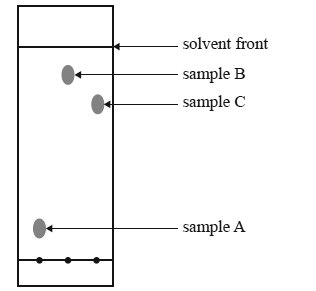
Why is polarity important in paper chromatography?
In paper chromatography, polarity is the key factor separating the mixture's components. In the image to the left, the solvent in the base of the jar is non-polar. Polar components of the mixture will not dissolve in the solvent and thus will not travel very far.
Does polarity affect paper chromatography?
Larger molecules take longer to move up the chromatography paper or TLC plate, whereas smaller molecules are more mobile. Likewise, the polarity of the molecules can affect how far the spots travel, depending on the type of solvent used.
How does polarity affect thin layer chromatography?
The more polar the compound, the more it will adhere to the adsorbent and the smaller the distance it will travel from the baseline, and the lower its Rf value. Eluent: the solvent or mixture of solvents (mobile phase) used to develop a TLC chromatogram (plate).
How does a polar molecule affect chromatography?
In normal phase chromatography, where the stationary phase is polar, polar molecules will spend more time adsorbed on the stationary phase, while less polar ones will be carried more quickly by the non-polar mobile phase.
How does polarity affect column chromatography?
The polarity of the solvent which is passed through the column affects the relative rates at which compounds move through the column. Polar solvents can more effectively compete with the polar molecules of a mixture for the polar sites on the adsorbent surface and will also better solvate the polar constituents.
How does polarity affect retention time?
If the polarity of the stationary phase and compound are similar, the retention time increases because the compound interacts stronger with the stationary phase. As a result, polar compounds have long retention times on polar stationary phases and shorter retention times on non-polar columns using the same temperature.
What happens if the TLC solvent is too polar?
If a development solvent of too high a polarity is used, all components in the mixture will move along with the solvent and no separation will be observed (Rf's will be too large). If the solvent is of too low a polarity the components will not move enough, and again separation will not occur (Rf's will be too small).
What factors affect separation in TLC chromatography?
Rf values and reproducibility can be affected by a number of different factors such as layer thickness, moisture on the TLC plate, vessel saturation, temperature, depth of mobile phase, nature of the TLC plate, sample size, and solvent parameters.
Do polar and polar attract?
If they don't, we call them non-polar. Things that are polar can attract and repel each other (opposite charges attract, alike charges repel). The two magnets in the image above will attract because their opposite poles are near. Reverse one of them and they will repel each other.
How does polarity affect solubility?
Substances with similar polarities tend to be soluble in one another ("like dissolves like"). Nonpolar substances are generally more soluble in nonpolar solvents, while polar and ionic substances are generally more soluble in polar solvents.
What is polar and non polar in chromatography?
The nonpolar solvent acts as the mobile phase. Nonpolar solvents interact more with the mobile solvent, travelling quickly along the polar stationary phase, while polar solutes are attracted to the stationary phase and travel more slowly. This property allows for separation based on polarity.
Is chromatography paper polar or nonpolar?
Paper is comprised of cellulose, which is a polymer of the simple sugar glucose, and as such is very polar due to the –OH groups present in glucose.
How does polarity affect chemical attraction?
Polarity has a huge affect on how attracted a chemical is to other substances. Some molecules have a positively charged side and a negatively charged side. For example, the positive side is attracted to the negative side of another molecule (opposites attract). The larger the charge difference, the more polar a molecule is.
What happens to the mixture as you increase the polarity of the solvent?
You will find that as you increase the polarity of the solvent, all the components of the mixture move faster during your chromatography experiment.
What is the purpose of chromatography?
Chromatography is a method for separating mixtures based on differences in the speed at which they migrate over or through a stationary phase. This will separate complex mixtures of chemicals or proteins into their various different components. Polarity has a huge affect on how attracted a chemical is to other substances.
Which pigment has a greater solubility in water?
The different colors of pigments have different solubilities based on their polarity. The blue pigment has a greater solubility in water so it moves faster (goes higher) through the chromatography paper. The yellow pigment is less soluble so it moves more slowly. YouTube. Video from: Noel Pauller.
How does polarity affect chemistry?
Polarity has a huge affect on how attracted a chemical is to other substances. The larger the charge difference, the more polar a molecule is. You will find that as you increase the polarity of the solvent, all the components of the mixture move faster during your chromatography experiment.
What happens in thin layer chromatography?
Furthermore, what happens in thin layer chromatography? The mobile phase flows through the stationary phase and carries the components of the mixture with it. Different components travel at different rates. Thin layer chromatography is done exactly as it says - using a thin, uniform layer of silica gel or alumina coated onto a piece of glass, metal or rigid plastic.
What is chromatography used for?
Chromatography is a technique used to separate the components of a mixture. Different solvents will dissolve different substances. A polar solvent (water) will dissolve polar substances (water soluble ink in the video below). Similar Asks.
Does polarity increase adsorbent?
In general, the adsorptivity of compounds increases with increased polarity (i.e. the more polar the compound then the stronger it binds to the adsorbent). Non-polar compounds move up the plate most rapidly (higher Rf value), whereas polar substances travel up the TLC plate slowly or not at all (lower Rf value). Click to see full answer.
Uses of Chromatography
Chromatography is an important biophysical analytical tool that helps to separate and identify the different components in a mixture. The method has been widely used in protein analysis. Chromatography is commonly used in food and beverage industries.
Answer and Explanation: 1
A stationary phase and a mobile phase are provided in a chromatographic column where the component gets eluted by the application of a suitable solvent. Several factors affect the rate of separation of components in the chromatographic method.
What is the solvent front in chromatography?
The solvent will wick vertically up the paper, much like a paper towel soaks up a spilled drink. The farthest it moves up the paper during the experiment is called the solvent front . In paper chromatography, polarity is the key factor separating the mixture's components.
What is chromatography in biology?
Section Complete! Chromatography is a method of separating mixtures. Different components within mixtures each have their own unique properties, such as molecular weight and polarity. Chromatography utilizes these differences to sort out the individual components within a mixture.
Is the solvent in the base of a jar polar or nonpolar?
In the image to the left, the solvent in the base of the jar is non-polar. Polar components of the mixture will not dissolve in the solvent and thus will not travel very far. Non-polar components will dissolve and will move with the solvent as it travels up the paper.
Does increasing the polarity of the mobile phase raise R f of aspirin?
So increasing the polarity of the mobile phase does raise R f of aspirin (or anything) on regular silica gel.
Is aspirin polar or nonpolar?
Because aspirin is polar (I believe would be considered polar because it dissolves in water despite some other sources saying that it is actually non-polar) and the silica in the TLC plates are also polar, aspirin would not be able to travel very far because it would interact with the silica.