How do the endocrine and exocrine glands differ in structure and function? Endocrine glands are ductless glands. They produce hormones, Exocrine
Exocrine gland
Exocrine glands are glands that produce and secrete substances onto an epithelial surface by way of a duct. Examples of exocrine glands include sweat, salivary, mammary, ceruminous, lacrimal, sebaceous, and mucous. Exocrine glands are one of two types of glands in the human body, the other being endocrine glands, which secrete their products directly into the bloodstream. The liver and pancreas are b…
What are the 10 glands of the endocrine system?
What the endocrine system’s glands do
- Hypothalamus. The hypothalamus is part of the brain. ...
- Pituitary Gland. The pituitary gland is under the control of the hypothalamus and is connected to the hypothalamus by a stalk.
- Pineal Gland. The pea-sized pineal gland is near the centre of the brain. ...
- Thyroid Gland. ...
- Parathyroid Glands. ...
- Adrenal Glands. ...
- Pancreas. ...
- Thymus. ...
- Testes. ...
- The Ovaries. ...
Is endocrine good or bad?
Paying It Forward in a Bad Way. Do you know that endocrine disruptors have been found in umbilical cord blood and breastmilk? Fetuses, newborns and young children are much more negatively impacted by EDs because of their small size and underdeveloped immune systems. EDs affect them at critical developmental stages.
What diseases are caused by the endocrine system?
Potential endocrine disorders according to the specific neurologic manifestations
- Headache
- Altered mentality
- Abnormal muscle strength, muscle tone and gait
- Movement disorders
- Developmental delay
What are the four functions of the endocrine system?
The three main functions of the endocrine system are to:
- Produce hormones.
- Release hormones into the blood to control bodily functions, such as mood, appetite, sleep and more.
- Regulate the release of hormones so that they are in homeostasis with the body.
How do exocrine and endocrine glands differ in structure?
How do the endocrine and exocrine glands differ in structure and function? Exocrine glands contain ducts, but endocrine glands lose their surface connection (duct) as that develop. Endocrine glands release hormones directly into the blood or lymphatic vessels.
How do the endocrine and exocrine glands differ in structure and function quizlet?
How do the endocrine and exocrine glands differ in structure and function? Endocrine glands are ductless glands. They produce hormones, Exocrine glands maintain their ducts and manufacture secretions of various types, which are ducted to the body or membrane surface.
How do endocrine and exocrine glands differ quizlet?
What is the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands? Endocrine glands release hormones directly into the bloodstream, whereas exocrine glands release chemical substances through ducts, releasing outside the body.
What is the difference between endocrine and endocrine glands?
Endocrine glands are the glands that secrete hormones without ducts, while exocrine glands secrete hormones through ducts....Difference Between Endocrine and Exocrine Glands.Difference Between Exocrine Glands and Endocrine GlandsEndocrine GlandsExocrine GlandsDuctsEndocrine glands do not have ductsExocrine glands have ductsSecretory Products5 more rows
How does it differ structurally from other stratified squamous epithelium quizlet?
how does it differ structurally from other stratified squamous epithelia? the cells change shape to allow stretching, which are only in the bladder. transitional epithelium is classified as stratified squamous. how does transitional epithelium reflect its function in the body?
How do exocrine glands differ from exocrine glands?
Exocrine glands secrete their products in duct system as happens in case of enzymes, milk, sebum or sweat. ... Merocrine glands secrete product through exocytosis of secretory vacuoles. No part of cell is lost in the process.10-Nov-2017
How do endocrine and exocrine glands differ Chapter 4?
Endocrine glands secrete substances (hormones) into blood without the use of ducts, whereas exocrine glands use ducts to secrete substances into the external environment. ... Absorption, the movement of substances into the body, is a role of epithelial tissue.
How do endocrine glands differ from other body glands such as sweat glands?
Some of your body's glands, such as sweat glands, release their chemicals into tiny tubes called ducts. ... Endocrine glands, on the other hand, do not have ducts. Instead, they release substances directly into the bloodstream. The blood then carries those substances throughout the body.
What is the difference between an endocrine and an exocrine gland?
A helpful tip to remember the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands is to look at their prefixes. "Endo" means "inside," and endocrine glands release their products to the internal environment. "Exo" means "outside," and exocrine glands release their product to the external environment.
How do exocrine glands work?
These glands create a wide variety of products and excrete them through a network or ducts. The products that are created in the exocrine glands are released to the outside environment (such as on the skin or in the mouth) and not into the blood stream. A helpful tip to remember the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands is to look ...
What is the endocrine system?
Endocrine glands are part of the endocrine system, which is a system of structures within the body that work together to monitor, produce, and secrete hormones throughout the body. Endocrine glands do not use ducts to release their products. Exocrine glands are note considered part of the endocrine system. These glands create a wide variety of ...
What are the different types of exocrine glands?
There are multiple exocrine glands in the body, and they are broken into 3 types: 1 Holocrine gland: A holocrine gland creates a product and stores it within a cell. To release that product, the entire cell ruptures and its contents are thus dumped. An example of a holocrine gland is the serous glands on the skin. 2 Apocrine gland: An apocrine gland concentrates its products into a portion of itself. To release its product, it loses the portion of itself that contains that product. The gland regrows the portion it lost and starts the process over again. An example of an apocrine gland is the mammary glands in women. 3 Merocrine gland: A merocrine exocrine gland secretes a substance with vesicles. The substance is created within the gland, then expelled in small pockets through the cellular membrane. This leaves an intact membrane behind. An example of a merocrine gland is the salivary glands of the mouth.
How to observe glands in the body?
The easiest way to observe examples of glands in the body is to break them into their various types. Below, investigate examples of endocrine glands, exocrine glands, and glands that act as both endocrine and exocrine glands.
Which glands release hormones into the bloodstream?
Endocrine glands release hormones into the bloodstream. They are part of the endocrine system which monitors and controls the release of hormones throughout the body. Exocrine glands secrete substances through ducts into the external environment. The following are examples of endocrine glands and their functions:
Which gland is responsible for creating sex hormones?
The posterior pituitary gland helps create hormones that monitor water balance in the body, as well as oxytocin (which helps mothers and babies bond after birth). Ovaries and Testes: The ovaries and testes are found in females and males respectfully and are responsible for creating the sex hormones.
What is the role of exocrine glands in the pancreas?
Ans. Exocrine glands play a crucial role in secreting digestive juices. When the glands fail to do so, that is when the pancreas becomes unable to produce enzymes, which can lead to Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. Such unavailability in the production of enzymes can lead to a loss in weight and a lack of vitamins.
How many types of endocrine glands are there?
Ans. There are three types of endocrine glands. These are -
What is the pituitary gland?
Pituitary glands - The pituitary gland is that of a pea-sized gland located deep inside the skull. It's considered very superior to other glands because it controls them. It even controls our metabolism, reproductive system, blood pressure and sexual growth. The failure of these glands can cause hair loss, anxiety, high blood pressure, irregular menstrual cycles and other problems.
What are the two types of glands?
Endocrine and exocrine are the two types of glands present in our bodies. Glands are organs which are essential for sustaining life and are concerned solely with the production of substances that have unique functions. The substances which are released are known as ‘ hormones’.
What is the master gland?
The ‘master gland’, or commonly known as the pituitary gland is an example of the endocrine gland. It is the size of a pea and is important for the growth and development of our brain, organs, skin and even our mood. The failure of this gland or apoplexy can lead to tissue death.
Which glands are responsible for secreting secretions?
Exocrine gland is a gland that pours its secretion on the surface or into a particular region by means of ducts for performing a metabolic activity, e.g., sebaceous glands, sweat glands, salivary glands and intestinal glands .
Which glands have ducts?
Exocrine glands- these glands have ducts present in them.
What is the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands?
Anatomically, these glands are broadly classified into two types based on the presence or absence of ducts. Endocrine glands are the glands that secrete hormones without ducts, ...
Which glands secrete hormones without ducts?
Endocrine glands are the glands that secrete hormones without ducts, while exocrine glands secrete hormones through ducts. Read on to explore more differences between the two. Secretory products released directly into the bloodstream, eventually reaching the target organ.
How are the endocrine and nervous systems different?
In what ways are they different? Both systems regulate body functions to maintain homeostasis. The endocrine system's reaction to stimuli is slow, whereas the reaction of the nervous system to stimuli is fast. The endocrine system's duration of effects is long, whereas the duration of effects of the nervous system is short.
Why is the pituitary gland called the master endocrine gland?
The pituitary gland is often called the master endocrine gland because many of its hormones direct the activity of other endocrine glands.
What is the study of the endocrine system?
The study of the endocrine system. epinephrine. Commonly called adrenaline. A hormone secreted by the medulla of the adrenal gland under stimulation by the sympathetic portion of the autonomic nervous system.
What is the system of blood vessels that regulates the anterior pituitary gland?
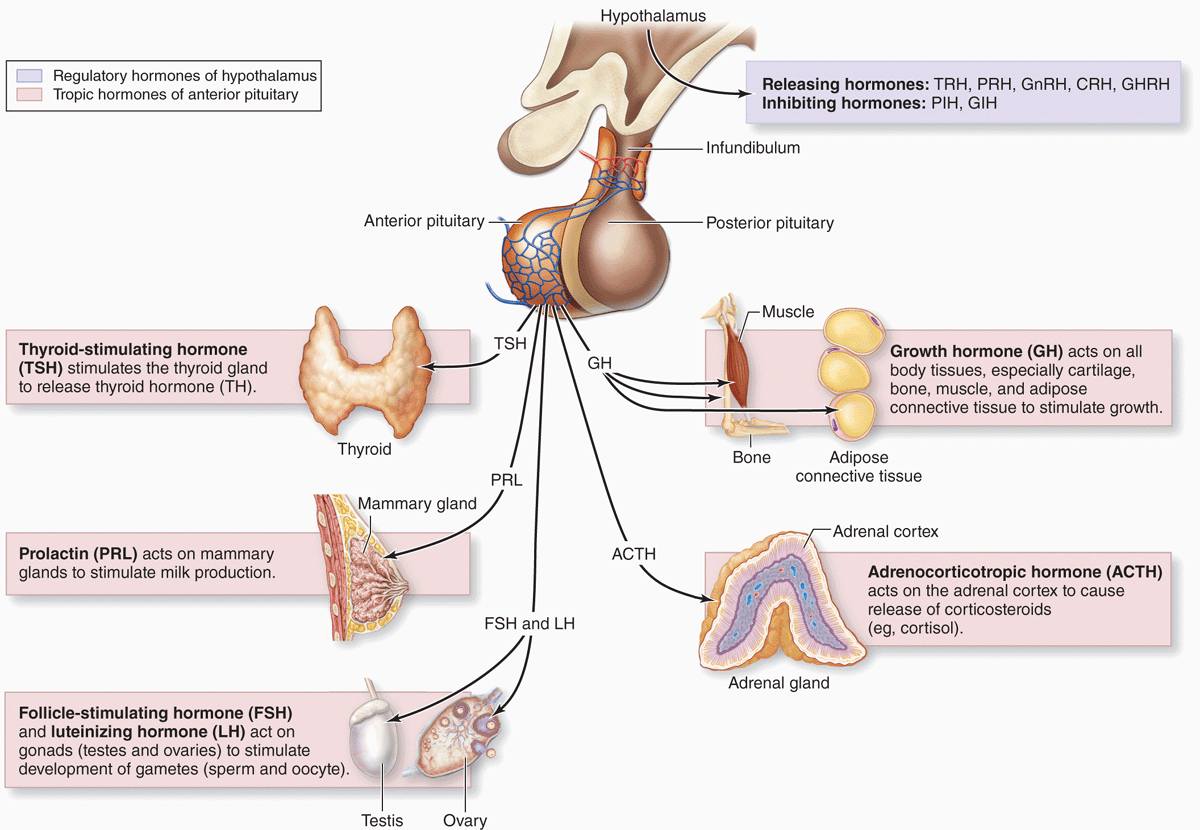
A system of tiny blood vessels called a portal system links the hypothalamus with the anterior portion of the pituitary gland. Modified neurons in the hypothalamus secrete hormones into these portal blood vessels. The hormones travel the short distance down to the anterior pituitary and regulate much of its function. These hypothalamic hormones, called releasing and inhibiting factors, are each specific for a particular anterior pituitary hormone. As their names imply, a releasing factor causes the anterior pituitary to produce and release a particular hormone, and an inhibiting factor has the opposite effect of inhibiting the production and release of a hormone. Because some anterior pituitary hormones influence all of the body's cells, the hypothalamus indirectly affects the whole body by regulating anterior pituitary gland functions. The effect of the hypothalamus on the posterior part of the pituitary gland is more direct. Modified neurons in the hypothalamus produce two hormones, antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin, that are transported down nerve fibers to the posterior pituitary gland, where they are stored. They are then released into the bloodstream by nerve impulses from the hypothalamus.
What are hormones produced by?
Hormones are chemical messengers produced by endocrine glands and are secreted directly into blood vessels.
What glands secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream?
Endocrine glands secrete tiny amounts of hormones directly into the bloodstream and not through ducts. This feature differentiates them from exocrine glands, which secrete their products onto epithelial surfaces through tiny tubes called ducts. Click again to see term 👆. Tap again to see term 👆.
What are the messenger producing cells of the endocrine gland?
The messenger-producing cells of the endocrine gland are cells or modified neurons , whereas the messenger-producing cells of the nervous system are neurons.