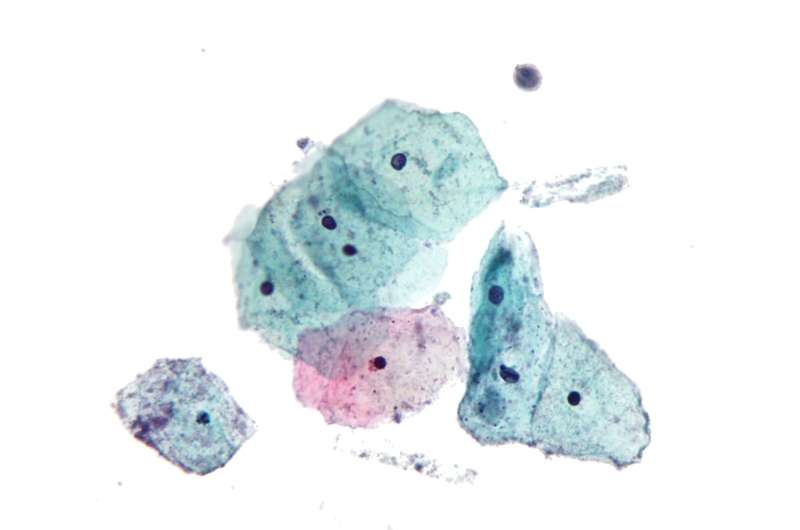
Cervical smear tests sometimes note the presence of trichomonads, however false positives can occur (less likely with liquid based cytology) so this should be confirmed with culture. A cervical smear test cannot be used as a screening test for trichomoniasis, due to the high number of false negatives.
Can trichomoniasis clear up on its own?
Trichomoniasis is unlikely to go away without treatment. The infection may cure itself in rare cases, but you risk passing the infection on to someone else if you're not treated. See full answer to your question here.
How long will Trichomonas last if untreated?
The duration of untreated trichomoniasis has never been systematically studied. Since it often is diagnosed in women who have not had sex for many years, obviously it sometimes can last very long. However, many (most?) cases may clear up on their own. There is even less information in men.
Is there an over the counter treatment for trichomoniasis?
No over the counter treatment exist for trichomoniasis. The CDC recommended treatment for trich requires a prescription, but you do not need to visit the doctor's office in person to get a prescription. Technology has made doctor visits online quick and easy.
What antibiotics can be used to treat trichomoniasis?
Trichomoniasis - Treatment. Trichomoniasis can be treated with commonly prescribed medications - similar to bacterial vaginosis, chlamydia and gonorrhea.Medications typically prescribed for the treatment of trichomoniasis symptoms fall within a class of drugs known as antibiotics.The actual choice of medication depends on the judgement of the medical provider and, in most cases, the ...
How accurate are trichomoniasis tests?
Cultures can correctly detect an active infection in 70% to 85% of patients with trichomoniasis, although this can vary based on the type of test sample being evaluated.
Why do I keep testing positive for trichomoniasis?
If you do test positive for trichomoniasis, you might also be tested for chlamydia or gonorrhea. People with trichomoniasis often have these STIs, too. Having trichomoniasis can also increase your risk of developing another STI, including HIV, in the future, so it's important to follow up with treatment.
Can I test positive for trich and my partner test negative?
A: It is quite common for one partner to test positive and the other negative, even if they have been having sex without condoms.
Can you be a carrier of trich and test negative?
While it's easy to diagnose trich, it's also easy to miss. Since the culture requires at least 10^3/ml of living protozoa, you may show up negative even if you do have the STI.
How long can trich lay dormant?
Trichomonas can lie dormant in the body for a long period of time before causing symptoms. However, most individuals develop symptoms within 5-28 days of exposure. WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS? About 70% of those infected do not have any signs or symptoms.
Can trichomoniasis be caused by poor hygiene?
Poor sexual practices such as multiple partners and bad hygiene regarding reproductive organs increase incidence of vaginal trichomoniasis.
How did I get trichomoniasis without cheating?
So, can you catch Trich if nobody cheated? Yes. You or your partner may have unknowingly caught the infection from a previous relationship, especially if you have only been together for a few months. Sometimes symptoms can take a little while to present, if at all.
How can I treat my partner for trich without him knowing?
What if I don't want my partner(s) to know it's me who has Trichomoniasis?send an anonymous email from this website.send an anonymous SMS.send or drop in a letter that you don't sign.ask your doctor if she/he can help you contact your partner(s)
Can you test too early for trich?
To obtain correct results, you should get tested for trichomoniasis 28 days after exposure, which is the incubation period of this parasite.
Why does my trichomoniasis keep coming back?
Recurrent Trichomoniasis. A recurrent infection can result from treatment failure (antimicrobial-resistant T. vaginalis or host-related problems), lack of adherence, or reinfection from an untreated sex partner.
Can BV turn into trichomoniasis?
Research has shown that untreated or improperly treated BV is associated with increased risk of: Research has shown that untreated or improperly treated BV is associated with increased risk of: Getting STIs like HPV, herpes, trichomoniasis (trich), chlamydia, gonorrhea, and HIV.
Can you have trich for years and not know it?
About 70% of people with the infection do not have any signs or symptoms. When trich does cause symptoms, they can range from mild irritation to severe inflammation. Some people get symptoms within 5 to 28 days after getting the infection. Others do not develop symptoms until much later.
What if you test positive for trichomoniasis?
If you do test positive for trichomoniasis, you might also be tested for chlamydia or gonorrhea. People with trichomoniasis often have these STIs, too. Having trichomoniasis can also increase your risk of developing another STI, including HIV, in the future, so it’s important to follow up with treatment.
What is trichomoniasis caused by?
What is trichomoniasis? Trichomoniasis, sometimes called trich, is an infection caused by a parasite. It’s one of the most common curable sexually transmitted infections (STI).
How did the parasites in Zambia spread?
from Zambia, the parasite spread through bathwater that was used by multiple girls. Public pools. The parasite can spread if the water in the pool isn’t cleaned. Clothing or towels. It’s possible to spread the parasite if you share damp clothing or towels with someone.
Can trichomoniasis be spread through sexual contact?
If you’re in a committed relationship and your partner suddenly develops an STI, your mind probably immediately jumps to infidelity. While trichomoniasis is almost always spread through sexual contact, about 70 percent. of people with the infection don’t show any symptoms.
Can you get trichomonasis from a toilet seat?
Toilets. Trichomoniasis can be picked up from a toilet seat if it’s damp. Using an outdoor toilet may be an added risk, since it puts you in closer contact with others’ urine and feces. Shared baths. In one study. Trusted Source. from Zambia, the parasite spread through bathwater that was used by multiple girls.
Can you carry a parasite without knowing?
People can also carry the parasite for many months without knowing it . This means that your partner may have gotten it from a past relationship and only just started showing symptoms. It also means that you might have developed an infection in a past relationship and unknowingly passed it to your current partner.
Can you have trichomoniasis without symptoms?
People can have trichomoniasis for months without showing any symptoms. If you or your partner suddenly have symptoms or test positive for it, it doesn’t necessarily mean that someone’s cheating. Either partner may have gotten it in a previous relationship and unknowingly passed it on. While it’s tempting to jump to conclusions, try have an open, honest conversation with your partner about their sexual activity.
What kind of medication are required for trichomonas?
Flagyl: The antibiotic Metronidazole (trade name flagyl) is used to kill protozoans like giardia and trichomonas. It is not without side effects but it does t... Read More
What is a probable infection?
Probable infection: You may have a cervical or vaginal infection. You should see a gynecologist to determine if there is an infection and, if so, to treat it.
Can trichomonas be tested?
NAAT yes, others no: There are 3 kinds of trichomonas testing, but the only one that detects all infections (and really the only one that should be used) is the nucleic ac ... Read More
Can you get reinfected if you have a tre?
Not certain: But sometimes this is because a sexual partner hasn't been treated. Even if you are treated, you can get reinfected if a partner does not get the tre... Read More
Is there a test for trichomoniasis?
Trichomoniasis: There is not a reliable, accurate commercially available test for trichomoniasis testing in men. Urethral swabs and urine testing can be done. A posit... Read More
Is trichomonas good for vaginal swab?
Probably yes: The gram stain of the vaginal swab does not suggest an infecting organism. No trichomonas is good.
Where was T. vaginalis collected?
Routine T. vaginalis -positive samples were collected in the microbiology laboratory serving the Israeli Defence Force. Clinical data were retrieved from the military medical records.
Can amplification test detect T. vaginalis?
Nucleic acid amplification tests for T. vaginalis detection allow easier diagnosis compared with classic smears and cultures. Many laboratories use commercial multiplex PCR tests for STI screening. After implementing a commercial test for use in soldiers of the Israeli Defence Force, we detected T. vaginalis in pharyngeal samples, raising questions regarding mis-identification. The study aimed to elucidate the origin of this finding and its clinical significance.
What are the signs and symptoms of trichomoniasis?
About 70% of infected people do not have any signs or symptoms. When trichomoniasis does cause symptoms, they can range from mild irritation to severe inflammation. Some people with symptoms get them within 5 to 28 days after being infected. Others do not develop symptoms until much later. Symptoms can come and go.
What are the complications of trichomoniasis?
Trichomoniasis can increase the risk of getting or spreading other sexually transmitted infections. For example, trichomoniasis can cause genital inflammation that makes it easier to get infected with HIV, or to pass the HIV virus on to a sex partner.
What is trichomoniasis?
Trichomoniasis (or “trich”) is a very common sexually transmitted disease (STD). It is caused by infection with a protozoan parasite called Trichomonas vaginalis. Although symptoms of the disease vary, most people who have the parasite cannot tell they are infected.
How do people get trichomoniasis?
The parasite passes from an infected person to an uninfected person during sex. In women, the most commonly infected part of the body is the lower genital tract (vulva, vagina, cervix, or urethra). In men, the most commonly infected body part is the inside of the penis (urethra). During sex, the parasite usually spreads from a penis to a vagina, or from a vagina to a penis. It can also spread from a vagina to another vagina. It is not common for the parasite to infect other body parts, like the hands, mouth, or anus. It is unclear why some people with the infection get symptoms while others do not. It probably depends on factors like a person’s age and overall health. Infected people without symptoms can still pass the infection on to others.
How does trichomoniasis affect a pregnant woman and her baby?
Pregnant women with trichomoniasis are more likely to have their babies too early (preterm delivery). Also, babies born to infected mothers are more likely to have a low birth weight (less than 5.5 pounds).
How long does it take for trichomoniasis to get back?
People who have been treated for trichomoniasis can get it again. About 1 in 5 people get infected again within 3 months after receiving treatment. To avoid getting reinfected, all sex partners should get treated with antibiotics at the same time.
How to avoid STDs?
The only way to avoid STDs is to not have vaginal, anal, or oral sex. If you are sexually active, you can do the following things to lower your chances of getting trichomoniasis: Be in a long-term mutually monogamous relationship with a partner who has been tested and has negative STD test results;
How to prevent trichomoniasis?
Among persons who are sexually active, the best way to prevent genital trichomoniasis is through consistent and correct use of condoms (external or internal) ( 18 ). Partners of men who have been circumcised might have a somewhat reduced risk for T. vaginalis infection ( 1072, 1073 ). Douching is not recommended because it might increase the risk for vaginal infections, including trichomoniasis ( 1074 ).
How long after a T vaginalis test can you retesting?
For women with HIV who receive a diagnosis of T. vaginalis infection, retesting is recommended 3 months after treatment; NAAT is encouraged because of higher sensitivity of these tests. Data are insufficient to support retesting of men with trichomonas and HIV infection.
What is the best treatment for T. vaginalis?
The nitroimidazoles are the only class of medications with clinically demonstrated efficacy against T. vaginalis infections. Tinidazole is usually more expensive, reaches higher levels in serum and the genitourinary tract, has a longer half-life than metronidazole (12.5 hours versus 7.3 hours), and has fewer gastrointestinal side effects ( 1106, 1107 ). In randomized clinical trials, recommended metronidazole regimens have resulted in cure rates of approximately 84%–98% ( 1108 ), and the recommended tinidazole regimen has resulted in cure rates of approximately 92%–100% ( 1108 – 1112 ). Randomized controlled trials comparing single 2-g doses of metronidazole and tinidazole indicated that tinidazole is equivalent or superior to metronidazole in achieving parasitologic cure and symptom resolution ( 1110, 1113, 1114 ).
What percentage of women with HIV have T. vaginalis?
Up to 53% of women with HIV have T. vaginalis infection ( 1115, 1138 ). T. vaginalis infection among these women is substantially associated with pelvic inflammatory disease ( 1082 ). Among women who are not virally suppressed, treatment of trichomoniasis is associated with decreases in genital tract HIV viral load and viral shedding ( 1079, 1139 ); however, no difference might occur among women who are virally suppressed ( 1140 ). Because of the high prevalence of T. vaginalis among women with HIV and the potential for adverse reproductive health, poor birth outcomes, and possibly amplified HIV transmission, routine screening and prompt treatment are recommended for all women with HIV infection; screening should occur at entry to care and then at least annually thereafter.
Does metronidazole reduce T. vaginalis?
Treatment reduces symptoms and signs of T. vaginalis infection and might reduce transmission. Treatment recommendations for women are based on a meta-analysis ( 1104) and a multicenter, randomized trial of mostly symptomatic women without HIV infection ( 1105 ). The study demonstrated that multidose metronidazole (500 mg orally 2 times/day for 7 days) reduced the proportion of women retesting positive at a 1-month test of cure visit by half, compared with women who received the 2-g single dose. No published randomized trials are available that compare these doses among men.
Does T. vaginalis increase risk of HIV?
T. vaginalis infection is associated with a 1.5-fold increased risk for HIV acquisition and is associated with an increase in HIV vaginal shedding, which is reduced with T. vaginalis treatment among women without viral suppression ( 1078, 1079 ). Among women with HIV infection, T. vaginalis infection is associated with increased risk for PID ( 1080 – 1082 ).
Can a Pap smear detect T. vaginalis?
Although T. vaginalis might be an incident al finding on a Pap test, neither convention al nor liquid-based Pap smears are considered diagnostic tests for trichomoniasis; however, women with T. vaginalis identified on a Pap smear should be retested with sensitive diagnostic tests and treated if infection is confirmed ( 1102, 1103 ).
How to test for trichomoniasis in men?
Diagnosing a trichomoniasis infection usually requires a sample of discharge, requiring a pelvic exam for women and a urethral swab or urine sample for men. However, the least invasive way to test for trichomoniasis in men or women is simply via a urine sample. The most common testing method for women is a “wet mount” or “wet preparation,” which ...
How long after exposure to trichomoniasis can you test?
Even if the infection is years old, a test will confirm the presence of the parasite so that treatment can begin. To reduce chances of false negatives, wait 28 days after potential exposure to be tested for trichomoniasis and always practice safe sex and regular STD testing (at least once a year).
When to Get Tested & are there False Negatives?
The parasite is easily spread during this time and can return false negative test results. Testing for trich can be conducted without concern for false negatives any time after the incubation period. Even if the infection is years old, a test will confirm the presence of the parasite so that treatment can begin. To reduce chances of false negatives, wait 28 days after potential exposure to be tested for trichomoniasis and always practice safe sex and regular STD testing (at least once a year). Like we mentioned earlier, trichomoniasis can be easily cured and does not always show symptoms so get tested if you think you might have been exposed.
How long does trich last?
An untreated trich infection can last for months or years. The infection is easily cured with a single dose of antibiotics. Condoms prevent the spread of the infection. Trich increases the likelihood of transmitting or contracting HIV and other STDs. 1 in 5 people become reinfected within three months after being cured.
What is the cause of trichomonasis?
Trichomoniasis infection is caused by a parasitic protozoan ( Trichomonas vaginalis) .
How long should you not pee before a blood test?
Individuals should not have urinated for at least one hour prior to specimen collection. Rapid antigen and nucleic acid probe blood tests can be used for on-the-spot tests with results available in minutes, but do not offer the accuracy of a test conducted using a discharge sample.
What is the most common test for a woman?
The most common testing method for women is a “wet mount” or “wet preparation,” which allows for evaluation of the discharge under a microscope to confirm the presence of the parasite.
What is the cause of trichomoniasis?
Trichomoniasis (pronounced trik-uh-muh-nahy-uh-sis), or “trich” for short, is caused by a protozoan called Trichomonas Vaginalis.
How long does it take for trichomoniasis to become reinfected?
In fact, according to a study done by the CDC, 1 out of 5 people who get treated for trichomoniasis become reinfected within 3 months of treatment. This is most likely due to partners not getting tested, diagnosed, or treated.
What is the cause of trich?
As we stated before, Trichomonas Vaginalis is the protozoan that causes trich. This makes trich a little different from other STDs, which aren’t caused by protozoa, but rather viruses and bacteria. Now it may have been a while since you took a biology class, so let’s break down the difference:
How many people with trich have symptoms?
In fact, according to the CDC, only 30 percent of people with trich report any symptoms at all. That means 70 percent of the time, people do not experience any symptoms or the symptoms are so mild that they go unnoticed. That’s right; most of the symptoms are seen as mild annoyances rather than big, scary STD symptoms.
Where do trich live?
In women, trich tends to live in the vagina, while in men, trich typically inhabits the urethra. FYI, the urethra is the canal that connects the bladder and the ejaculatory ducts to the penis. Since these two trich hotbeds come into direct contact with one another during male/female sexy time, trich spreads almost seamlessly.
Why did Lauren join STDcheck?
In 2018, she joined the STDcheck.com editorial staff because of her passion for communicating information about public health and destigmatizing sexual health. Before becoming a member of the STDcheck.com team, Lauren worked as a communication skills teacher, marketing coordinator, and freelance writer and designer.
Is trichomoniasis a STD?
Trichomoniasis isn’t an STD you often hear about. It’s not flashy or in your face, it’s not portrayed on TV, and there aren’t entire organizations dedicated to help stop the spread of it. But did you know that it’s the most prevalent non-viral STD in the world? Astonishing, right? And what’s even more astonishing is that even though it’s is so widespread, there is so little information about trichomoniasis in men.