How many core electrons does uranium have? Uranium is a chemical element of atomic number 92, meaning there are 92 electrons orbiting 92 protons and about 143 neutrons. The protons and neutrons make up the center nucleus of an atom, and contributes to almost all the mass of the atom.
How many neutrons are there in uranium?
How many neutrons does uranium have? 143 neutrons. What is the number of protons in a ...
What are facts about uranium?
radioactive gas produced naturally by uranium decay in rocks and soil. Without proper testing, there is no way to know whether radon is in your home. Here are three facts you should know about radon. Radon causes cancer Radon is “as cancer-causing as ...
What is the number of protons in uranium - 238?
Uranium-238 has 92 protons, 92 electrons and 146 neutrons.The mass number is 238 and the atomic number is 92. Number of particles find in an atom of uranium 238? Uranium 238 has: 92 protons, 92 electrons, 146 neutrons; protons and neutrons has quarks and gluons.
How many protons neutrons and electrons have uranium 238?
Write the symbol for this isotope. The atomic number of uranium (see periodic table) is 92, and the mass number of the isotope is given as 238. Therefore, it has 92 protons, 92 electrons, and 238 — 92 : 146 neutrons.
How many electrons does uranium have?
2,8,18,32,21,9,2Uranium / Electrons per shell
How many shells does uranium have?
Data ZoneClassification:Uranium is an actinide metalElectrons:92Protons:92Neutrons in most abundant isotope:146Electron shells:2,8,18,32,21,9,27 more rows
How many neutrons do uranium have?
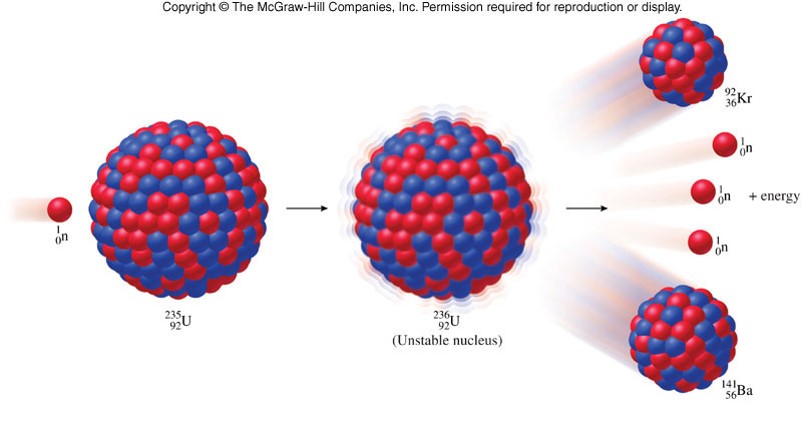
143 neutronsEnergy from the uranium atom The nucleus of the U-235 atom comprises 92 protons and 143 neutrons (92 + 143 = 235).
How many protons are in uranium?
92Uranium / Atomic number
How many electrons does uranium-235 have?
A neutrally charged atom of uranium-235 will have 92 electrons orbiting its nucleus.
Can you touch uranium?
With a half-life of 4 billion years, uranium is only very weakly radioactive. In fact, since uranium is a heavy metal, its chemical toxicity is actually more of a danger than its radioactivity. If you touch it directly with your hands, you should wash your hands afterwards. You should not eat it.
How many protons and electrons does uranium have?
Uranium is a silvery-white metallic chemical element in the periodic table, with atomic number 92. It is assigned the chemical symbol U. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons.
How many protons neutrons and electrons does uranium-235 have?
In the nucleus of each atom of uranium-235 (U-235) are 92 protons and 143 neutrons, for a total of 235.
Can you eat uranium?
Eating large doses of uranium would be very dangerous; if you consumed 25 milligrams of it, you'd immediately start to experience kidney damage, and anywhere past 50 milligrams could cause complete kidney failure and even death.
How do you find number of electrons?
The number of electrons in an atom is equal to the atomic number of an element, for neutrally charged species. This means the number of electrons and the number of protons in an element are equal. Therefore, the number of electrons in oxygen is 8.
How much uranium is in a nuke?
According to the Union of Concerned Scientists, a nuclear bomb needs about 33 pounds (15 kilograms) of enriched uranium to be operational.
What is the full electron configuration for uranium?
[Rn] 5f3 6d1 7s2Uranium / Electron configuration
How many shells can an atom have?
Each successive shell can only hold a certain number of electrons. The innermost shell is filled first. This shell can contain a maximum of two electrons. The second shell can hold a maximum of eight electrons....Electron shells.Energy shellMaximum number of electronsFirst2Second8Third8
Can you make a sword from uranium?
Posted: Fri 19 Mar, 2004 3:04 pm Post subject: Is it possible to forge a sword out of depleted uranium? That would be interesting. There's no such thing as truly depleted uranium, so it would be considerably more radioactive than, for instance, almost any other metal.
What are uranium bullets?
SILVER BULLET made from depleted uranium can pierce even the heaviest armor. Uranium shells burn away at the edges upon impact¿a "self-sharpening" that helps them bore into armor. Used as ammunition, it penetrates the thick steel encasing enemy tanks; used as armor, it protects troops against attack.
What are the 4 quantum numbers for uranium?
Uranium Atomic and Orbital Properties Uranium atoms have 92 electrons and the electronic shell structure is [2, 8, 18, 32, 21, 9, 2] with Atomic Term Symbol (Quantum Numbers) 5L6.
How many protons are in Uranium?
Uranium is a chemical element with atomic number 92 which means there are 92 protons in its nucleus. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number of the atom and is given the symbol Z. The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to 1,602 x 10-19 coulombs.
What is the mass number of isotopes of Uranium?
Mass numbers of typical isotopes of Uranium are 238, 235.
What is the oxidation number of an element?
and the term oxidation number is nearly synonymous. An element that is not combined with any other different elements has an oxidation state of 0. Oxidation state 0 occurs for all elements – it is simply the element in its elemental form. An atom of an element in a compound will have a positive oxidation state if it has had electrons removed. Similarly, adding electrons results in a negative oxidation state. We have also distinguish between the possible and common oxidation states of every element. For example, silicon has nine possible integer oxidation states from −4 to +4, but only -4, 0 and +4 are common oxidation states.
How do neutrons stabilize the nucleus?
Neutrons stabilize the nucleus, because they attract each other and protons , which helps offset the electrical repulsion between protons. As a result, as the number of protons increases, an increasing ratio of neutrons to protons is needed to form a stable nucleus. If there are too many or too few neutrons for a given number of protons, the resulting nucleus is not stable and it undergoes radioactive decay . Unstable isotopes decay through various radioactive decay pathways, most commonly alpha decay, beta decay, or electron capture. Many other rare types of decay, such as spontaneous fission or neutron emission are known. It should be noted that all of these decay pathways may be accompanied by the subsequent emission of gamma radiation. Pure alpha or beta decays are very rare.
What is the periodic table?
The periodic table is a tabular display of the chemical elements organized on the basis of their atomic numbers , electron configurations, and chemical properties. The electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements.
What is the number of neutrons in an atom?
The total number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called the neutron number of the atom and is given the symbol N. Neutron number plus atomic number equals atomic mass number: N+Z=A. The difference between the neutron number and the atomic number is known as the neutron excess: D = N – Z = A – 2Z.
How are the chemical properties of a solid, liquid, gas, and plasma determined?
The chemical properties of the atom are determined by the number of protons, in fact, by number and arrangement of electrons. The configuration of these electrons follows from the principles of quantum mechanics. The number of electrons in each element’s electron shells, particularly the outermost valence shell, is the primary factor in determining its chemical bonding behavior. In the periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number Z.
Overview
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weakly radioactive because all isotopes of uranium are unstable; the half-lives of its naturally occurring isotopes range between 159,200 years and 4.5 billion years…
Characteristics
When refined, uranium is a silvery white, weakly radioactive metal. It has a Mohs hardness of 6, sufficient to scratch glass and approximately equal to that of titanium, rhodium, manganese and niobium. It is malleable, ductile, slightly paramagnetic, strongly electropositive and a poor electrical conductor. Uranium metal has a very high density of 19.1 g/cm , denser than lead (11.3 g/cm ), but sli…
Applications
The major application of uranium in the military sector is in high-density penetrators. This ammunition consists of depleted uranium (DU) alloyed with 1–2% other elements, such as titanium or molybdenum. At high impact speed, the density, hardness, and pyrophoricity of the projectile enable the destruction of heavily armored targets. Tank armor and other removable vehicle armor can …
History
The use of uranium in its natural oxide form dates back to at least the year 79 CE, when it was used in the Roman Empire to add a yellow color to ceramic glazes. Yellow glass with 1% uranium oxide was found in a Roman villa on Cape Posillipo in the Bay of Naples, Italy, by R. T. Gunther of the University of Oxford in 1912. Starting in the late Middle Ages, pitchblende was extracted from the Habsburg silver mines in Joachimsthal, Bohemia (now Jáchymov in the Czech Republic), and was …
Occurrence
Along with all elements having atomic weights higher than that of iron, uranium is only naturally formed by the r-process (rapid neutron capture) in supernovae and neutron star mergers. Primordial thorium and uranium are only produced in the r-process, because the s-process (slow neutron capture) is too slow and cannot pass the gap of instability after bismuth. Besides the two extant primordial ura…
Compounds
Calcined uranium yellowcake, as produced in many large mills, contains a distribution of uranium oxidation species in various forms ranging from most oxidized to least oxidized. Particles with short residence times in a calciner will generally be less oxidized than those with long retention times or particles recovered in the stack scrubber. Uranium content is usually referenced to U 3…
Isotopes
Natural uranium consists of three major isotopes: uranium-238 (99.28% natural abundance), uranium-235 (0.71%), and uranium-234 (0.0054%). All three are radioactive, emitting alpha particles, with the exception that all three of these isotopes have small probabilities of undergoing spontaneous fission. There are also four other trace isotopes: uranium-239, which is formed when U undergoe…
Human exposure
A person can be exposed to uranium (or its radioactive daughters, such as radon) by inhaling dust in air or by ingesting contaminated water and food. The amount of uranium in air is usually very small; however, people who work in factories that process phosphate fertilizers, live near government facilities that made or tested nuclear weapons, live or work near a modern battlefield where depleted uranium weapons have been used, or live or work near a coal-fired power plant, fa…