The hydrosphere
Hydrosphere
The hydrosphere in physical geography describes the combined mass of water found on, under, and over the surface of a planet. Igor Shiklomanov, the man selected by the United Nations to do its world inventory of water resources, estimated that there are 1386 million cubic kilometres of water on Ear…
How do processes affect the hydrosphere?
how does photosynthesis affect the flow of energy in the biosphere
- Biosphere, Flow of energy
- Biology 20: Flow of Energy in the Biosphere
- A guide to the energy of the Earth – Joshua M. Sneideman
- Flow of energy and matter through ecosystem | Ecology | Khan Academy
How do human activities affect the hydrosphere?
There are three main issues in the current debate:
- Eutrophication
- Acid rain
- The buildup of the so-called greenhouse gases.
How does the hydrosphere interact with the other spheres?
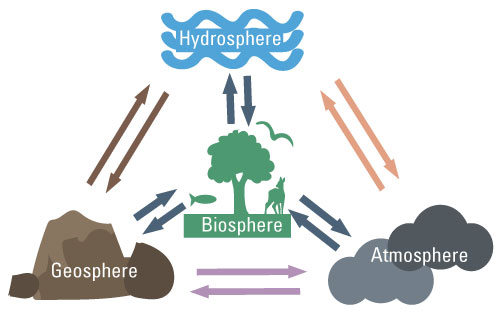
How do the Earth's spheres interact?
- Think of the many ways that the hydrosphere and the atmosphere connect. ...
- In what way do the geosphere and hydrosphere connect? ...
- The atmosphere provides the geosphere with heat and energy needed for rock breakdown and erosion. ...
- The biosphere receives gases, heat, and sunlight (energy) from the atmosphere. ...
How does the atmosphere affect the hydrosphere?
- Blog
- Jan. 8, 2022 Big Ideas in sales: A look at what’s next for better sales kickoffs and presentations
- Dec. 21, 2021 Using Prezi Video to make virtual events more immersive and engaging
- Dec. 3, 2021 6 ways virtual sellers can stand out on LinkedIn
- Latest posts
How does the biosphere interact with the geosphere hydrosphere and atmosphere?
Plants (biosphere) draw water (hydrosphere) and nutrients from the soil (geosphere) and release water vapor into the atmosphere. Humans (biosphere) use farm machinery (manufactured from geosphere materials) to plow the fields, and the atmosphere brings precipitation (hydrosphere) to water the plants.
How does hydrosphere and atmosphere interact?
The atmosphere and hydrosphere interact to create the Earth's climate. The atmosphere holds heat and moisture while the hydrosphere stores water vapor. The interactions between the two help to distribute heat and moisture around the planet creating climates that are suitable for life.
What is the importance of hydrosphere to the biosphere?
The major importance of the hydrosphere is that water sustains various life forms and plays an important role in ecosystems and regulating the atmosphere. Hydrosphere covers all water present on the Earth's surface.
What is the interaction between biosphere and atmosphere?
Biosphere-Atmosphere Interactions focuses on the sources and sinks of greenhouse gases (GHGs), air pollutants, particulate matter, water, and energy between the Earth's surface and the atmosphere.
How does climate affect the biosphere?
Cooler climate affects the biosphere by shortening the growing season. Yet another example is soil erosion, which occurs when rain (hydrosphere) falls on land (geosphere) denuded of vegetation (biosphere) by fire or clear-cutting. Streams and rivers (hydrosphere) become muddy or murky from erosion. ADVERTISEMENT.
What are some examples of interactions between spheres?
A classic example of an interaction between spheres is when a plant (part of the biosphere), takes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and water (the hydrosphere) through its roots from underground (geosphere) to perform photosynthesis, which provides the plant with food and releases oxygen into the atmosphere.
How many spheres are there on Earth?
The Earth's four spheres interact in all six possible combinations: lithosphere and hydrosphere, lithosphere and biosphere, lithosphere and atmosphere, hydrosphere and biosphere, hydrosphere and atmosphere, and biosphere and atmosphere.
What is the name of the change in one sphere?
When an event in one sphere affects another sphere, it is called an interaction. A classic example of an interaction between spheres is when a plant (part of the biosphere), ...
What is the name of the Earth's system of water?
The Earth system consists of rocks, magma and core, called the lithosphere; all of its water as liquid, ice or gas, called the hydrosphere; the atmosphere or air; and living organisms, called the biosphere. The spheres get their energy and power from the sun and Earth's internal heat.