How many ATP are produced from acetyl CoA?
How many ATP are produced from acetyl CoA? Every acetyl-CoA yields 3 NADH + 1 FADH2 + 1 GTP (=ATP) during Krebs cycle. Considering an average production of 3 ATP/NADH and 2 ATP/FADH2 using the respiratory chain, you have 131 ATP molecules.
How many ATP are produced by beta oxidation?
The NADH and FADH2 produced by both beta oxidation and the TCA cycle are used by the mitochondrial electron transport chain to produce ATP. Complete oxidation of one palmitate molecule (fatty acid containing 16 carbons) generates 129 ATP molecules.
How many ATP are produced per 20-carbon fatty acid?
A) About 1,200 ATP molecules are ultimately produced per 20-carbon fatty acid oxidized. B) One FADH2 and two NADH are produced for each acetyl-CoA. Can you then calculate how many ATP? Since 1 NADH2 = 3 ATP and 1 FADH2 = 2 ATP, total ATP formed are 34.
How many ATP molecules are produced in glycolysis?
Considering an average production of 3 ATP/NADH and 2 ATP/FADH2 using the respiratory chain, you have 131 ATP molecules. Click to see full answer. Besides, how many ATP molecules are produced in glycolysis? One glucose molecule produces four ATP, two NADH, and two pyruvate molecules during glycolysis.
How many ATP are produced from pyruvate to acetyl CoA?
GlycolysisPyruvate Acetyl-CoAProducts2 pyruvate 4 ATP 2 NADH2 Acetyl-Coa 2 NADH 2 CO2ATP required2NoneATP produced4NoneNet ATP2None2 more rows
How many ATP are produced in oxidation?
The theoretical maximum yield of ATP for the oxidation of one molecule of glucose during aerobic respiration is 38.
How many ATP are produced in TCA?
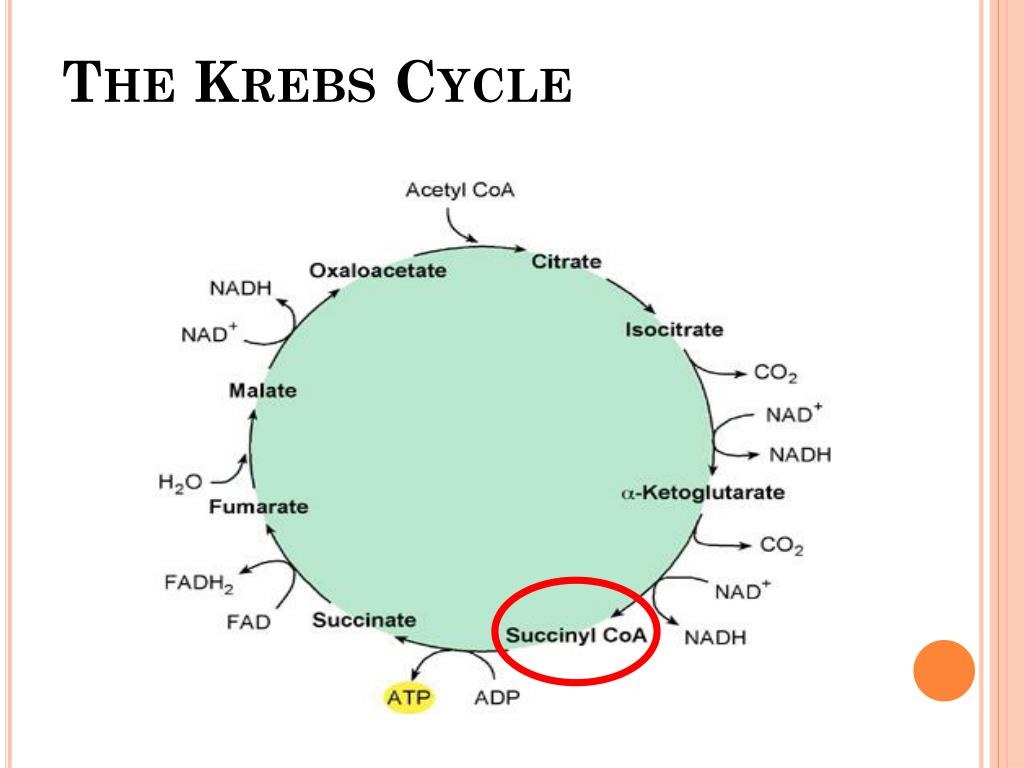
2 ATPs are produced in the TCA cycle per glucose molecule (2 acetyl CoA). ATP is produced when Succinyl CoA produces succinate by the enzyme succinyl CoA synthetase. It is important to note that most of the ATP produced in cellular respiration account for oxidative phosphorylation in the electron transport chain.
How many ATP will be produced during the production of 1 molecule of acetyl CoA?
Acetyl CoA produces 12 ATP molecules accounting for 3 NADH (9 ATP), 1 FADH2 (2 ATP) and 1 GTP (1 ATP) in the TCA cycle and oxidative phosphorylation in the electron transport system.
What is the final yield of acetyl CoA molecules from the oxidation of a 16 carbon fatty acid?
A 16-carbon fatty acid will yield 8 molecules of acetyl-CoA after complete beta oxidation (16/2 = 8).
What is the number of ATP obtained from one acetyl CoA in the citric acid cycle?
Citric Acid Cycle Summary In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle uses one molecule of acetyl CoA to generate 1 ATP, 3 NADH, 1 FADH2, 2 CO2, and 3 H+.
How is 36 ATP produced?
Explanation: Out of 36 ATP molecules 2 are produced in glycolysis outside mitochondria and the rest of the ATP molecules are produced inside mitochondria in the Krebs cycle and electron transport chain (respiratory chain).
What is the oxidation of acetyl CoA?
The acetate of acetyl CoA undergoes a stepwise oxidation to carbon dioxide and water in a cyclic pathway, the citric acid cycle, shown in Figures 5.17 and 5.18. This pathway is sometimes known as the Krebs cycle, after its discoverer, Sir Hans Krebs.
What is the citric acid cycle?
Although it appears complex at first sight, the citric acid cycle is a simple pathway. A four-carbon compound, oxaloacetate, reacts with acetyl CoA to form a six-carbon compound, citric acid. The cycle is then a series of steps in which two carbon atoms are lost as carbon dioxide, followed by a series of oxidation and other reactions, ...
What is the precursor to gluconeogenesis?
Although, as discussed below (section 5.7), oxaloacetate is the precursor for gluconeogenesis, fatty acids and other compounds that give rise to acetyl CoA ...
Can oxaloacetate be withdrawn from gluconeol?
Therefore, when acetyl CoA is the substrate, there is no increase in the pool of citric acid cycle intermediates, and therefore oxaloacetate cannot be withdrawn for gluconeogenesis.