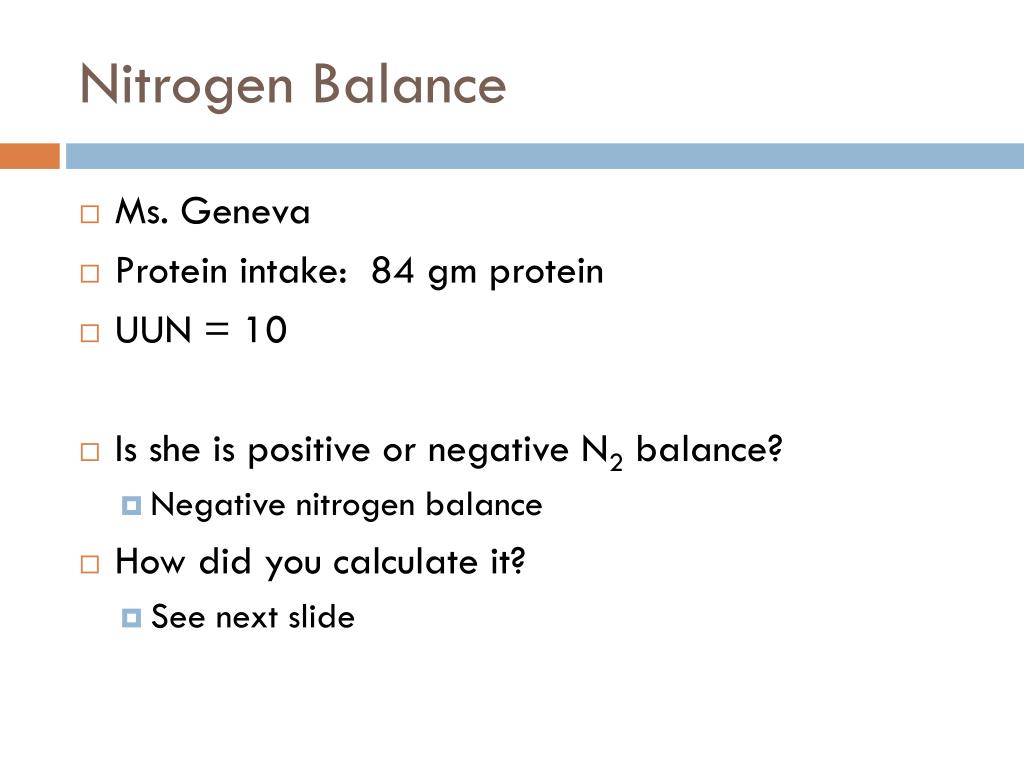
Steps to Calculate Nitrogen Balance
- Determine nitrogen lost in urine by a 24 hour urinary urea nitrogen test.
- Add 4* to the UUN to account for non-urinary losses of nitrogen
- Determine nitrogen intake by dividing the daily protein intake by 6.25
- N-bal.= value from #3 - value from #4
- Determine nitrogen lost in urine by a 24 hour urinary urea nitrogen test.
- Add 4* to the UUN to account for non-urinary losses of nitrogen.
- Determine nitrogen intake by dividing the daily protein intake by 6.25.
- N-bal.= value from #3 - value from #4.
What is the equation for nitrogen balance?
What is the equation for nitrogen balance? Nitrogen Balance = Protein intake/6.25- (UN + 4*) * For average loss via sweat and feces. What is a normal nitrogen balance? The concept of nitrogen balance is that the difference between nitrogen intake and loss reflects gain or loss of total body protein.
What causes negative nitrogen balance?
Nitrogen Balance
- Protein Nutrition and Status and Bariatric Surgery. V. ...
- Amino Acids and Nitrogen Compounds. ...
- Protein and Amino Acids in Human Nutrition. ...
- PROTEIN. ...
- PROTEIN | Requirements. ...
- The monitoring of nitrogen surpluses from agriculture. ...
- Nitrogen efficiency in global animal production. ...
- Protein: Requirements and Role in Diet
What does nitrogen balance mean?
nitrogen balance noun the balance between the amount of nitrogen taken in (to the soil or the body) and the amount given off (lost or excreted) Freebase (0.00 / 0 votes) Rate this definition: Nitrogen balance Nitrogen balance is the measure of nitrogen input with the nitrogen output subtracted from it.
What is an example of negative nitrogen balance?
Negative nitrogen balance is associated with burns, serious tissue injuries, fevers, hyperthyroidism, wasting diseases, and during periods of fasting. This means that the amount of nitrogen excreted from the body is greater than the amount of nitrogen ingested.
What is the equation for nitrogen balance?
0:054:46Nitrogen Balance - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSimple process and that is calculating nitrogen balance nitrogen balances we know is nitrogen. ThatMoreSimple process and that is calculating nitrogen balance nitrogen balances we know is nitrogen. That you take n minus the nitrogen that you put out and that's going to equal your nitrogen balance.
How do you calculate protein balance?
The urea nitrogen appearance, U, equals the urine urea nitrogen + the non urea nitrogen (weight in kg X 0.031 g nitrogen/kg/day). Calculated Protein Intake is urine nitrogen excreted in grams/day + (weight in kilograms X 0.031 g nitrogen/kg/day) multiplied by 6.25.
Why do you add 4 to UUN when calculating nitrogen balance?
Parenteral Nutrition Tutorial | Preparation | Calculation of Nitrogen Balance. Determine nitrogen lost in urine by a 24 hour urinary urea nitrogen test. Add 4* to the UUN to account for non-urinary losses of nitrogen.
What is nitrogen balance in protein?
The concept of nitrogen balance is that the difference between nitrogen intake and loss reflects gain or loss of total body protein. If more nitrogen (protein) is given to the patient than lost, the patient is considered to be anabolic or “in positive nitrogen balance”.
What is a nitrogen balance test?
The urinary urea nitrogen test is used to determine a patient's nitrogen balance. If the urinary nitrogen balance is positive, the patient is metabolizing sufficient protein, and as a result, nitrogen is excreted in the urine.
How do you calculate urea nitrogen?
A double-linear formula to calculate TUN from UUN is proposed (for UUN ⩽ 15 g/ day: TUN = UUN × 1.17 + 0.7; for UUN > 15 g/ day: TUN = UUN + 4).
What factors affect nitrogen balance?
Insufficient caloric intake, lack of non-essential nitrogen, potassium depletion, corticosteroid administration, infection or cardiac insufficiency have been found to cause a deterioration of the nitrogen balance and an increase of plasma urea or concentration.
What is neutral nitrogen balance?
Nitrogen balance (Bn) is the classic method of assessing dietary protein requirements. A neutral or positive Bn indicates that protein stores are maintained or increased, while a negative Bn indicates protein mass is declining.
What is the normal nitrogen balance?
Nitrogen Balance. Normal, healthy adults are in neutral balance with a nitrogen balance that is equal to about + 0.5 g/d (to account for unmeasured nitrogen losses from sweat, skin desquamation, hair and nail growth, respiration, flatus and, if present, sputum and salivary losses and menstruation).
What causes a deterioration of the nitrogen balance?
Insufficient caloric intake, lack of non-essential nitrogen, potassium depletion, corticosteroid administration, infection or cardiac insufficiency have been found to cause a deterioration of the nitrogen balance and an increase of plasma urea or concentration.
How to get N from cover crop?
Multiply dry biomass by N content to get total above ground N in the cover crop biomass. Multiply that result by 50% to get the portion of the cover crop N from BNF (assuming an average of 50% of the N in the legume comes from BNF and remainder from the soil).
Why do we use manure total N?
One reason why is that manure application rate determinations generally also consider the proportion of Manure_Nfrom current and prior years available in the current year.
What is the name of the process of converting N into a plant-useable form?
is N converted from the air into a plant-useable form by rhizobia on the legume roots, also known as biological N fixation (BNF).
How to dry biomass?
Throw the frame onto four to six random areas of the field. For each area, cut the cover crop vegetation to the soil surface and put it into a paper bag. Dry it after sampling is complete, and open bags as soon as possible to avoid mold growth on wet samples. The typical drying time is 48 hours at 104 degrees F. Weigh the dried biomass and calculate the mass per area (lbs./acre or kg/hectare). For example:
Can you measure BNF in legumes?
For legumes, it is impractical to measure BNF at a field level, so the N balancecalculation instead uses an estimate of the BNF as a standard proportion of legume yield.7
Where does N come from in legumes?
The N in legume crops, including winter cover crops, comes both from the soil and from N fixed by rhizobium bacteria on the legume roots. For a field with little soil N supply, nearly all the N in the crop is added to the system by BNF, i.e., from the N
Do non-leguminous cover crops affect the N input portion of the N balance calculation?
21Non-leguminous cover crops do not affect the N input portion of the N balance calculation .
How is nitrogen balance measured?
Nitrogen balance is measured by deducting N outputs and changes in soil total N storage from N inputs as follows:
What does a positive N balance mean?
A positive value of N balance indicates that N is gained in the system and negative value indicates loss. When all sources, sinks, and losses of N are accounted, there should be no net gain or loss of N if N is recycled efficiently. This, however, occurs rarely due to various factors, such as variations in soil and climatic conditions, N management, soil and crop management practices, and difficulty in measurement of some parameters, such as atmospheric N depositions, biological N fixation, and N losses through various processes.
How to find bulk density?
The formula for bulk density is (mass of dry soil) / (total volume of soil), 1 - (bulk density/particle density) for porosity, and (volume of pores) / (volume of solids) for void ratio.
How do you calculate nitrogen in proteins?
The nonprotein kcalorie to nitrogen ratio (NPC:N) is calculated as follows: Calculate grams of nitrogen supplied per day (1 g N = 6.25g protein) Divide total nonprotein kcalories by grams of nitrogen.
How to determine nitrogen intake?
Determine nitrogen intake by dividing the daily protein intake by 6.25.
What is a negative nitrogen balance?
Negative nitrogen balance is associated with burns, serious tissue injuries, fevers, hyperthyroidism, wasting diseases, and during periods of fasting. This means that the amount of nitrogen excreted from the body is greater than the amount of nitrogen ingested.
How much protein does urea have?
That is, the nitrogen portion of urea is used as the building block for the production of protein by rumen microbes. Most urea contains about 45% nitrogen, and protein contains 16% nitrogen. Therefore, when urea is converted to protein, the crude protein equivalent value of urea is about 281%.
How do you calculate fractional excretion of uric acid?
It is calculated by dividing the product of (urinary uric acid [mg/mL] x serum creatinine [mg/mL]) by the product of (serum uric acid [mg/mL] x urinary creatinine [mg/mL]) and multiplying the result by 100%. Normal values are less than 10%.
How do diuretics affect FENa?
Use of diuretics can cause the FeNa to be falsely elevated in a pre-renal state. In response, researchers evaluated the FeUrea, generally using a cutoff of less than 30% for pre-renal and greater than 30% for ATI. Urea is passively absorbed, and its urinary concentrations are regulated by volume status.
Is urine high in nitrogen?
Urine is very high in nitrogen (can be over 10% in a high protein diet), low in phosphorus (1%), and moderate in potassium (2-3%).