Do all animal cells have Golgi bodies?
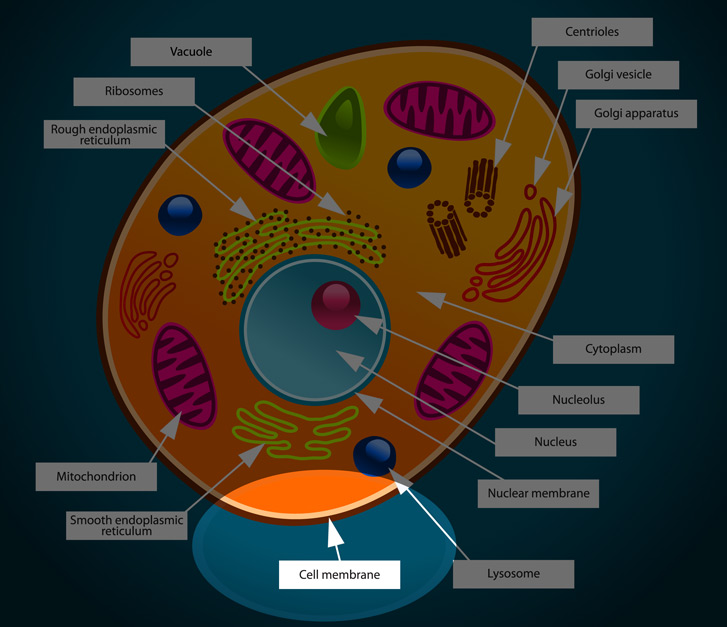
Quick look: Golgi apparatus(or complex, or body, or 'the 'Golgi') is found in all plant and animal cells and is the term given to groups of flattened disc-like structures located close to the endoplasmic reticulum. Destination 1: within the cell, to organelles called lysosomes.
Do animal cells have contractile vacuoles?
Animal cells have small sized vacuoles whereas plant cells have large vacuoles. It provides turbidity and rigidity to the plant cell. It acts as storage sacs of cell and stores food, water, sugar, ... What is the function of contractile vacuoles in the cell quizlet?
Do plant cells and animal cells both have a nucleolus?
They hold the DNA, which is the genetic material that tells the cell what to do. Protists, fungi, animals, and plants all have a nucleolus inside the nucleus. All cells have ribosomes. They are organelles in cytoplasm and on rough Endoplasmic Reticulum that make proteins. Click to read full detail here. Thereof, do fungal cells have a nucleus?
Do animal and plant cells have a cell membrane?
Plant cells are somewhat unique because unlike animal cells, plant cells contain both a cell wall and cell membrane. Animal cells only have the cell membrane. The cell membrane is a semi-permeable covering surrounding the outside of the cell. Plant cell membranes are found on the outside of the cell cytoplasm and just inside the cell wall.
Is there a endoplasmic reticulum in an animal cell?
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in animal cells is an extensive, morphologically continuous network of membrane tubules and flattened cisternae.
How many parts does endoplasmic reticulum have?
two subunitsIt is a type of organelle made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER).
Is the endoplasmic reticulum in plant and animal cells?
Key Takeaways. A cell's endoplasmic reticulum (ER) contains a network of tubules and flattened sacs. The ER performs multiple functions in both plant and animal cells. Endoplasmic reticulum has two major regions: smooth endoplasmic reticulum and rough endoplasmic reticulum.
Is rough ER in plant and animal cells?
RER occurs in both animal and plant cells.
What is the endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of tubules and flattened sacs that serve a variety of functions in plant and animal cells . The two regions of the ER differ in both structure and function. Rough ER has ribosomes attached to the cytoplasmic side of the membrane. Smooth ER lacks attached ribosomes.
What is the role of the endoplasmic reticulum in eukaryotic cells?
It plays a major role in the production, processing, and transport of proteins and lipids. The ER produces transmembrane proteins and lipids for its membrane and many other cell components including lysosomes, secretory vesicles, ...
What is the Golgi complex?
Golgi Complex: composed of groupings of flattened sacs known as cisternae, the Golgi generates, processes, stores, and ships cellular products. Lysosomes: membrane-bound sacs of enzymes that digest cellular macromolecules. Mitochondria: organelles that provide energy for the cell by performing cellular respiration.
What are the structures of eukaryotic cells?
The following cell structures can also be found in a typical animal eukaryotic cell: Centrioles: cylindrical groupings of microtubules found in animal cells but not plant cells.
Which cells produce antibodies?
In certain leukocytes (white blood cells), the rough ER produces antibodies. In pancreatic cells, the rough ER produces insulin. The rough and smooth ER are usually interconnected and the proteins and membranes made by the rough ER move into the smooth ER to be transferred to other locations.
What are the protrusions of a cell that aid in movement and cellular locomotion?
Cilia and flagella : protrusions from a cell that aid in movement and cellular locomotion. Cell membrane: a thin, semi-permeable membrane that surrounds the cytoplasm and encloses the contents of a cell. It protects the integrity of the interior of the cell. Cytoskeleton: a network of fibers throughout the cytoplasm that helps support ...
What is the endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a large, dynamic structure that serves many roles in the cell including calcium storage, protein synthesis and lipid metabolism. The diverse functions of the ER are performed by distinct domains; consisting of tubules, sheets and the nuclear envelope. Several proteins that contribute to ...
How big are ribosomes in eukaryotes?
aER sheets and tubules have a diameter of 30–50 nm in eukaryotes. Eukaryotic ribosomes are 25–30 nm and localize to the flat regions of ER sheets, giving the sheets a rough appearance (rough ER). Ribosomes are present in much lower numbers on tubules, giving the tubules a more smooth appearance (smooth ER).
What enzymes are involved in rab10?
Rab10 was found to co-localize with several lipid-synthesizing enzymes, including phosphoinositol synthase (IS) and choline/ethanolamine phosphotransferase (CEPT1) [71], leading to the possibility that this may represent a previously unidentified ER subdomain or compartment.
What is the ER?
The ER is the largest organelle in the cell and is a major site of protein synthesis and transport, protein folding, lipid and steroid synthesis, carbohydrate metabolism and calcium storage [1–7]. The multi-functional nature of this organelle requires a myriad of proteins, unique physical structures and coordination with ...
Do frogs have calcium transients?
Frogs, as well as sea urchin [143] and starfish [133, 144] have a single calcium transient at fertilization [145]. Other animals, including mice and humans, have multiple smaller calcium transients following fertilization, and these differences may be reflected in the ER organization in mature eggs [145].
What is the endoplasmic reticulum?
Endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranes inside a cell through which proteins and other molecules move.
Why is the endoplasmic reticulum engorged?
They're retained and the endoplasmic reticulum becomes engorged because it seems to be constipated, in a way, ...
Which organelle is a workhorse in producing proteins and substances needed by the rest of the cell?
So the endoplasmic reticulum is an organelle that's really a workhorse in producing proteins and substances needed by the rest of the cell. William Gahl, M.D., Ph.D.