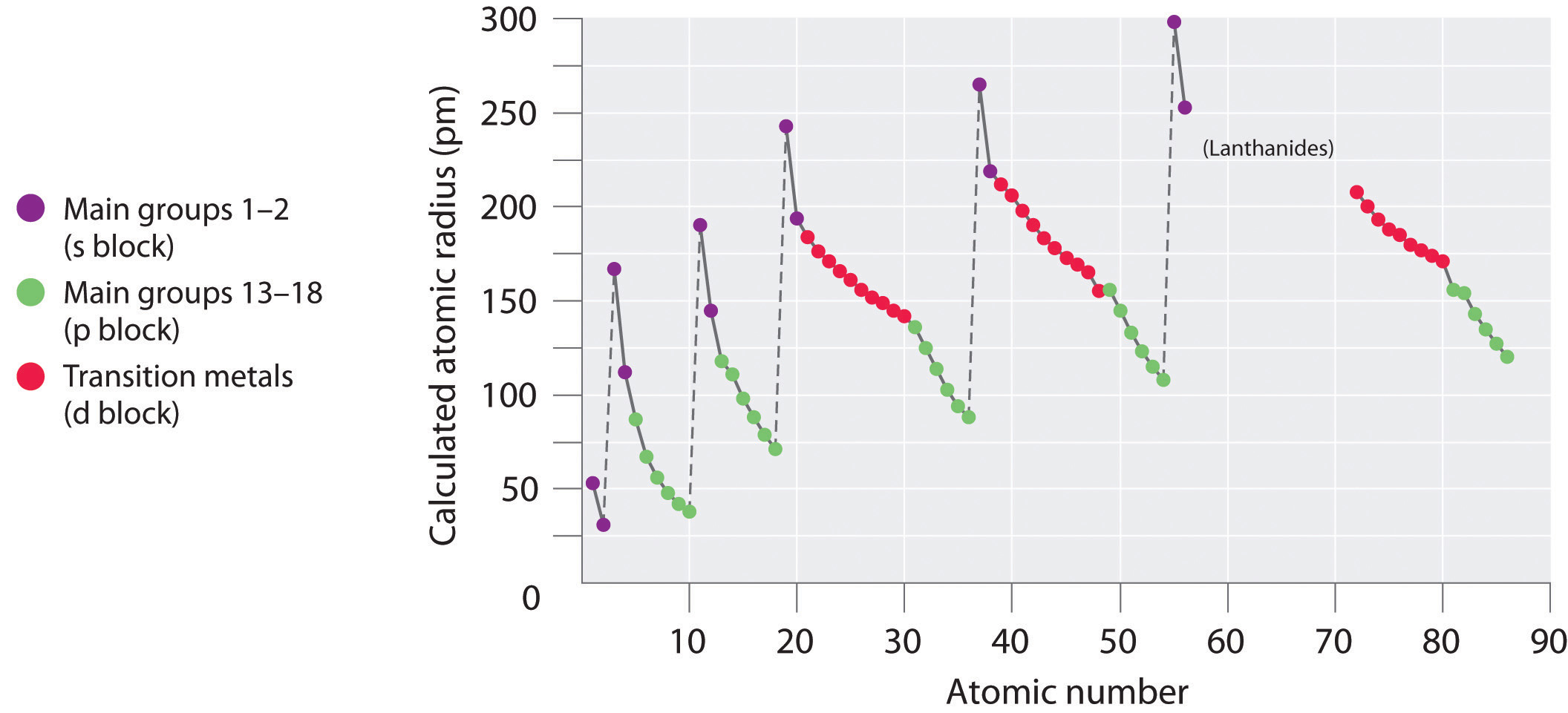
In general, atomic radius decreases across a period and increases down a group. Down a group, the number of energy levels (n) increases, so there is a greater distance between the nucleus and the outermost orbital. This results in a larger atomic radius.
Does atomic radius increase from top to bottom within a group?
Atomic radius increases from top to bottom within a group. This is caused by electron shielding. Why do alkali metals have large atomic radii? Explanation: Every time we move down the group, the number of electron shells of the element increases by one. E.g. sodium has 3 electron shells, potassium has 4, rubidium has 5.
Why does atomic radius decrease across a period?
Atomic radius decreases across a period because valence electrons are being added to the same energy level at the same time the nucleus is increasing in protons. The increase in nuclear charge attracts the electrons more strongly, pulling them closer to the nucleus.
What happens to ionic radius down a group?
As you move down a column or group, the ionic radius increases. This is because each row adds a new electron shell. Ionic radius decreases moving from left to right across a row or period. Thereof, does atomic radius increase down a group?
What is the relationship between atomic radius and energy levels?
Therefore, the atomic radius increases as the group and energy levels increase. In other words, the number of shells increases as we go down the group. The outermost electrons are repelled by the inner shell electrons (Screening effect) and hence, the atomic size increases.
What is the trend of atomic radius?
Group Trend The atomic radius of atoms generally increases from top to bottom within a group. As the atomic number increases down a group, there is again an increase in the positive nuclear charge. However, there is also an increase in the number of occupied principle energy levels.
What happens to the nucleus as one moves down the group?
As one moves down the group there is significant jump in the size of the nucleus (Protons (atomic number) + Neutrons). The additions of new shells increases the distance between nucleus and valance electrons. this increases the pull effect of nucleus resulting in the increase in atomic radius of the atom.
Why does electronegativity decrease?
From top to bottom down a group, electronegativity decreases. This is because atomic number increases down a group, and thus there is an increased distance between the valence electrons and nucleus, or a greater atomic radius.
Does the atomic radius decrease or increase?
In general, atomic radius decreases across a period and increases down a group. Down a group, the number of energy levels (n) increases, so there is a greater distance between the nucleus and the outermost orbital. Why does the atomic size increase down the group?
What trend in atomic radius occurs across a period?
This is caused by the increase in the number of protons and electrons across a period. One proton has a greater effect than one electron; thus, electrons are pulled towards the nucleus, resulting in a smaller radius.
Why does electronegativity decrease?
From top to bottom down a group, electronegativity decreases. This is because atomic number increases down a group, and thus there is an increased distance between the valence electrons and nucleus, or a greater atomic radius.
Why does the ionic radius increase as you move down a column?
As you move down a column or group, the ionic radius increases. This is because each row adds a new electron shell. Ionic radius decreases moving from left to right across a row or period.
Why is the ionic radius smaller than the atomic radius?
If the atom loses its outermost electron (positively charged or cation), the ionic radius is smaller than the atomic radius because the atom loses an electron energy shell.
Why do ionic radii decrease?
An ionic radius is defined as the radius of an atom's ion (ex. the radius of Na+). Ionic radii decrease across periods because effective nuclear charge increases. That is, the net positive charge experienced by an electron in the atom increases as a result of the number of protons in the nucleus increasing.
What happens when you go across a period?
As we go across a Period, a row, of the Periodic Table, from left to right as we FACE the Table, we add another positive charge (a proton, a fundamental, positively charged nuclear particle) to the nucleus. This results in a DECREASE in atomic radii across the Period, due to the increased nuclear charge which draws in the valence electrons.
Do atomic radii increase down the group?
Atomic radii thus INCREASE down the Group. This contest between nuclear charge, i.e. Z, and shielding by other electrons, underlies the structure of the Periodic Table. And note that incomplete valence electronic shells, shield the nuclear charge VERY ineffectively. AS a scientist, however, you should seek data that inform your argument.
Do you want details of atomic radii only?
You want details of atomic radii only, not ionic radii! If you can remember Atomic size INCREASES down a Group, but DECREASES across a Period, where a Group is a column and Period is a row of the Periodic Table, you have mastered a fundamental principle of chemistry.
Why does the atomic radius decrease over time?
Atomic radius decreases across a period because valence electrons are being added to the same energy level at the same time the nucleus is increasing in protons. The increase in nuclear charge attracts the electrons more strongly, pulling them closer to the nucleus.
Why do atomic radii increase when we go top to bottom?
When we go top to bottom in a group, the number of shells in an atom increases as the atomic number is increasing. Also the effective nuclear charge I,e the force of a proton per electron also decreases. Protons are now unable to hold the electrons tightly. Therefore the shells are more farther off than in lighter atoms. This is the reason why the atomic radii increase when we go top top to bottom.
What happens when the valence shell of an atom is less than half full?
If the valence shell of an atom is less than half full, it requires less energy to lose an electron than to gain one. Conversely, if the valence shell is more than half full, it is easier to pull an electron into the valence shell than to donate one.
Why do radii increase when going down a vertical row?
Going down a vertical row the atomic radii increase simply because additional electron shells get filled. These shells are more distant from the nucleus than elements in the previous vertical position of a group of similar elements, hence the increased radii.
What happens when you face the periodic table?
Well, as we face the Periodic Table, we know that FROM LEFT to RIGHT, atomic size decreases across the Period, a row of the Periodic Table, and this is the effect of increasing Z the atomic number. The INCREASED nuclear charge acts on the valence electrons, and draws them inwards with the result that atomic radius decreases…
What happens to the number of protons as you go down the group?
As we go down the group, the the number of protons in the nucleus goes on increasing and attracts the outer electrons more towards the center of the atom, thus decreasing the radius of that atom.
How does atomic size change?
Atomic size gradually decreases from left to right across a period of elements. This is because, within a period or family of elements, all electrons are added to the same shell. However, at the same time, protons are being added to the nucleus, making it more positively charged. The effect of increasing proton number is greater than that of the increasing electron number; therefore, there is a greater nuclear attraction. This means that the nucleus attracts the electrons more strongly, pulling the atom's shell closer to the nucleus. The valence electrons are held closer towards the nucleus of the atom. As a result, the atomic radius decreases.