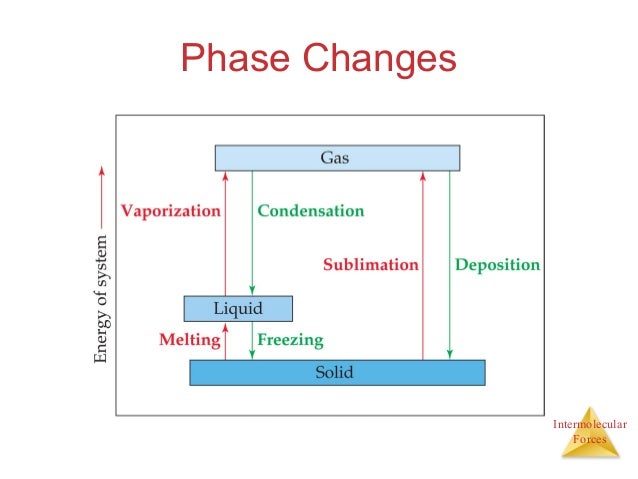
Intermolecular force
Intermolecular forces (IMFs) are forces of attraction or repulsion which act between neighboring particles (atoms, molecules, or ions). They are weak compared to the intramolecular forces, the forces which keep a molecule together. For example the covalent bond, involving the sharing of electron pairs between atoms is much stronger than the forces present between the neighboring molecules.
Does high viscosity have strong intermolecular forces?
The stronger the intermolecular interactions, the greater the surface tension. Liquids that have strong intermolecular forces tend to have high viscosities. Therefore, Viscosity and surface tension of liquids increase as intermolecular forces become stronger.
What are the factors affecting intermolecular force?
What factors increase boiling point?
- The relative strength of the four intermolecular forces is: Ionic > Hydrogen bonding > dipole dipole > Van der Waals dispersion forces. …
- Boiling points increase as the number of carbons is increased.
- Branching decreases boiling point.
How do you determine the strength of intermolecular forces?
How do you determine the strength of intermolecular forces?
- Boiling points are a measure of intermolecular forces.
- The intermolecular forces increase with increasing polarization of bonds.
- The strength of intermolecular forces (and therefore impact on boiling points) is ionic > hydrogen bonding > dipole dipole > dispersion.
How to determine strong and weak intermolecular forces?
• When intermolecular forces are strong the atoms, molecules or ions are strongly attracted to each other, and draw closer together. These are more likely to be found in condensed states such as liquid or solid. • When intermolecular forces are weak, the atoms, molecules or ions do not have a strong attraction for each other and move far apart.
What would happen if two molecules were only connected using van der Waals dispersion forces?
Ionic bonds. So, if two molecules are only connected using van der Waals dispersion forces, then it would require very little energy to break those molecules apart from each other.
What are the forces that bind two molecules together?
Lower vapor pressure. Lesson Summary. Intermolecular forces are the forces that bind two molecules together. Physical properties are affected by the strength of intermolecular forces . Melting, boiling, and freezing points increase as intermolecular forces increase. Vapor pressure decreases as intermolecular forces increase.
What happens when two molecules are connected?
On the other hand, if two molecules are connected using ionic bonds, it takes a whole lot more energy to break those two apart. Stronger intermolecular forces will also result in a higher physical properties such as higher melting or boiling points, which require breaking molecules apart.
What forces hold a lamp together?
Intermolecular forces are like the glue, only instead of holding a lamp together, intermolecular forces hold molecules together. There are strong and weak forces; the stronger ...
What is van der Waals dispersion force?
At any given moment, the electrons in a molecule or atom may not be evenly distributed around the molecule. If more electrons are on the left side of the molecule than on the right side, then there will be a slight negative charge on the left side of the molecule. The side with fewer electrons will have a slight positive charge .
What is an ionic bond?
Ionic bonds are so strong that sometimes we even consider this a new compound instead of two molecules interacting with each other. An ionic bond occurs when a compound has a full positive charge and another compound (or another place on the same compound) has a full negative charge.