What is the temperature at which steel becomes brittle?
This condition, while the steel remains hard, causes it to be brittle and susceptible to cracking. Unmixed steel will reach a brittle point at less than -30 degrees Celsius. Many areas on the Earth reach colder temperatures. What happens if you freeze metal?
What is the brittle point of carbon steel?
As a result, carbon steel needs to be mixed with other metals to retain flexibility at colder temperatures. Unmixed steel will reach a brittle point at less than -30 degrees Celsius. Many areas on the Earth reach colder temperatures. When steel gets cold it tends to develop condensation.
What happens to carbon steel in cold weather?
Brittle Effect in Cold Carbon steel does lose its flexibility when exposed to cold, however. This condition, while the steel remains hard, causes it to be brittle and susceptible to cracking. Unmixed steel will reach a brittle point at less than -30 degrees Celsius.
What is the best temperature for tempering carbon steel?
With lower carbon steels they measured a lower DBTT at 300 or 400°F tempering. Here is the effect of tempering on DBTT with steels between 0.33 and 0.41% carbon showing that lower tempering temperatures are better:
At what temperature is steel most brittle?
Cheap, non-alloyed steel typically becomes brittle at about -30 ºC. Adding expensive metals like nickel, cobalt and vanadium to steel reduces that temperature by strengthening the connections between grains. Kimura's steel lacks such additives, but only becomes brittle at -100 ºC, matching the performance of alloys.
What temperature can carbon steel withstand?
For a prolonged service life, such as 20 years, plain carbon steels are usually limited to a maximum operating temperature of 750°F (399°C); the ½% molybdenum alloy steels to approximately 850°F (454°C); and the stainless steels to considerably higher temperatures depending upon the type used.
At which temperature do the carbon steels used for shipbuilding become brittle?
We should be cautious in assuming a carbon steel vessel will become brittle only at temperatures below -20F unless it is specifically rated by the mechanical designers with a MDMT. “Fracture toughness” describes a material's ability to resist brittle fracture by arresting crack (flaw) propagation.
What temperature does steel start to weaken?
Phases of Steel Ferrite is essentially iron, and at room temperature, conventional steels are a mix of this material and cementite. However, when steel is heated to above 1340 degrees Fahrenheit, the cementite dissolves and forms the austenite phase. Eventually, the steel loses its magnetic charge at this temperature.
What happens to carbon steel at high temperatures?
Another example of microstructural degradation is decarburization of carbon or alloy steel when exposed to an oxidizing atmosphere at high temperature. There is a loss of strength in the surface layer of the steel.
Does steel get brittle when cold?
Brittle Effect in Cold Carbon steel does lose its flexibility when exposed to cold, however. This condition, while the steel remains hard, causes it to be brittle and susceptible to cracking.
What causes steel to brittle?
Primarily, the steel became brittle when it was exposed to the cold water, and the colder it got the more brittle it became. When it finally hit the iceberg, the steel fractured much easier than it would have at warmer temperatures.
What is brittle transition temperature?
Ductile–brittle Transition Temperature – Testing+ The ductile–brittle transition temperature (DBTT) is the temperature at which the fracture energy passes below a predetermined value (e.g., 40 J for a standard Charpy impact test).
At what temperature is steel ductile?
Above 1250°C the steels are ductile to near the melting temperature. Below 1250°C the ductility decreases, the amount of decrease, and the temperature range over which the change occurs depending on composition, cast structure and heat treatment.
How hot can steel get before it deforms?
Iron, out of the ground, melts at around 1510 degrees C (2750°F). Steel often melts at around 1370 degrees C (2500°F).
Does hardening steel make it brittle?
The two part process begins with hardening the steel so that it becomes hard and does not wear over time. However, very often, this process leaves the steel very brittle and susceptible to breaking during use.
How do you make steel less brittle?
Gently heating a hardened metal and allowing it to cool slowly will produce a metal that is still hard but also less brittle. This process is known as tempering.
What temperature should carbon steel be rated at?
Engineers often expect carbon steel equipment to be, if not rated, at least suitable for service temperatures to -20 F. This is an often-assumed point below which many grades of carbon steel can undergo a transition from a ductile to a brittle material. Once a ASME code-rated pressure vessel becomes brittle, there is always a risk ...
Is steel brittle or ductile?
There is a temperature below which fracture toughness starts to decrease rapidly with decreasing temperature. The material is not ductile, but not entirely brittle. After this transition range and at very cold temperatures, fracture toughness becomes constant again, but the steel is now completely brittle.
Why is carbon steel brittle?
Carbon steel does lose its flexibility when exposed to cold, however. This condition, while the steel remains hard, causes it to be brittle and susceptible to cracking. U.S. Liberty ship crews found this problem out the hard way as hulls strained by cargo began to split up at the seams when traveling through cold Atlantic waters in World War II. So did the ill-fated Titanic. As a result, carbon steel needs to be mixed with other metals to retain flexibility at colder temperatures. Unmixed steel will reach a brittle point at less than -30 degrees Celsius. Many areas on the Earth reach colder temperatures.
Why does steel get cold?
This can be a significant problem for builders using steel for framing where the metal may be close to or exposed to the elements. The resulting temperature transfer can cause water condensation which can then travel into the building, resulting in dry rot or water damage over time.
How does quenching affect steel?
This just creates simple pot metal. Good carbon steel goes through a process of melting, forming and fast cooling. This act of immediate quenching reshapes the molecular structure of carbon steel, causing it to develop stronger bonds.
What does quenching do to carbon steel?
This act of immediate quenching reshapes the molecular structure of carbon steel, causing it to develop stronger bonds. The result is stronger, harder steel that doesn't wear down quickly and handles pressure stress better.
Can cold weather make steel harder?
However, it is still susceptible to the effects of cold temperatures. In some cases, the production treatment of the steel can improve its strength and make it harder. But at a certain point, even hardened steel can become brittle when it gets cold enough. Advertisement.
Can steel freeze?
However, at a certain point below freezing, the metal can completely freeze over. When that point occurs depends on how much carbon is in the steel. For practical purposes the steel will not freeze over in most normal weather conditions.
Does carbon steel melt at high temperature?
eHow may earn compensation through affiliate links in this story. Iron and steel melt into liquid at high temperature but become brittle in cold climates. Carbon steel can be one of the strongest materials available for building and reinforcing. However, it is still susceptible to the effects of cold temperatures.
What steels are good for low temperature toughness?
Rather than tempering down to a lower hardness, use a lower carbon steel. Using a steel that is at a higher toughness to begin with (higher fracture strength) will also lead to higher low temperature toughness. Buying steel with minimal impurities and nickel additions also help with improving low temperature toughness.
What is the toughness of knife steel?
Knife steel toughness is temperature sensitive , and can fall steeply at a point called the “ductile to brittle transition temperature” (DBTT). High carbon, high hardness steel has a higher DBTT (lower toughness in the cold) which is significant for knives that will be used at cold temperatures. The DBTT is often above room temperature for knife steels but this is in part due to testing with notched specimens which promotes brittle behavior in an impact test. A reduction in carbon content, grain size, and impurities, and an increase in nickel or manganese, improves cold temperature toughness. Knifemakers that are making knives for cold environments should therefore use steels that are high in toughness, low in impurities, and with nickel additions to ensure the DBTT is low. A steel like 4340 with relatively low carbon and a nickel addition is a good choice though is limited in terms of hardness because of its carbon content. L6 is an option with higher potential hardness but good low temperature toughness data is not available. Low temperature toughness can be maximized through heat treatment by avoiding TME and minimizing grain size and carbon in solution through methods like low austenitizing temperatures or cycling.
Why is DBTT above room temperature?
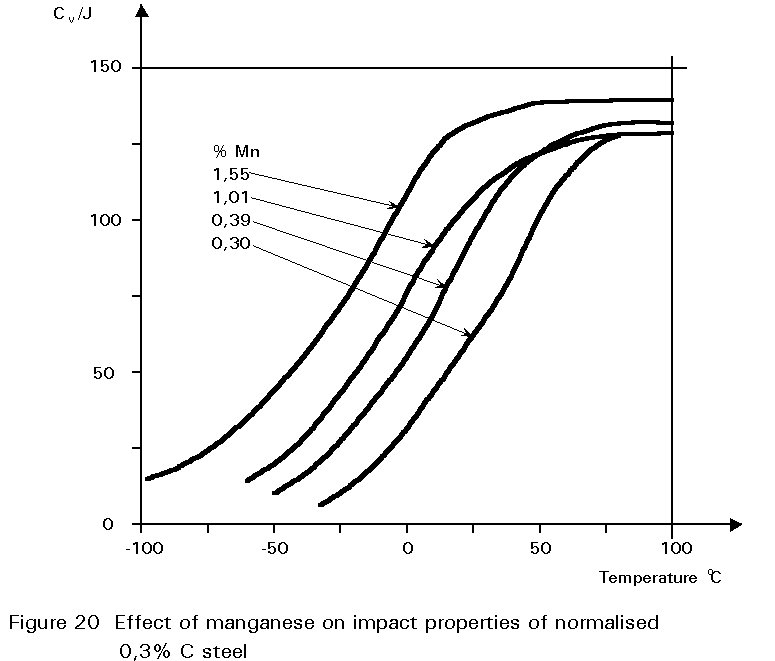
The DBTT is often above room temperature for knife steels but this is in part due to testing with notched specimens which promotes brittle behavior in an impact test. A reduction in carbon content, grain size, and impurities, and an increase in nickel or manganese, improves cold temperature toughness.
Why is the reduction in toughness at low temperatures more gradual?
Perhaps this is why the reduction in toughness at low temperatures is more gradual, because the yield strength is already higher than the fracture strength at room temperature. As mentioned before, low temperature toughness testing of tool steels and martensitic stainless steels is pretty limited.
How to improve knife toughness?
One way is minimizing the carbon content, especially for a given hardness. Rather than tempering down to a lower hardness, use a lower carbon steel.
What can change the temperature of a DBT?
We want the temperature to be as low as possible to both maximize room temperature toughness but also to increase cold temperature toughness. Carbon is a major factor as described, but there are many other variables to keep in mind.
What does a smaller grain size in steel mean?
I previously wrote about this in How Does Grain Refinement Lead to Improved Properties? The many small grains means that the fracture strength is increased. When a crack is growing through steel, each time it meets a grain boundary the crack has to re-initiate, and therefore many small grains means fracture is more difficult.
Does steel break like glass?
Steel won't break like glass. The need for toughness depends on you part's use: at a gas tank you want deformation without rupture, at a ball bearing any plastic deformation equals a failure. For comparison, most hard aluminium alloys have around 6% elongation at break, and brass about 2%.
Is plastic deformation at impact acceptable?
Very uneasy.#N#Typically at a ship hull, a plastic deformation at impact is acceptable but a crack isn't.#N#Toughness is defined by dozens of incompatible figures and methods because none works properly, nor permits any numerical prediction - they aren't even repeatable.#N#If the ship you designed sinks you must provide an answer that judges or their "experts" understand. Not with MPa*sqrt (m) but like "I applied this standard".#N#So the method I would apply, hence recommend to you, is to look after what the profession does and stick to it. Unless the boat is only for you and needs no certification.