What is the ratio of current to resistance?
Ohm's law gives current as a ratio of voltage to resistance: 1 volt flowing through 1 ohm of resistance produces 1 ampere of current. Resistance is the property of an object, and resistivity is the property of the substance of which the object is made. Resistivity varies between materials. Copper, silver and aluminum have very low electrical ...
What happens when a wire is passed through a negative charge?
When current is passed through a wire, the negative charges repel free electrons through the wire from one atom to the next until the reaction reaches the other end of the wire. Electrical resistance occurs when substances have few or no electrons that may travel. Heat also affects electrical resistance. In most metals, more heat means more ...
Why do metals have more heat?
In most metals, more heat means more resistance because the molecules vibrate more strongly and collide, taking energy from the electrons. In wire, thicker wires carry more current because there is more space for electrons to travel without rubbing against one another, creating excess heat and potentially starting a fire.
How does high resistance affect current?
The reverse effect is that high resistance increases the temperature of the conductor through which current is passing. This property is made use in incandescent bulbs made of the tungsten filament in electric heaters and radiators.
Why does heat increase resistance?
Resistance and Temperature. Heat is due to the motion of atoms in a material. The higher the temperature, the more is this movement. Therefore, with high temperature, resistance increases as the electrons collide more with the atoms surrounding them.
How does resistance relate to cross sectional area?
Resistance is inversely proportional to the cross-sectional area of the conductor .#N#R ∝ 1 A#N#In simple words, the thicker the conductor, the smaller is its resistance. It means that resistance is high in a thin conductor.#N#A conductor with more cross-sectional area has more area for the charges to flow. So, they encounter less opposition. We can see the analogies for this in our daily life:#N#1. It is easier to walk in a wide corridor than a narrow one. However, in a narrow corridor, we bump into people more, hindering our movement. This hindrance is equivalent to the resistance to current.#N#2. Traffic is smooth with less crowding on a wide road than a narrow lane or a bottleneck.#N#3. There is more pressure of water in a thin pipe than in a wider pipe.
What is the potential difference between a wire and a wire?
It states that the potential difference across a wire is directly proportional to the current flowing through the wire when the temperature of the wire is constant. According to Ohm’s law, the potential difference is the product of the resistance of the wire and the current flowing through it.
What is resistance in electrical engineering?
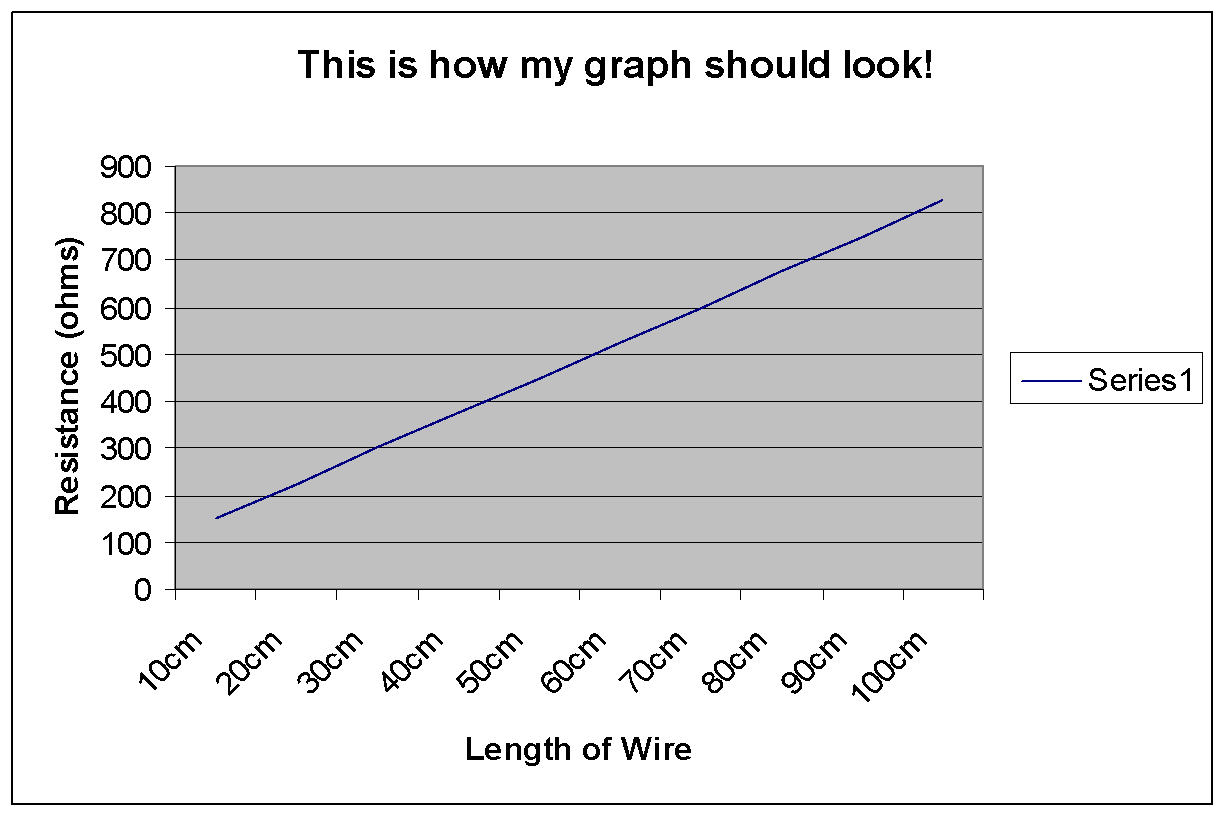
3. The material it is made of. 4. The temperature of the conductor. The resistance is: 1. directly proportional to the length ( l) of the conductor. 2. inversely proportional to the cross-sectional area or thickness ( A) of the conductor.
What is the unit of resistance?
S I unit of resistance is Ohm ( Ω), after Georg Simon Ohm ( 1784 – 1854), a German physicist who postulated the law relating voltage, current with resistance.
What is the measure of how well a material resists (or opposes) current flowing through it?
Resistivity of Materials. Resistivity is a measure of how well a material resists (or opposes) current flowing through it. It is the inherent property of a material to oppose current and is fixed for a particular material. It is also called specific resistance.