How does the skin on your palm differ from your forearm?
How does the skin on your palm differ from that on the back (posterior) of your hand? The palm doesnt have hair follicles, and and it has an extra skin layer for protection. Describe the differences you observed in the type and distribution of hair on the front and back of your forearm Anterior has more hair because it has a thicker layer of skin.
Why does the palm have hair on the inside?
The palm doesnt have hair follicles, and and it has an extra skin layer for protection. Anterior has more hair because it has a thicker layer of skin. Hair is a protein filled with keratin that grows from epidermal (layer of skin) cells below the hair follicles. Melanocytes cells produce pigment Melanin that gives hair black color.
Why do my hands and feet look so different from others?
The skin on your hands and feet is noticeably different from that on most other areas of your body. Unlike those other areas, the skin on your palms and soles doesn't have hair. And when you soak in water, most of your skin looks normal while your hands and feet wind up looking like wrinkled prunes.
How does the dermis connect to the epidermal layer?
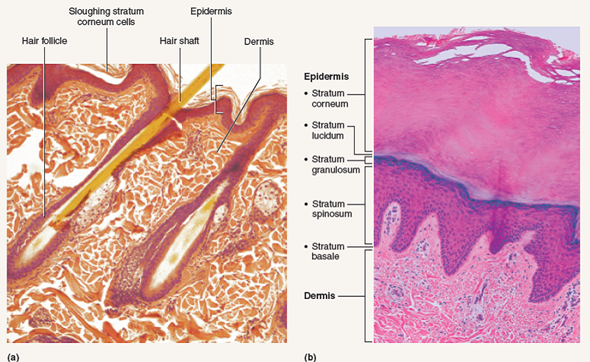
The middle layer of skin, the dermis, connects to the epidermal layer through many papillae, which are tiny fingerlike projections of connective tissue. Fingerprints and footprints result when double rows of papillae occur.
How does skin on Palm differ from back of hand?
How does the skin of your palm differ from that on the back of your hand? The skin on your palm is thick skin. Think skin has an extra layer of skin for protection and does not grow hair as where the back of your hand is thin skin, grows hair, and the nerve endings are closer to the surface making it more sensitive.
Is the skin on the palm of your hand is thicker than the skin on the back of your hand?
The main difference is the thickness of the epidermis and dermis, which are the top two layers of skin. Thin skin covers most of the body and can vary in thinness, with the thinnest skin covering the eyelids. Thick skin is present on the soles of the feet and palms of the hands.
How do the stratum basale and stratum corneum differ?
The topmost layer, the stratum corneum, consists of dead cells that shed periodically and is progressively replaced by cells formed from the basal layer. The stratum basale also contains melanocytes, cells that produce melanin, the pigment primarily responsible for giving skin its color.
How does the hair differ between the front and the back of your forearm in type and distribution?
Describe the differences you observed in the type and distribution of hair on the front and back of your forearm. Anterior has less hair because it has a thinner layer of skin. The posterior of your forearm has more hair because it has a thicker layer of skin.
How thick is the skin on your palm?
1.5mm thickMentioned earlier, the skin on the bottom of feet and on the palms of your hands is the thickest, which is on average 1.5mm thick. The thinnest skin on the body is found on the eyelids, which is on average 0.05mm thick. Male skin is generally thicker in all areas compared to female skin.
What type of skin is on your palms?
glabrousUnlike other areas of the body, the skin of the palm is glabrous (hairless) and unable to tan. It is also durable, yet touch sensitive. In order for the skin layer to remain anchored to the bone structure, a layer of connective fibrous tissue (fascia) links the skin with the skeleton.
What are the different layers of the skin and how do they differ from one another?
Skin has three layers: The epidermis, the outermost layer of skin, provides a waterproof barrier and creates our skin tone. The dermis, beneath the epidermis, contains tough connective tissue, hair follicles, and sweat glands. The deeper subcutaneous tissue (hypodermis) is made of fat and connective tissue.
Why is thick skin so important on the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet?
Thicker skin on your hands and feet help you endure friction while picking things up or walking. The skin on your hands and feet is noticeably different from that on most other areas of your body. Unlike those other areas, the skin on your palms and soles doesn't have hair.
How does the shape of the cells in each layer of the epithelium of skin change?
This epidermis of skin is a keratinized, stratified, squamous epithelium. Cells divide in the basal layer, and move up through the layers above, changing their appearance as they move from one layer to the next. It takes around 2-4 weeks for this to happen.
Are hair and nails the same?
Nails and hair are essentially made up of a tough protective protein called keratin. While the hair grows in a hair follicle, nails grow from the matrix (the base of the nail bed).
Why do we have hair on our fingers?
Researchers believe that the appearance of hair on your fingers may be the result of prenatal exposure to androgens — a hormone often associated with male traits, though everyone has it.
Where is the location of melanin in dark skin?
Melanin is produced in melanocytes—the cells, which at normal conditions are localized in the basal layer of the epidermis.
How do the cells of the stratum corneum and stratum basale differ?
The basale layer is the deepest layer of the epidermis . The cells of the basale are cube shaped and alive. The cells of the corneum are dead and filled with keratin, the same as found in nails and hair.
Which cells are dead and filled with keratin?
The cells of the corneum are dead and filled with keratin, the same as found in nails and hair. The cells of the stratum corneum are sqamous-shaped, amitotic (dead actually), and contain a high percentage of keratin. Cells of the statum basale are columnar-shaped, actively mitotic and has relatively little keratin.
Why does anterior have more hair than posterior?
Anterior has more hair because it has a thicker layer of skin. Posterior has less & thinner layers than he anterior; so less hair. Explain how hair is formed. Hair is a protein filled with keratin that grows from epidermal (layer of skin) cells below the hair follicles.