How many milligrams are in 1 unit of insulin?
26/12/2017 · The U refers to actual units of active insulin. Units are a standard measurement system for many drugs. A U-100 insulin has 100 units of active insulin in each mL of liquid. You can think of it as being 100 pieces of insulin in each mL of liquid. A U-40 insulin has 40 units of insulin in each milliliter (mL) of liquid.
What is the difference between units and concentration of insulin?
Each small black mark equals 0.01 ml. Considering this, How many units are in 10 mL of insulin? That means there are 100 units of insulin in each milliliter (mL) of insulin. Humalog® insulin comes in 3 mL (300 units) vials or 10 mL (1000 units) vials. All other types of insulin come in 10 mL (1000 units) vials.
How much insulin is in a vial of insulin?
18/03/2020 · Each small black mark equals 0.01 ml. Considering this, How many units are in 10 mL of insulin? That means there are 100 units of insulin in each milliliter (mL) of insulin. Humalog® insulin comes in 3 mL (300 units) vials or 10 mL (1000 units) vials. All other types of insulin come in 10 mL (1000 units) vials.
How many units in a U100 syringe of insulin?
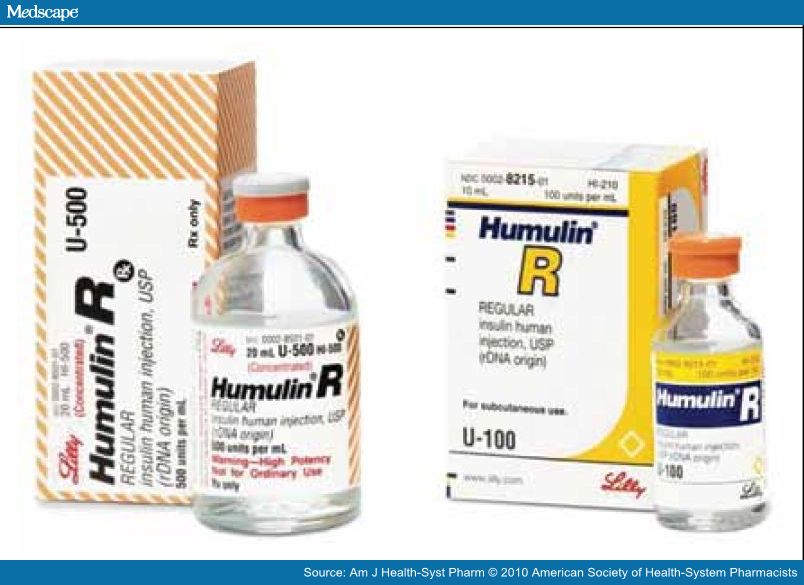
06/02/2019 · 100 Units of insulin per 1mL (milliliter) U500 stands for: 500 Units of insulin per 1mL (milliliter) So, if you have a U100 insulin product, and you need to inject 50 units, that would come out to 0.5 mL. Similarly, if you have a U500 insulin product, and you need to inject 50 units, that would come out to 0.1 mL.
What is 1 unit of insulin in mL?
0.3 mL syringes are for insulin doses under 30 units of insulin and are numbered at 1-unit intervals. 0.5 mL syringes are for 30 to 50 units of insulin and are numbered at 1-unit intervals. 1.0 mL are for doses more than 50 units of insulin and are numbered at 2 units per interval.
How many mL is 30 units of insulin?
0.3 milliliters30 units of a U-100 insulin are equal to 0.3 milliliters (0.3 ml).02-Mar-2015
How many units is 40 mL of insulin?
How to Convert Insulin Units to Milliliters (ml) Using U-100 InsulinTo administer this amount of U-100 insulinDraw to this level in a 1 ml syringe38 units0.38 mls39 units0.39 mls40 units0.40 mls41 units0.41 mls46 more rows•18-Mar-2020
Is 1 unit the same as 1 mL?
Although it is labeled in “units” at the bottom of the syringe, each unit actually is one-hundredth of a milliliter (0.01 ml or 0.01 cc).
How many units is 300 mL of insulin?
Now, logically starting at the logical start, a 3ml pen of U-100 insulin has 300 units, as there are 100 units per mL, which is where the whole “U-100” thing comes from (3 x 100 = 300).
How many units of insulin is 0.15 mL?
To administer 3 to 90 micrograms: 30 unit insulin or 0.3 milliliter syringeMicrograms (mcg)cc or ml syringeInsulin syringe30 micrograms0.10 milliliters10 units45 micrograms0.15 milliliters15 units60 micrograms0.20 milliliters20 units90 micrograms0.30 milliliters30 units9 more rows
How many units is 100 mL of insulin?
Each ml contains 100 units insulin glargine* (equivalent to 3.64 mg). Each cartridge contains 3 ml of solution for injection, equivalent to 300 units. *Insulin glargine is produced by recombinant DNA technology in Escherichia coli.
How many mL is an IU?
IU/L↔IU/mL 1 IU/mL = 1000 IU/L.
What is a unit of insulin?
Officially, one unit is defined at the biological equivalent of 34.7 micrograms of pure crystalline insulin, a measure that comes from the dawn of insulin, and just happens to be the amount required to induce hypoglycemia in a rabbit (don't ask).01-Jun-2018
How do you convert insulin units to milliliters?
The correct conversion factor between conventional and SI units for human insulin is 1 μIU/mL = 6.00 pmol/L.13-Oct-2018
How many units are in a mL of insulin syringe?
100Syringe size and unitsSyringe sizeNumber of units the syringe holds1/4 mL or 0.25 mL251/3 mL or 0.33 mL301/2 mL or 0.50 mL501 mL100
How do you convert insulin units to mL mL using U 40 insulin?
U40 insulin has 40 units of insulin in every ml and the U100 has 100 units. Therefore when converting from a U40 syringe to a U100 syringe you are required to multiply your U40 units by 2.5.08-Jun-2020
What is the fastest insulin?
For example, there are several 'rapid' acting insulin analogs, and have a faster onset of action than human insulin products. These include: 1 Insulin aspart (Novolog) 2 Insulin lispro (Humalog) 3 Insulin glulisine (Adipra)
Why isn't insulin listed in milligrams?
There is also another, very important reason, why insulin products aren't listed in milligrams and that has to do with the existence of Insulin analogs. Insulin analogs and human insulin technically use the same conversion (1 Unit = 0.0347 milligrams) and are considered 'equipotent'.
What does U100 mean in insulin?
The insulin products you get at the pharmacy will always be labeled in units, or as a concentration in terms of units (e.g., U100 means 100 units of insulin per 1mL of liquid). The term 'units' refers to International Units (IU), which is a measure of the "biological activity" of a specific drug or substance. ...
How many units of insulin are needed for a U100?
Insulin products are listed in terms of a concentration, such as U100 or U500. So, if you have a U100 insulin product, and you need to inject 50 units, that would come out to 0.5 mL. Similarly, if you have a U500 insulin product, and you need to inject 50 units, that would come out to 0.1 mL. You can convert between units and mL for ...
Which insulin has a faster onset of action than human insulin?
These include: Insulin aspart (Novolog) Insulin lispro (Humalog) Insulin glulisine (Adipra) There are also long-acting insulin analogs, with a longer duration of action than NPH insulin.
Can you use U100 syringes for insulin?
For example, you cannot use U100 syringes if you are utilizing a U500 insulin product. Drawing up half-way, to 0.5 mL, on a U100 syringe will equal a dose of 50 units of a U100 insulin.
What is NPH insulin?
NPH (Neutral Protamine Hagedorn) insulin is also known as isophane insulin and is intermediate-acting. It is regular human insulin with added zinc and protamine, which causes a delay in absorption and prolongs the duration of action.
How Are Insulin Syringes Calibrated?
Insulin, a human hormone, is taken by diabetics to control blood glucose levels. Insulin can not be swallowed because it will not survive digestion, and is most commonly injected subcutaneously (under the skin) in the abdomen.
Misuse Of New Insulin Strengths. U 200, U 300, U 500 ..
We certainly have important education to accomplish with patients and health professionals regarding the new higher concentration insulin products that are available only in a pen, including U-300 TOUJEO (insulin glargine), U-200 TRESIBA (insulin degludec), and U-200 HUMALOG (insulin lispro).
Math Calculations With Humulin Insulin
www.TakeRx.com Calculate the total quantity and the total days supply for the following drug: Humulin N (U-100); #10 mL vial; Sig: 18 units AM and 26 units PM ------------------------------------------------------------ The total quantity to be dispensed is 10 mL as stated by the doctor.
How To Read An Insulin Syringe
As with all medicine, it is important to take the right dose each time Injecting yourself with the right dose of insulin is very important. This is why you need to know how to read a syringe. Parts of an Insulin Syringe An insulin syringe has three parts: a needle, a barrel and a plunger. The needle is short and thin.
Syringe Capacity And Dose Scale
Left to right: 3/10 cc syringe with half-unit markings 3/10 cc syringe with whole unit markings 1/2 cc syringe 1 cc syringe BD insulin syringes are available in these sizes: If your dose is… Use this capacity syringe 30 units or less, measured in whole or half-units 3/10 cc/mL (30 units) with half-unit markings 31 to 50 units 1/2 cc/mL (50 units) 51 to 100 units 1 cc/mL (100 units) Choose the smallest syringe that's big enough to hold the largest dose you take in a day.
How I Find My Dose Of Hcg On An Injection Syringe
Finding the Right HCG Injection Dose. When you are new to the hCG diet, and HCG Injections, it can be pretty overwhelming. Phrases like “syringe” “iu’s” and “bac water” can really throw us off and make the HCG diet feel intimidating. But it doesn’t have to be that way.
Insulin Delivery Options
There are many ways to take NovoLog®. You and your health care provider will choose the way that works best for you. Some people take their insulin injection using a vial and syringe or an insulin pump. But many people who take NovoLog® use an insulin pen called NovoLog® FlexPen®.
Why is glargine soluble in acid?
Glargine forms a depot effect because it is only soluble at an acidic pH.1 In the vial (pH 4) , the drug is completely soluble. Once injected, the solution is neutralized to biologic pH (7.4), which causes the insulin molecules to precipitate. These microprecipitates slowly dissolve over a 24-hour period.
What is the U in insulin?
The U refers to actual units of active insulin.
How many units of insulin are in a U-40?
You can think of it as being 100 pieces of insulin in each mL of liquid. A U-40 insulin has 40 units of insulin in each milliliter (mL) of liquid. This means that the same volume (liquid amount) of a U-100 insulin has 2.5 times more insulin in it than a U-40 insulin.
Is U-100 insulin stronger than U-40?
Or, the U-100 insulin is 2.5 times stronger than the U-40 insulin. Most commercially available insulins are U-100 and the syringes we purchase at the pharmacy are U-100 syringes. U-100 syringes are specially designed to provide the proper dose of U-100 insulin.
What is the function of a plunger?
Its function is to either draw the insulin into the barrel or push the insulin out of the barrel through the needle.
Can you use U-100 insulin with U-40?
If you use a U-100 insulin and a U-100 syringe, you fill the syringe the way the vet showed you. If you use a U-40 insulin and the U-40 syringes that are provided with that insulin, you fill the syringe in the normal manner and don't need to do any conversions.
What is insulin shock therapy?
For the psychiatric treatment, see Insulin shock therapy. Insulin is used as a medication to treat high blood sugar. [3] . This includes in diabetes mellitus type 1, diabetes mellitus type 2, gestational diabetes, and complications of diabetes such as diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic states. [3] .