reduction in rapidly digested starch (the kind that causes blood sugar to spike right after a meal) and an 11% increase in slowly digested starch (which gets converted to sugar more slowly, if at all).7 Together, that means approximately 40% of the starch you ingest is less likely to be rapidly absorbed into your bloodstream. Human clinical studies have confirmed the ability of transglucosidase to reduce blood glucose and insulin levels. F Continue reading >>
What is starch made of?
What is Starch? Starch is a type of carbohydrate formed by long strings of glucose units bonded together–also known as a “polysaccharide (poly=many; saccharide=sugars).”. By contrast, simple sugars (or simple carbs) are individual sugars (monosaccharides such as fructose) or 2 sugar units held together by a single bond (such as lactose, ...
How is starch produced?
Starch is produced by plants through photosynthesis and stored as granules as a source of nutrition for the plant to grow and stay healthy. It might be in the seed (as in the case of corn) or tuber (in the case of a potato ). When we eat foods with starch, we are consuming this nutrition in the form of carbohydrates.
How to test blood glucose levels?
Here’s an interesting test you can try so you understand how foods impact your blood glucose levels. Day 1. Eat a low carb breakfast, for instance, a mixed veggie egg scramble or some egg muffins. Measuring the change in your blood glucose over 2 hours and record the number. Day 2.
How is resistant starch digested?
Resistant starch is digested differently to other starches. It passes through the small intestine undigested – similar to solu ble fiber . It makes its way to the colon where it is then fermented by microbes that produce byproducts called short chain fatty acids – butyrate, acetate and propionate.
How to measure glucose change?
Measuring the change in your blood glucose over 2 hours and record the number. Eat a breakfast of complex higher-form carbs – say oatmeal. Measuring the change in your blood glucose over 2 hours and record the number. Then, compare the two numbers .
What is the most common form of carbohydrate consumed in modern diets?
Starch is the most common form of carbohydrate consumed in modern diets. To us, we all know these foods as ‘staples.’
What are some healthy carbs?
These are what some people refer to as “ healthy carbs ,” which include: whole grains, oats, sweet potatoes, beans, lentils etc – foods with complex carbohydrates that are also high in fiber.
What is a snack high in refined starch?
Pretzels are a popular snack high in refined starch.
How much starch is in a cup of sorghum flour?
One cup (121 grams) of sorghum flour contains 82 grams of starch, or 68% by weight. Although it is high in starch, sorghum flour is a much better choice than most types of flour. That’s because it is gluten-free and an excellent source of protein and fiber. One cup contains 10.2 grams of protein and 8 grams of fiber ( 19.
How much starch is in saltine crackers?
In addition, they are very high in starch. For instance, a serving of five standard saltine crackers (15 grams) contains 11 grams of starch, or 67.8% by weight ( 26 ).
How many carbs are in cornmeal?
Although cornmeal contains some nutrients, it is very high in carbs and starch. One cup (159 grams) contains 126 grams of carbs, of which 117 grams (74%) is starch ( 8 ).
How many carbs are in a packet of instant noodles?
In addition, they are typically high in fat and carbs. For instance, a single packet contains 54 grams of carbs and 13.4 grams of fat ( 32 ). Most of the carbs from instant noodles come from starch. A packet contains 47.7 grams of starch, or 56% by weight.
How many grams of rice krispies are in a serving?
They are often fortified with vitamins and minerals. A 1-ounce (28-gram) serving contains over a third of your daily needs for thiamine, riboflavin, folate, iron, and vitamins B6 and B12. That said, Rice Krispies are highly processed and incredibly high in starch.
What is the main carbohydrate in the diet?
Starch is the main carbohydrate in the diet and a major part of many staple foods. In modern diets, foods high in starch tend to be highly refined and stripped of their fiber and nutrients. These foods include refined wheat flour, bagels and cornmeal. To maintain a healthy diet, aim to limit your intake of these foods.
How are sucrose, glucose and starch related?
Sucrose, glucose and starch are related because they're all forms of carbohydrate. One of the essential macronutrients in foods along with protein and fat, carbohydrates supply energy to your body. Carbohydrates, which consist of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, are classified according to their chemical makeup. Glucose is a single sugar molecule that your body can absorb directly in the intestine. Sucrose and starches are carbohydrates formed by two or more sugars bonded together. The sugars in sucrose and starch must be broken down into glucose molecules in the gastrointestinal tract before your intestines can absorb them. Classifications Carbohydrates are classified by the number of sugar units, called saccharides, that they contain. A monosaccharide is one basic sugar unit that cannot be further broken down. Few foods are monosaccharides. Disaccharides are two monosaccharides linked together. Monosaccharides and disaccharides are also called simple sugars. Starches and fiber, the indigestible parts of plants, are polysaccharides, meaning that they contain many saccharide molecules linked together. Your body can only absorb monosaccharides directly; all other carbohydrates must be broken down into monosaccharides before they can enter your bloodstream from the small intestine. Glucose, a monosaccharide, is a form of sugar absorbed through the intestine into your bloodstream. Foods do not contain pure glucose, although diabetics sometimes carry pure glucose tablets or gels to raise their blood sugar quickly if they develop hypoglycemia, the medical term of low blood sugar. Many foods contain glucose mixed with another sugar; fruits, for example, often contain glucose and fructose. Glucose makes up the main energy source for the human body. Sucrose is the scientific name f Continue reading >>
What is starch made of?
Starch is an inexpensive thickener, water binder, and gelling agent. Starch is is the most abundant biomolecule on earth after cellulose and the major carbohydrate reserve in plant tubers and seed endosperm. It is found as granules [ 330 , 1758 ] each typically containing several million amylopectin molecules accompanied by a much larger number of smaller amylose molecules. By far the largest source of starch is corn (maize) with other commonly used sources being wheat, potato, tapioca, and rice. Amylopectin (without amylose) can be isolated from 'waxy' maize starch whereas amylose (without amylopectin) is best isolated after specifically hydrolyzing the amylopectin with pullulanase [ 405 ]. Genetic modification of starch crops has recently led to the development of starches with improved and targeted functionality [ 593 ]. Starch consists of two types of molecules, amylose (normally 20-30%) and amylopectin (normally 70-80%). Both consist of polymers of -D-glucose units in the 4 C1 conformation. In amylose these are linked - (1 4)-, with the ring oxygen atoms all on the same side, whereas in amylopectin about one residue in every twenty or so is also linked - (1 6)- forming branch-points. The relative proportions of amylose to amylopectin and - (1 6)- branch-points both depend on the source of the starch, for example, amylo-maizes contain over 50% amylose whereas 'waxy' maize has almost none (~3%) [ 260 ]. Representative partial structure of amylose Representative partial structure of amylopectin Amylose and amylopectin are inherently incompatible molecules; amylose having lower relative molecular mass (molecular weight) with a relatively extended shape whereas amylopectin has huge but compact molecules. Determination of the molecular mass distribution of starch molecules Continue reading >>
What are the three elements that make up carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates (also called saccharides) are molecular compounds made from just three elements: carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Monosaccharides (e.g. glucose) and disaccharides (e.g. sucrose) are relatively small molecules. They are often called sugars. Other carbohydrate molecules are very large (polysaccharides such as starch and cellulose). Carbohydrates are: a source of energy for the body e.g. glucose and a store of energy, e.g. starch in plants building blocks for polysaccharides (giant carbohydrates), e.g. cellulose in plants and glycogen in the human body components of other molecules eg DNA, RNA, glycolipids, glycoproteins, ATP Monosaccharides Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrates and are often called single sugars. They are the building blocks from which all bigger carbohydrates are made. Monosaccharides have the general molecular formula (CH2O)n, where n can be 3, 5 or 6. They can be classified according to the number of carbon atoms in a molecule: n = 3 trioses, e.g. glyceraldehyde n = 5 pentoses, e.g. ribose and deoxyribose ('pent' indicates 5) n = 6 hexoses, e.g. fructose, glucose and galactose ('hex' indicates 6) There is more than one molecule with the molecular formula C5H10O5 and more than one with the molecular formula C6H12O6. Molecules that have the same molecular formula but different structural formulae are called structural isomers. Glyceraldehyde's molecular formula is C3H6O3. Its structural formula shows it contains an aldehyde group (-CHO) and two hydroxyl groups (-OH). The presence of an aldehyde group means that glyceraldehyde can also be classified as an aldose. It is a reducing sugar and gives a positive test with Benedict's reagent. CH2OHCH (OH)CHO is oxidised by Benedict's reagent to CH2OHCH (OH)COOH; the aldehyde group is oxidised to Continue reading >>
How are polysaccharides made?
They are constructed by animals and plants from simpler, monosaccharide molecules, by joining together large numbers of the simpler molecules using glycosidic bonds (-O-). In some of the largest polysaccarhide structures there can be 10,000 individual units joined together. There is a large diversity of polysaccharide form; they can differ in the type of sugar, the connections between the sugars and the complexity of the overall molecule. Sometimes known as glycans, there are three common and principal types of polysaccharide, cellulose, starch and glycogen, all made by joining together molecules of glucose in different ways. It has been estimated that 50% of the world's organic carbon is found in one molecule; cellulose. This molecule is synthesized, stored, modified and used as a building material by plants. It is certainly the most abundant of all the polysaccharides. In the cellulose molecule the individual glucose monosaccharides are all linked to one another in the form of a long, long, linear chain. The carbon atom number 1 (C1) in one sugar is linked to the fourth carbon atom (C4) of the next sugar in an extended array. All the glucose molecules in cellulose have the beta-configuration at the C1 atom, so all the glycosidic bonds that join the glucose molecules together are also of the beta type. This means that the cellulose molecule is straight, and many such molecules can lay side by side in a parallel series of rows. Tiny forces called hydrogen bonds hold the glucose molecules together, and the chains in close proximity. Although each hydrogen bond is very, very weak, when thousands or millions of them form between two cellulose molecules the result i Continue reading >>
What are the two main components of carbohydrates?
The carbohydrates are the compounds which provide energy to living cells. They are compounds of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen with a ratio of two hydrogens for every oxygen atom. The carbohydrates we use as foods have their origin in the photosynthesis of plants. They take the form of sugars , starches , and cellulose . The name carbohydrate means "watered carbon" or carbon with attached water molecules. Many carbohydrates have empirical formuli which would imply about equal numbers of carbon and water molecules. For example, the glucose formula C6H12O6 suggests six carbon atoms and six water molecules. The sugars are the carbohydrates which are used directly to supply energy to living organisms. A key group of the sugars have the molecular formula C6H12O6. This group includes glucose , which may exist in either straight-chain or ring forms. Others are fructose , galactose, and mannose. Such sugars are called monosaccharides. Pairs of ring-form sugars can link to form disaccharides such as common table sugar (sucrose), lactose, and maltose. More complicated linked structures form polysaccharides. Starches are carbohydrates in which 300 to 1000 glucose units join together. It is a polysaccharide which plants use to store energy for later use.Starch forms in grains with an insoluble outer layer which remain in the cell where it is formed until the energy is needed. Then it can be broken down into soluble glucose units. Starches are smaller than cellulose units, and can be more readily used for energy. In animals, the equivalent of starches is glycogen, which can be stored in the muscles or in the liver for later use. Foods such as potatoes, rice, corn and wheat contain starch granules which are important energy sources for humans. The human digestive process breaks down th Continue reading >>
How are starch and cellulose made?
Did you know that the polymers starch and cellulose are both made by plants? In fact, plants make both starch and cellulose by connecting glucose molecules together. Every time they add a glucose to make the chain longer, a water molecule pops out! Add a glucose, out pops H2O! Add a glucose, out pops H2O! And so on and so on until the chains are really long. A starch chain can have 500 to 2 million glucose units. Cellulose can have 2,000 - 14,000 glucoses. That's a lot of sweetness! Glucose is a funny little molecule. Glucose likes to be in a ring, but sometimes the ring opens up. (Why? Why not? You can stand up, you can sit down. So sometimes you stand up!) When the ring closes again, the -OH can be pointed down, or it can be pointed out. Either way, it's still glucose! The -OH is pointed down instead of out. (We didn't draw in the C and H atoms that just hang out. See? The -OH is pointed outward instead of down. Look at the blue H atoms. They've moved around, but they're still there. (By the way, here in science land we call these molecules isomers, because they're made up of the same atoms that are put together differently.) Compare this guy to the other open chain form on the left. It's almost the same, but one of the bonds turned around, making the red O point up instead of down. Yep, it's allowed to do that! It's like swinging your arm around. Energy or Strength? Starch to store energy Plants really know how to use glucose. To make starch, they use α-glucose, with the -OH pointed down. That -OH is right where the next glucose will go. Since that one -OH is pointing down, it gives the chain a built-in curve. That curve is what makes starch so good for storing glucose. The starch polymer curls around and makes a nice little package. Many starch polymers have a lot Continue reading >>
What is the most important source of carbohydrates in plants?
Starch is the chief storage form of carbohydrate in plants and the most important source of carbohydrate in human nutrition. A starch molecule is a polysaccharide assembled from the simple sugar glucose ; it can contain anywhere from five hundred to several hundred thousand glucose molecules joined by covalent bonds into a single structure. In addition to its importance in human nutrition, starch has many industrial applications: it is used in the manufacture of paper, textiles, pharmaceuticals, and biodegradable polymers, and it is an additive in foods. Chemically, starch is composed of two different molecules, amylose and amylopectin. In amylose, the glucose molecules are linked in a "linear" fashion; however, the tetrahedral chemistry of carbon (and the bond angles that result from this chemistry) gives amylose an overall spiral shape. Amylopectin, on the other hand, has a linear arrangement of glucose molecules that includes, at regular intervals, a different kind of linkage between two adjacent glucoses. This different linkage results in the formation of a branched structure and an overall treelike shape for this molecule. Plant starch is typically 20 to 30 percent amylose and 70 to 80 percent amylopectin. The classic test for the presence of starch is reaction with iodine. If starch molecules are present in a substance, the addition of iodine yields a deep blue color, which results from I 2 being trapped inside the spiral structures of amylose molecules. Starch molecules are broken down by enzymes known as amylases. The digestibility of a specific starch is influenced by its physical form. In plants starch is present in microscopic granules, which impair the enzymatic digestion of starch molecules obtained from plants. Cooking starch-containing items results in t Continue reading >>