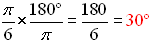What is the formula for converting radians to degrees?
- Angles are measured using two basic units: degrees and radians.
- One complete counterclockwise revolution is equal to 2π rad in radians.
- 1° equals 0.017453 radians and 1 rad equals 57.2958°.
- To convert an angle from radians to degrees, we multiply it by 180°/π.
- To convert an angle from degrees to radians, we multiply it by π/180°.
How do you convert radian measures to degrees?
Things You'll Need
- Pen or Pencil
- Paper
- Calculator
How to convert degrees to radians calculator?
radians = degrees × 0.017453. The angle in radians is equal to the degrees multiplied by 0.017453. For example, here's how to convert 5 degrees to radians using the formula above. 5° = (5 × 0.017453) = 0.087266 rad. Since pi radians is equal to 180°, this conversion formula is preferred because it is more precise and convenient in advanced ...
How do you calculate radians?
How do you find radians on a unit circle? The radian measure of an angle is the ratio of the length of the arc to the radius of the circle (θ=sr) ( θ = s r ) . In other words, if s is the length of an arc of a circle, and r is the radius of the circle, then the central angle containing that arc measures radians.
See more
Is Wolfram in radians or degrees?
While most angle-related functions in the Wolfram Language take radian measures as their arguments and return radian measures as results, the symbol Degree can be used as a multiplier when entering values in degree measures (e.g. Cos[30 Degree]).
How do you use radians in Mathematica?
To use Radian, you first need to load the Units Package using Needs["Units`"]. Convert[n Radian,newunits] converts n Radian to a form involving units newunits. 2 Pi Radian is equivalent to 360 Degree. Radian is typically abbreviated as rad.
What programming language does Mathematica use?
The Wolfram LanguageThe Wolfram Language is the programming language used in Mathematica.
How does Mathematica define pi?
Pi is the symbol representing the mathematical constant , which can also be input as ∖[Pi]. Pi is defined as the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter and has numerical value .
How do you set degrees in Mathematica?
This special constant is called Degree in Mathematica. The symbol ° is a handy shorthand for Degree and is entered as Esc-d-e-g-Esc. You can also find this symbol in the Basic Math Assistant palette in the Palettes menu of Mathematica.
How do you write sin inverse in Mathematica?
ArcSin is the inverse sine function. For a real number , ArcSin[x] represents the radian angle measure such that . ArcSin automatically threads over lists. For certain special arguments, ArcSin automatically evaluates to exact values.
Is Stephen Wolfram a billionaire?
But many of Wolfram's big, and often controversial, theories are self-published. His net worth is estimated between $2-3 billion, which gives him the financial backing that many of his scientific peers do not have.
Which is better Matlab or Mathematica?
When we compare Mathematica and Matlab, Mathematica is more powerful. Mathematica is good at handling numerical work and it is a perfect programming system whereas Matlab is not a perfect programming system. Symbolic manipulation is better and easy in Mathematica than in Matlab.
Is Mathematica a scripting language?
Long popular as a scripting language in the advanced R&D community, Mathematica is considered by many to be the world's single most productive programming language—combining a uniquely powerful multiparadigm approach to programming with built-in access to the world's largest web of advanced algorithms.
How do you write an equation in Mathematica?
0:006:21Mathematica Equation Entry - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipI'm going to show you how to write this type of mathematical formulae or equations. UsingMoreI'm going to show you how to write this type of mathematical formulae or equations. Using Mathematica software of course you could always enter them as a over B. Like this and it will work perfectly.
Does Raspberry Pi come with Mathematica?
Mathematica is a computational programming tool used in science, maths, computing and engineering. It was first released in 1988. It is proprietary software that you can use for free on the Raspberry Pi and comes bundled for free with Raspbian.
How do I use Mathematica?
0:0035:05Hands-on Start to Mathematica 12 - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThen you've come to the right place. Today we're going to go over the basics of using Mathematica.MoreThen you've come to the right place. Today we're going to go over the basics of using Mathematica. So go ahead and start by opening up Mathematica on your computer. So you can work alongside me.
News, Views & Insights
How Odd Was the Full Moon on Halloween 2020? Once in a Blue Moon and a Lifetime!
Mathematica Q&A: Plotting Trig Functions in Degrees
Got a question about Mathematica? The Wolfram Blog has answers! We’ll regularly answer selected questions from users around the web. You can submit your question directly to the Q&A Team using this form.
What is the symbol for degrees?
Degree is the symbol representing the number of radians in one angular degree (1 ° ), which can also be input into the Wolfram Language as ∖ [ Degree]. Degree has exact value and numerical value . The use of Degree is especially common in calculations involving plane geometry and trigonometry. While most angle-related functions in the Wolfram Language take radian measures as their arguments and return radian measures as results, the symbol Degree can be used as a multiplier when entering values in degree measures (e.g. Cos [ 30 Degree]).
Is degree normal or uniform?
While (like Pi) it is not known if Degree is normal (meaning the digits in its base- expansion are equally distributed) to any base, its known digits are very uniformly distributed. Degree can be evaluated to arbitrary numerical precision using N.